Barrett Esophagus
Elizabeth A. Montgomery, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Columnar-lined esophagus
Change of esophageal mucosa
Any length
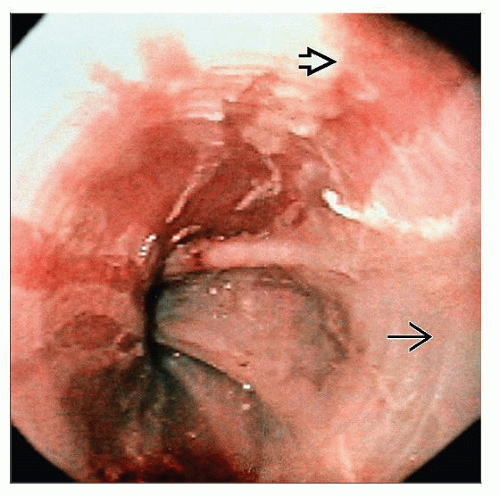
Visibility at endoscopy
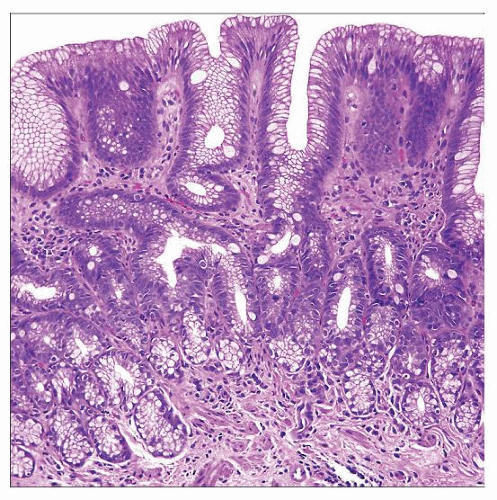
Contains intestinal metaplasia on biopsy
Outside USA: “Barrett esophagus” is often used for any columnar mucosa found in tubular esophagus
In USA: Term restricted to intestinal metaplasia and requires endoscopic correlation
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Male gender
Obesity
White race
Clinical Issues
10-20% of persons with longstanding gastroesophageal reflux
Overall incidence unknown in USA, but prevalence of 1.6% in general Swedish population
“Heartburn”
Key issue: BE is precursor to esophageal adenocarcinoma
Estimated annual risk of adenocarcinoma in patients with BE: 0.5-1%
Strong male predominance
Microscopic Pathology
Columnar metaplasia involving esophagus with goblet cells
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Barrett esophagus (BE)
Barrett oesophagus (British spelling) (BO)
Synonyms
Columnar-lined esophagus
Definitions
Change of esophageal mucosa
Any length
Visible at endoscopy
Contains intestinal metaplasia on biopsy
Outside USA: “Barrett esophagus” is often used for any columnar mucosa found in tubular esophagus
In USA: Term restricted to intestinal metaplasia and requires endoscopic correlation
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Risk Factors
Gastroesophageal reflux disease
Hiatal hernia
“Heartburn” symptoms
Male gender
Obesity
White race
Smoking
Alcohol use
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
10-20% of persons with longstanding gastroesophageal reflux
Overall incidence unknown in USA, but prevalence of 1.6% in general Swedish population
Age
Typically in 5th decade
Gender
Strong male predominance
Ethnicity
Whites most common
Rare in African-Americans
Rare in Southeast Asians
No word for “heartburn” exists in a host of Asian languages
Presentation
Cough
Some patients present with cough from reflux
“Heartburn”
Some patients asymptomatic
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Fundoplication is option to treat reflux; may not be good idea if patient already has Barrett mucosa
Drugs
Anti-reflux medications such as proton pump inhibitors are mainstay of treatment, although antacids and H2 blockers can also be used
Prognosis
Key issue: BE is precursor to esophageal adenocarcinoma
Estimated annual risk of adenocarcinoma in patients with BE: 0.5-1%
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree