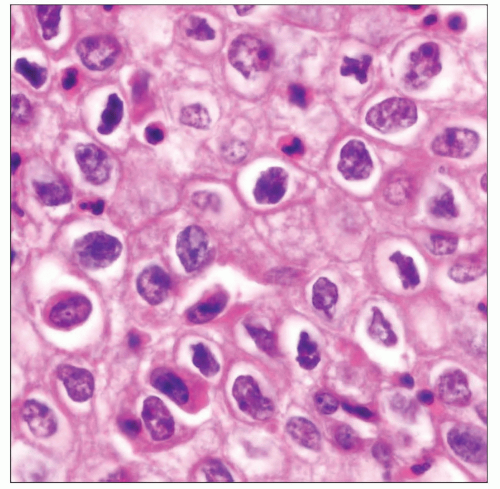
Atypical Thymoma
Key Facts
Terminology
WHO type B3, polygonal cell thymoma, well-differentiated thymic carcinoma
Moderately differentiated thymic epithelial neoplasm intermediate between thymoma and thymic carcinoma
Microscopic Pathology
Confluent sheets of epithelioid cells with scant lymphocytes
Prominent perivascular spaces
Palisading of epithelial tumor cells around perivascular spaces
Foci of squamous differentiation
Large epithelioid tumor cells with abundant cytoplasm and sharp cell borders
Large nuclei with dense chromatin pattern
“Raisinoid” nuclei with wrinkled nuclear membrane
Prominent nucleoli
Scattered mitoses
Cells may also be spindle or oval, with mild to moderate cytologic atypia
Lymphocytes are mainly mature T cells
Top Differential Diagnoses
Well-differentiated squamous cell carcinoma
Thymoma, mixed lymphoepithelial (WHO type B2)
Squamous cell carcinoma of lung origin
Diagnostic Checklist
Confluent sheets of epithelioid cells with scant lymphocytes
Perivascular spaces
Large epithelioid cells with sharp cell borders
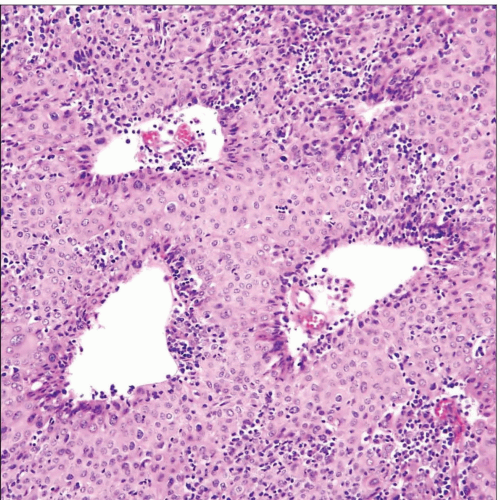 Atypical thymoma (WHO type B3) shows sheets of large, thymic epithelial cells with dilated perivascular spaces and a sprinkling of lymphocytes in the background. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Atypical thymoma (AT)
Synonyms
WHO type B3, polygonal cell thymoma, well-differentiated thymic carcinoma
Definitions
Moderately differentiated thymic epithelial neoplasm, intermediate between thymoma and thymic carcinoma
CLINICAL ISSUES
Site
Anterior-superior mediastinum
Presentation
Cough
Chest pain
Dyspnea
Superior vena cava syndrome
Frequent association with myasthenia gravis
Treatment
Surgical excision
Prognosis
Intermediate between encapsulated thymoma and thymic carcinoma
Earlier recurrences
More often invasive at time of presentation
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Large mass
Hemorrhage and necrosis are rarely present
Sections to Be Submitted
1 section per centimeter of greatest tumor dimension
Inked margins of resection
Sections should be taken from periphery of tumor
Size
Variable; from 3-20 cm
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Confluent sheets of epithelioid cells with scant lymphocytes
Prominent perivascular spaces
Palisading of epithelial tumor cells around perivascular spaces
Foci of squamous differentiation
Large epithelioid tumor cells with abundant cytoplasm and sharp cell borders
Large nuclei with dense chromatin pattern
“Raisinoid” nuclei with wrinkled nuclear membrane
Prominent nucleoli
Scattered mitoses
Cells may also be spindle or oval, with mild to moderate cytologic atypia
Cells can show prominent cytoplasmic clearing
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Well-differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Thymoma, Mixed Lymphoepithelial (WHO Type B2)
B2 thymoma shows more abundant lymphocytes
Nuclei in B2 thymoma are not as hyperchromatic as in atypical thymoma
Absence of squamous differentiation in WHO B2 thymoma
Squamous Cell Carcinoma of Lung Origin
Radiological evidence of lung tumor mass
Absence of T lymphocytes
DIAGNOSTIC CHECKLIST
Clinically Relevant Pathologic Features
Extent of invasiveness
Pathologic Interpretation Pearls
Confluent sheets of epithelioid cells with scant lymphocytes
Perivascular spaces
Large epithelioid cells with sharp cell borders
SELECTED REFERENCES
1. Wu M et al: Immunohistochemical detection of p63 and XIAP in thymic hyperplasia and thymomas. Am J Clin Pathol. 131(5):689-93, 2009
2. Suster S et al: Histologic classification of thymoma: the World Health Organization and beyond. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am. 22(3):381-92, 2008
3. Shiraishi J et al: Atypical thymoma (WHO B3) with neuroendocrine differentiation: report of a case. Virchows Arch. 449(2):234-7, 2006
4. Baran JL et al: Atypical thymoma: a report of seven patients. Ann Thorac Surg. 78(2):411-6, 2004
5. Pomplun S et al: Immunohistochemical markers in the differentiation of thymic and pulmonary neoplasms. Histopathology. 40(2):152-8, 2002
6. Kondo K et al: Two cases of repeatedly recurrent atypical thymoma. Chest. 115(1):282-5, 1999
7. Suster S et al: Primary thymic epithelial neoplasms: spectrum of differentiation and histological features. Semin Diagn Pathol. 16(1):2-17, 1999
8. Suster S et al: Thymoma, atypical thymoma, and thymic carcinoma. A novel conceptual approach to the classification of thymic epithelial neoplasms. Am J Clin Pathol. 111(6):826-33, 1999
9. Suster S et al: Thymoma with pseudosarcomatous stroma: report of an unusual histologic variant of thymic epithelial neoplasm that may simulate carcinosarcoma. Am J Surg Pathol. 21(11):1316-23, 1997
Tables
Immunohistochemistry | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
|
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree