Aspergillosis
Anthony Chang, MD
Key Facts
Etiology/Pathogenesis
A. fumigatus
A. flavus
A. niger
Clinical Issues
Treatment
Renal allograft nephrectomy
Nephrostomy drainage and systemic antifungal therapy
Voriconazole
Incidence
0.1% in kidney transplant patients after 1 year
Presentation
Fever
Flank pain
Hematuria
Laboratory tests
Cultures
Macroscopic Features
Abscesses, cortical or perinephric
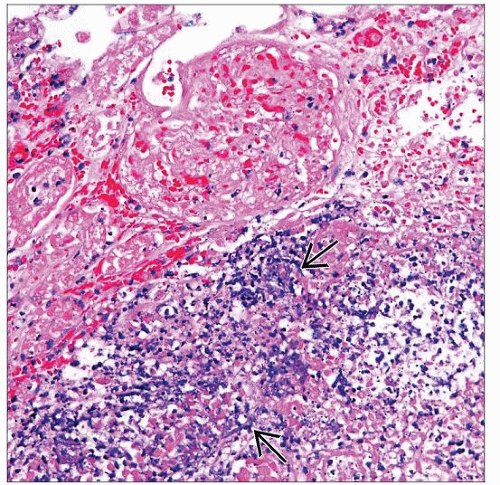
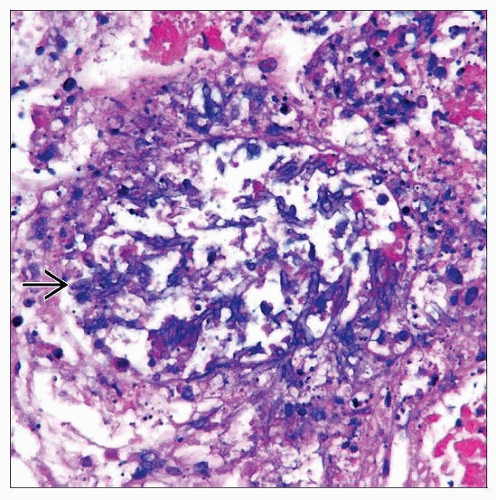
Microscopic Pathology
Microorganisms, fungus
Septate hyphae with 45° angle branching
Vascular invasion
Tubulointerstitial inflammation, neutrophil rich
Top Differential Diagnoses
Candidiasis
Mucormycosis
Pseudallescheriasis
Fusariosis
Bacterial pyelonephritis
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Aspergillus infection of kidney in immunosuppressed or immunocompromised patients
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Ubiquitous fungus in environment
Infectious Agents
Aspergillus
A. fumigatus
A. flavus
A. niger
A. terreus
A. nidulans
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
0.1% in kidney transplant patients after 1 year
Age
No age predilection
Gender
M:F = 4:1
Ethnicity
No ethnic predilection
Site
Lungs
Most common site of involvement
Kidneys
30-40% involvement in disseminated aspergillosis
Isolated involvement in some deceased donor kidney allografts
Probable transmission from deceased donor or during organ procurement
Fungi account for up to 2.5% of isolates cultured from perfusion solutions used for kidney preservation
Presentation
Fever
Flank pain
Hematuria
Laboratory Tests
Serologic tests
Enzyme-linked immunoassay
Detection of galactomannan antigen of Aspergillus
Immunodiffusion
Complement fixation
Cultures
Direct microscopy
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree