Alveolar Proteinosis
Key Facts
Terminology
Nonneoplastic condition in which alveoli are filled with proteinaceous material
Clinical Issues
Presentation
Cough
Dyspnea
Chest pain
Fever
Treatment
Pulmonary lavage
Spontaneous remission in some cases
Image Findings
Reticulonodular pattern
Small acinar pattern
Focal consolidation
Microscopic Pathology
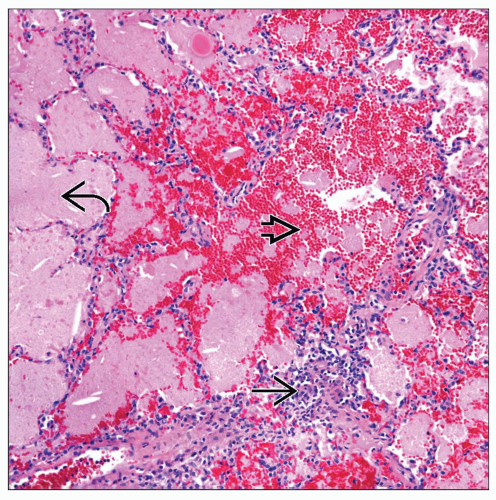
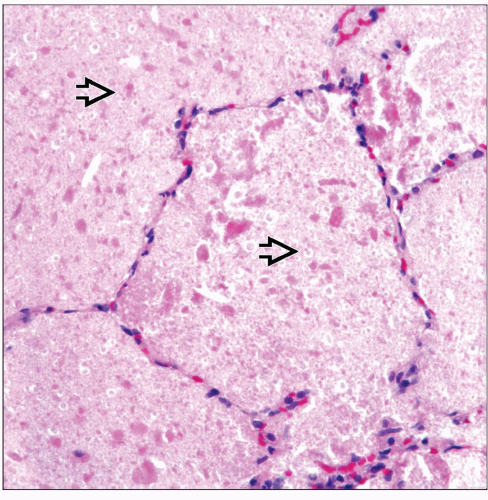
Alveolar filling by proteinaceous material
Preservation of normal alveolar architecture
Proteinaceous material is positive for periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)
Top Differential Diagnoses
Pneumocystis pneumonia
Silver stains will show presence of organisms
PAS histochemical stain is negative
Pulmonary edema
Pulmonary edema fluid is negative for PAS histochemical stain
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis (PAP)
Definitions
Nonneoplastic condition in which alveoli are filled with proteinaceous material
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Pulmonary alveolar proteinosis has been seen in association with the following
Infectious conditions
Immunosuppression
Hematologic malignancies
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Condition of unusual occurrence
Age
Condition has been reported to occur in any age group
Gender
No gender predilection
Presentation
Cough
Dyspnea
Chest pain
Fever
Treatment
Spontaneous remission in some cases
Pulmonary lavage
Prognosis
Generally good prognosis
Depends on associated condition
Some patients may not respond to treatment
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Reticulonodular pattern
Small acinar pattern
Focal consolidation
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Congested lung parenchyma
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Alveolar filling by proteinaceous material
Preservation of normal alveolar architecture
No evidence of interstitial fibrosis
Proteinaceous material is positive for periodic acid-Schiff (PAS)
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Diffuse
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Granular
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Pneumocystis Pneumonia
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree