Chapter 9 Anemia
Definitions
Anemia: Reduced red blood cell (RBC) mass.
Hemoglobin concentration (Hgb): Grams of hemoglobin per 100 mL of whole blood (g/dL).
Red blood cell (RBC) count: Number of RBCs (in millions) per microliter of whole blood.
Mean corpuscular volume (MCV): Average RBC size. The MCV is commonly used to classify anemia as “microcytic” (RBCs smaller than normal), “normocytic” (normal-sized RBCs), or “macrocytic” (RBCs larger than normal), which provides a framework for determining the cause of the anemia (Box 9-1). Since the MCV is an average measure of RBC size, the MCV may be normal if microcytic and macrocytic cells are simultaneously present (for example, concurrent iron and vitamin B12 deficiency). As a general rule of thumb, normal RBCs are approximately the size of a lymphocyte nucleus on the peripheral blood smear.
Box 9-1 Common Causes of Anemia
Adapted from Hematology/Oncology. In: Ferri FF, editor. Practical Guide to the Care of the Medical Patient, 6th ed. St. Louis: Mosby; 2004.
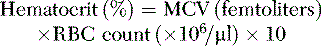
The normal value for the hematocrit depends on age, gender, and possibly race. The World Health Organization defines anemia as hematocrit < 39% in adult men and < 36% in adult women. Hemoglobin concentration, hematocrit, and RBC count are calculated using RBC mass and blood volume. Therefore, low blood volumes in patients with dehydration or acute blood loss may mask anemia that will become evident following volume repletion.
Mean corpuscular hemoglobin (MCH): Amount of hemoglobin (in picograms) per RBC and is calculated by:
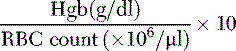
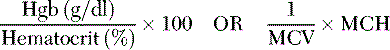
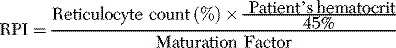
| Hematocrit (%) | Maturation Factor |
| 45 | 1.0 |
| 35 | 1.5 |
| 25 | 2.0 |
A low RPI (< 2) suggests a hypoproliferative anemia (i.e., impaired RBC production in response to the anemia). Typical causes of a low RPI include iron, folate, or vitamin B12 deficiency, or bone marrow injury, failure, or infiltration (Box 9-2). A high RPI (> 3) suggests a hyperproliferative anemia (i.e., increased RBC production in response to anemia), as occurs with hemolysis, acute blood loss, and recovery of the bone marrow from infection or nutrient deficiency.



