Adenoma, Stomach
Gregory Y. Lauwers, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Polypoid gastric dysplasia
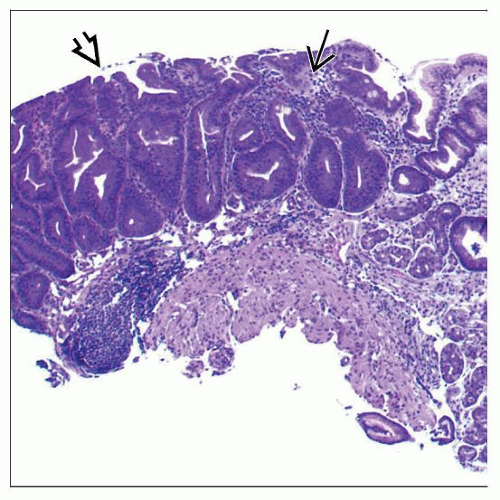
Unequivocal, noninvasive, polypoid, dysplastic gastric epithelium
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Secondary to Helicobacter pylori gastritis with intestinal metaplasia
Fundic gland polyps or hyperplastic polyps
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Clinical Issues
Incidence shows marked variations worldwide
6th to 7th decade
Excellent after complete excision and exclusion of concurrent adenocarcinoma
Enhanced risk of metachronous gastric adenocarcinoma
Common in countries with high prevalence of gastric cancer (e.g., Colombia)
Rare in countries with low prevalence of gastric cancer (e.g., USA)
Microscopic Pathology
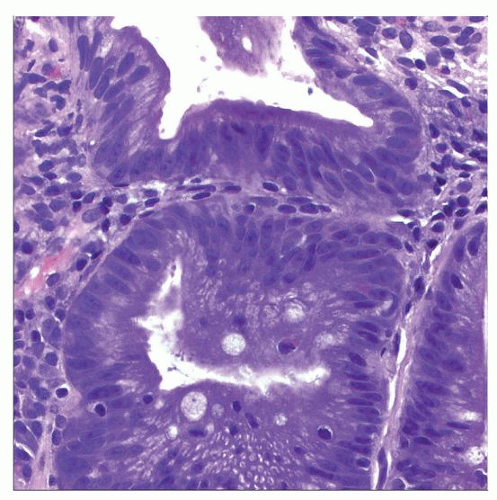
Variable degree of cyto-architectural atypia
Low-grade dysplasia shows minimal architectural
Changes and limited nuclear atypia
High-grade dysplasia shows severe architectural
Alterations and marked nuclear atypia
Top Differential Diagnoses
Regenerative atypia
Intramucosal adenocarcinoma
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Polypoid gastric dysplasia
Definitions
Unequivocal, noninvasive, polypoid, dysplastic gastric epithelium
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Infectious Agents
Gastric dysplasia often secondary to Helicobacter pylori gastritis with intestinal metaplasia
Polyposis Syndromes
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Peutz-Jeghers
Other Rare Predisposing Conditions
Ménétrier disease
Post-gastrectomy for benign gastric ulcer
Fundic Gland Polyps
Particularly in familial adenomatous polyposis setting
Hyperplastic Polyps
Reactive
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology