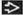Adenocarcinoma of the Extrahepatic Bile Ducts
Hanlin L. Wang, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Malignant neoplasm arising from epithelium lining right and left hepatic ducts, common hepatic duct, and common bile duct
Perihilar bile duct carcinoma
Distal bile duct carcinoma
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Developmental anomalies
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Clinical Issues
Poor prognosis with 10% overall 5-year survival
Surgical resection is only hope for long-term survival
Prognostic indicators include tumor stage, location, histology, and surgical margins
Image Findings
Biliary stricture, wall thickening, intraluminal mass
Microscopic Pathology
Wide spectrum of histologic appearance ranging from glandular structures to solid or cord-like clusters to individual tumor cells
Malignant glands are arranged in haphazard pattern, infiltrating duct wall
Often associated with desmoplastic stroma
Nuclear pleomorphism with increased N:C ratio, nuclear grooves, and brisk mitotic activity
Top Differential Diagnoses
Reactive periductal glands
Indistinguishable from pancreatic ductal carcinoma histologically and immunophenotypically
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Definitions
Malignant neoplasm arising from epithelium lining right and left hepatic ducts, common hepatic duct, and common bile duct
Perihilar bile duct carcinoma
Arises in extrahepatic bile ducts upstream to origin of cystic duct
Klatskin tumor occurs at confluence of right and left hepatic ducts
Comprises 70-80% of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Distal bile duct carcinoma
Arises in common bile duct (including intrapancreatic portion) above ampulla of Vater
Comprises 20-30% of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
Diffuse involvement of extrahepatic bile ducts is rare, comprising ˜ 2% of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Developmental Anomaly
Choledochal cyst
Abnormal choledochopancreatic junction
Chronic Inflammation
Primary sclerosing cholangitis
Cholelithiasis (controversial)
Parasitic Infection (Flukes)
Clonorchis sinensis
Opisthorchis viverrini
Genetic Syndromes
Familial adenomatous polyposis
Molecular Alterations
KRAS mutations in ˜ 30% of cases
Overexpression of p53 oncoprotein in ˜ 50% of cases
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
0.53-2 per 100,000 in population
Age
Primarily seen during 6th and 7th decades of life
Gender
Slight male predominance
Presentation
Nonspecific symptoms and signs
Abdominal pain, malaise, anorexia, nausea, vomiting, weight loss
Symptoms and signs of biliary obstruction
Jaundice, pruritus, acholic stools, dark urine
Laboratory Tests
Elevated serum CA19-9, CEA, and CA125 levels
Treatment
Surgical resection
Only hope for long-term survival
Segmental resection
May include partial hepatectomy for perihilar bile duct carcinoma
Whipple procedure for distal bile duct carcinoma
Combined modality therapy, including chemotherapy and radiotherapy
Prognosis
10% overall 5-year survival
Prognostic indicators
Tumor stage
Most important prognostic indicator
Tumor location
Better prognosis for distal bile duct carcinoma due to early detection and resectability
Histologic grade
Poorly differentiated tumors are associated with worse prognosis
Histologic variants
Poorer prognosis for signet ring cell carcinoma
More favorable outcome for papillary adenocarcinoma
Surgical resection margins
Improved overall survival for those with negative resection margins
Lymphovascular invasion
Associated with adverse outcome
Perineural invasion
Associated with adverse outcome
IMAGE FINDINGS
Ultrasonographic Findings
Duct dilation indicative of downstream obstruction
CT and MR Findings
Infiltrative pattern
Duct wall thickening, obliteration of duct lumen
Mass-like lesion
Distension of duct by intraluminal mass
Cholangiographic (ERCP) Findings
Bile duct stricture
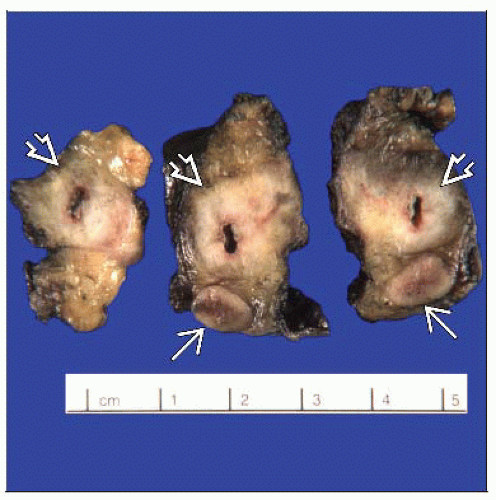
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Firm, white, and gritty cut surface
4 categories traditionally
Polypoid
Nodular
Scirrhous constricting
Diffusely infiltrating
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Wide variation in histologic appearance overall
Neoplastic glands with lumina
Well-formed, irregular, abortive, cribriforming, or with papilla formation
Arranged in random or haphazard pattern, infiltrating duct wall
Often widely spaced
May form solid or cord-like structures
Individual infiltrating cells may be present
Cytologic features
Range from deceptively bland to overtly high-grade nuclei
Acidophilic, basophilic, granular, pale, clear, foamy, or microvesicular cytoplasm
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree