Atypical Nevus of the Genital Tract
Russell Ball, MD
Marisa R. Nucci, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign melanocytic proliferation with architectural and cytologic features that differ from common nevi and may show some overlap with melanoma
Clinical Issues
Wide age range (mean: 26 years)
Labium majus > mons pubis > labium minus > clitoris > perineum
Macroscopic Features
Pink, tan, brown, or black macule or papule
Microscopic Pathology
Compound > intraepidermal
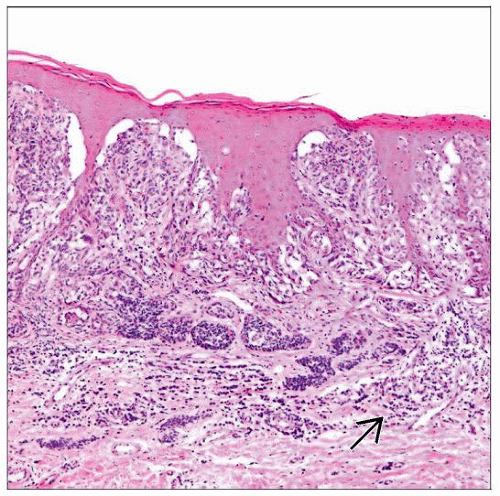
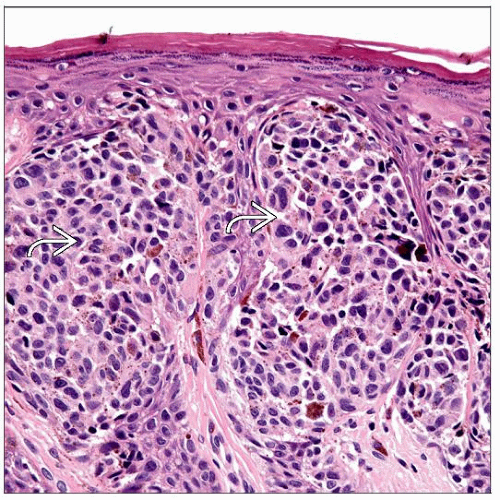
Florid junctional melanocytic proliferation of large variably sized nests
Nests with prominent retraction artifact and cellular dyscohesion
Melanocytes with variable but uniform degree of cytologic atypia
Predominantly epithelioid with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm; rarely spindled
Coarse > dusty cytoplasmic melanin pigment
Ancillary Tests
MART-1, Mel-5, S100 protein, HMB-45 positive
Low Ki-67 (MIB-1) expression
Top Differential Diagnoses
Melanoma
Dysplastic nevus
Recurrent or traumatized nevus
Lentigo
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Atypical nevus of genital tract (AGN)
Synonyms
Melanocytic nevus with site-specific changes
Nevus of special site
Atypical compound nevus, genital type
Nevus with site-related atypia
Definitions
Benign melanocytic proliferation with architectural and cytologic features that differ from common nevi and may show some overlap with melanoma
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Unknown
BRAF V600E mutation may occur
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare
< 5% of nevi occurring on vulva
Age
Wide range (mean: 26 years)
Half of patients are < 20 years
Site
In order of most to least common
Labium majus
Mons pubis
Labium minus
Clitoris
Perineum
In children, labia minora and clitoris more common (typically juxtamucosal)
Presentation
Incidental during gynecologic examination
Presentation during pregnancy or at time of delivery common
May exhibit gross abnormalities as defined by “ABCDE rule” (sharing features with dysplastic nevus and melanoma)
A = asymmetry
B = border irregularity
C = color variation (nonuniform)
D = diameter (malignant lesions rarely < 6 mm)
E = evolution (change in any feature may herald malignant transformation)
Treatment
Complete excision
Shave biopsies insufficient to exclude possibility of melanoma
Prognosis
Excellent
May recur if incompletely excised
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Pink, tan, brown, or black macule or papule
Usually well demarcated
Pigment typically evenly distributed within lesion
Size
Range: 2-20 mm (mean: 6 mm, median: 5 mm)
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree