Asbestos-related Interstitial Fibrosis
Key Facts
Terminology
Asbestosis
Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis secondary to inhalation of asbestos dust
Etiology/Pathogenesis
2 types of asbestos fibers have been identified
Serpentine
Chrysotile (more common in industry)
Somewhat soluble in lung fluids
Amphibole
Amosite
Crocidolite
Clinical Issues
Latent period
Varies from 15-20 years
Disease may occur earlier depending on exposure
Occupational exposure
Direct
Indirect
Symptoms
Shortness of breath
Cough
Dyspnea
Clubbing of finger
Pleural effusion
Laboratory tests
Pulmonary functions tests
Restrictive disease
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Asbestosis
Definitions
Interstitial pulmonary fibrosis secondary to inhalation of asbestos dust
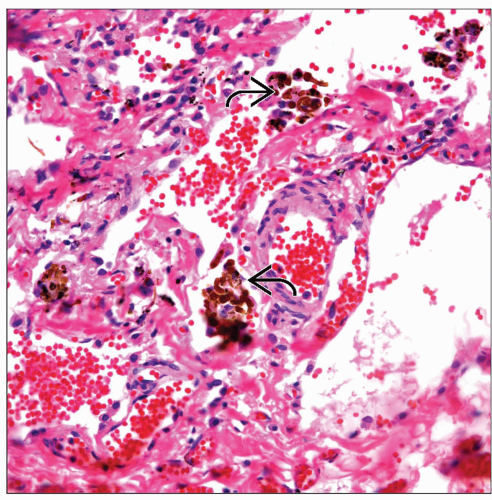
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Combination of hydrated silicates
Silica
Iron
Magnesium
2 types of asbestos fibers have been identified
Serpentine
Chrysotile (more common in industry)
Somewhat soluble in lung fluids
Amphibole
Amosite
Crocidolite
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Age
Usually occurs in adults
Gender
More common in males
Females may also be affected
Ethnicity
No ethnic predilection
Site
Lung
Pleura
Presentation
Shortness of breath
Cough
Dyspnea
Clubbing of fingers
Pleural effusion
Laboratory Tests
Pulmonary function test
Restrictive disease
Natural History
Latent period
Varies from 15-20 years
Disease may occur earlier depending on exposure
Occupational exposure
Direct
Indirect
Treatment
No specific treatment for asbestosis
Stop exposure
Prognosis
Pulmonary fibrosis may progress
May be fatal in patients with severe pulmonary fibrosis
IMAGE FINDINGS
Radiographic Findings
Bilateral interstitial opacities
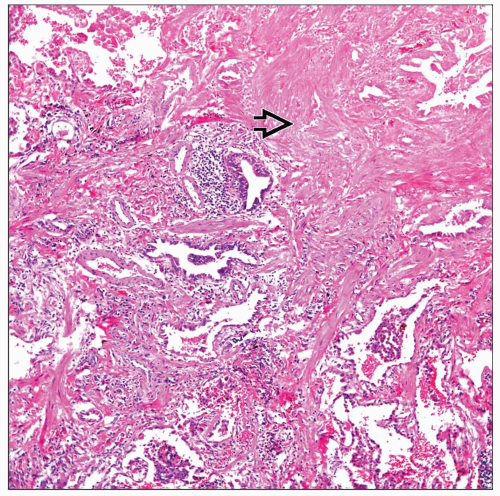
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Extensive areas of scarring
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree