Alveolar Microlithiasis
Key Facts
Terminology
Extensive deposition of microliths in alveolar spaces
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Rare condition of unknown etiology
Familial pattern has been observed in some cases
Can occur at any age
Clinical Issues
Decrease in respiratory performance
No metabolic abnormalities
No specific treatment
Variable
Protracted course
Rapid course with respiratory failure and death
Image Findings
“Sandstorm” pattern
Microscopic Pathology
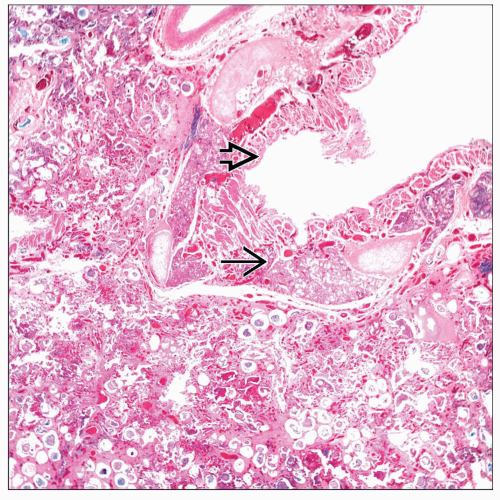
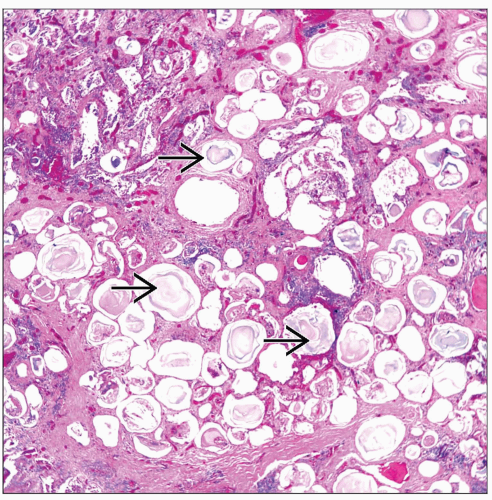
Intraalveolar deposition of spherical calcifications
Each calcospherite measures about 250-750 µm
Laminated bodies with “onion skin” features
Chemical analysis shows calcospherites to be made of phosphorus and calcium
Top Differential Diagnoses
Metastatic calcification (dendritic calcification)
Absence of calcospherites in intraalveolar spaces
Corpora amylacea
“Onion skin” features of microlithiasis are not present in corpora amylacea
Corpora is usually not intraalveolar location
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Pulmonary microlithiasis
Definitions
Extensive deposition of microliths in alveolar spaces
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Rare condition of unknown etiology
Familial pattern has been observed in some cases
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Cough
Shortness of breath
Malaise
Fatigue
Decrease in respiratory performance
No metabolic abnormalities
Laboratory Tests
Normal calcium and phosphates in serum
No signs of hyperparathyroidism
Decreased pulmonary function tests
Natural History
This condition may become apparent at any age and may follow a rapid fatal course
May become apparent in younger patients with variable course
Treatment
No specific treatment
Prognosis
Variable
Protracted course
Rapid course with respiratory failure and death
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
“Sandstorm” pattern
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Honeycomb changes in lung parenchyma
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Intraalveolar deposition of spherical calcifications
Each calcospherite measures about 250-750 µm
Laminated bodies with “onion skin” features
Interstitial fibrosis may be seen
Areas of ossification may be present
Minimal inflammatory reaction
Chemical analysis shows calcospherites to be made of phosphorus and calcium
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Calcification
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Metastatic Calcification (Dendritic Calcification)
Calcification follows alveolar wall and interstitium
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree