Alveolar Adenoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Benign intraparenchymal lung tumor
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Although the etiology of this tumor is not completely understood, it may originate from pneumocytes
Clinical Issues
General features
Unusual occurrence
Generally in adults
Solitary pulmonary lesion
Cough
Chest pain
Treatment
Lobectomy
Wedge resection
Prognosis
Excellent
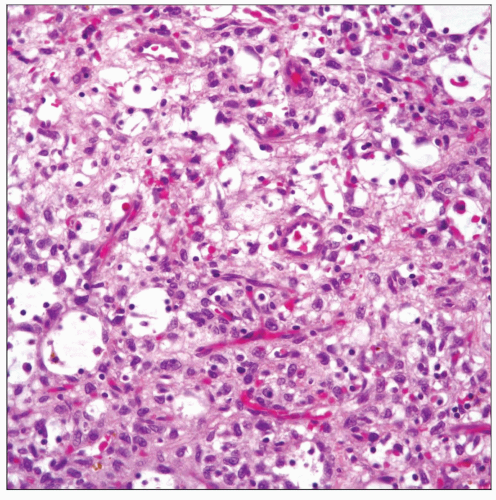
Microscopic Pathology
Well circumscribed
Generally cystic appearance
Dilated spaces of different sizes
Clear acellular material within cystic areas
PAS-positive material
Top Differential Diagnoses
Adenocarcinoma
Bronchioloalveolar carcinoma
Lymphangioma
Glomus tumor
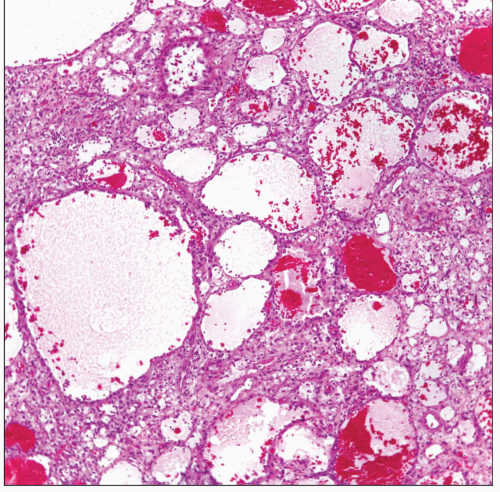 Pulmonary alveolar adenoma shows characteristic cystic areas alternating with more solid areas. The low power mimics a vascular neoplasm. |
TERMINOLOGY
Definitions
Benign intraparenchymal lung tumor
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Etiology
Although the etiology of this tumor is not completely understood, it may originate from pneumocytes
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Rare tumor
Age
Generally in adults
Gender
No gender predilection
Ethnicity
No ethnic predilection
Site
Intrapulmonary mass
Presentation
Cough
Chest pain
Asymptomatic
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Lobectomy
Wedge resection
Prognosis
Excellent
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Location
Solitary pulmonary mass
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Tumors may be cystic and hemorrhagic
Size
Tumors may vary from 1-3 cm in diameter
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Well circumscribed
Generally cystic appearance
Dilated spaces of different sizes
Clear acellular material within cystic areas
Dilated spaces lined by medium-sized cells with hobnail appearance
Focal areas of glandular appearance
Alternating solid areas
Mild inflammatory component composed of lymphocytes and plasma cells
Absence of mitotic activity
Absence of necrosis
ANCILLARY TESTS
Histochemistry
PAS-diastase
Reactivity: Positive
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree