Angiosarcoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Hemangiosarcoma
Clinical Issues
Symptomatology
Shortness of breath
Hemoptysis
Frank pulmonary hemorrhage
Macroscopic Features
Single or multiple pulmonary nodules
Microscopic Pathology
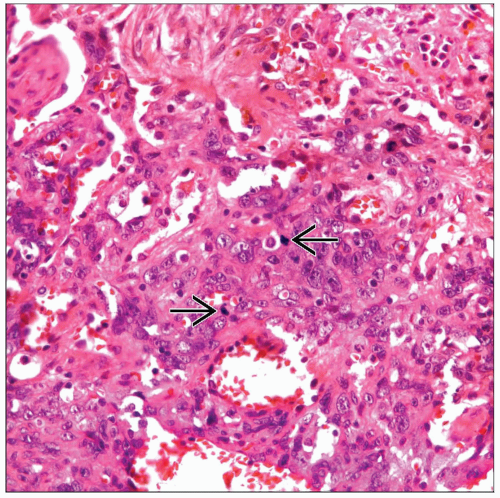
Epithelioid malignant cells forming vascular channels
Walls of vessels lined with hobnail-like cells
Miotic figures are common
Areas of hemorrhage
Areas of necrosis
Top Differential Diagnoses
Epithelioid hemangioendothelioma
Lacks increased mitotic activity
Extensive areas of necrosis are not a feature
Characteristically shows chondromyxoid background
Shares similar immunophenotype with angiosarcoma
Carcinoma
Carcinoma will show negative staining with vascular markers
Metastatic angiosarcoma
Clinical history is most important feature
Primary and metastatic angiosarcoma may share similar presentation
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Hemangiosarcoma
Definitions
Malignant vascular neoplasm
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Some cases have been linked to radiation and others to farming
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
It is estimated that angiosarcomas account for 0.02% of all lung tumors
Age
Tumor occurs in any age group
Gender
No predilection
Presentation
Shortness of breath
Hemoptysis
Pulmonary hemorrhage
Chest pain
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Lobectomy
Chemotherapy
Radiation
Prognosis
Poor
Widespread metastasis
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Single or multiple pulmonary nodules
Ill-defined tumor nodule
Hemorrhagic tumor nodule
Size
Varies from 1 to > 5 cm in diameter
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Epithelioid malignant cells forming vascular channels
Walls of vessels lined with hobnail-like cells
Miotic figures are common
Spindle cell component
Areas of hemorrhage
Areas of necrosis
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Hemorrhagic
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Epithelioid
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree