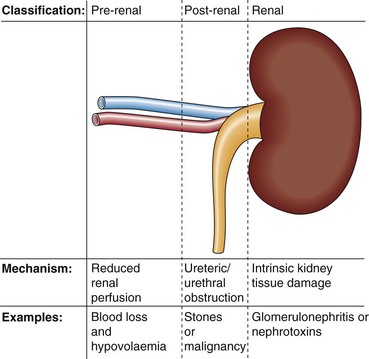
18 Kidney failure or uraemia can be classified as (Fig 18.1): Biochemical findings in pre-renal uraemia include the following:
Acute renal failure
Aetiology
 Pre-renal: the kidney fails to receive a proper blood supply.
Pre-renal: the kidney fails to receive a proper blood supply.
 Post-renal: the urinary drainage of the kidneys is impaired because of an obstruction.
Post-renal: the urinary drainage of the kidneys is impaired because of an obstruction.
 Renal: intrinsic damage to the kidney tissue. This may be due to a variety of diseases, or the renal damage may be a consequence of prolonged pre-renal or post-renal problems.
Renal: intrinsic damage to the kidney tissue. This may be due to a variety of diseases, or the renal damage may be a consequence of prolonged pre-renal or post-renal problems.
Diagnosis
 Serum urea and creatinine are increased. Urea is increased disproportionately more than creatinine because of its reabsorption by the tubular cells, particularly at low urine flow rates. This leads to a relatively higher serum urea concentration than creatinine, which is not so readily reabsorbed.
Serum urea and creatinine are increased. Urea is increased disproportionately more than creatinine because of its reabsorption by the tubular cells, particularly at low urine flow rates. This leads to a relatively higher serum urea concentration than creatinine, which is not so readily reabsorbed.
 Metabolic acidosis: because of the inability of the kidney to excrete hydrogen ions.
Metabolic acidosis: because of the inability of the kidney to excrete hydrogen ions.![]()
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


Acute renal failure