Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia with t(15;17)(q22;q21), PML-RARA and Variants
Mohammad A. Vasef, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
AML with increased abnormal promyelocytes and blasts
Account for < 10% of unselected AML cases
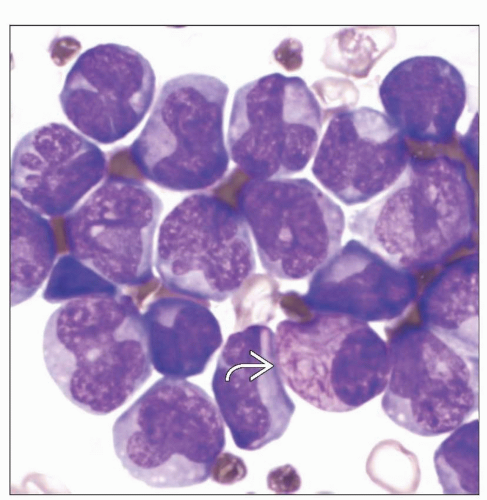
Typical or hypergranular variant
Abnormal promyelocytes with irregular and often bilobed nuclei
Numerous large cytoplasmic granules
Abnormal cells with numerous Auer rods (faggot cells) can be identified in majority of cases
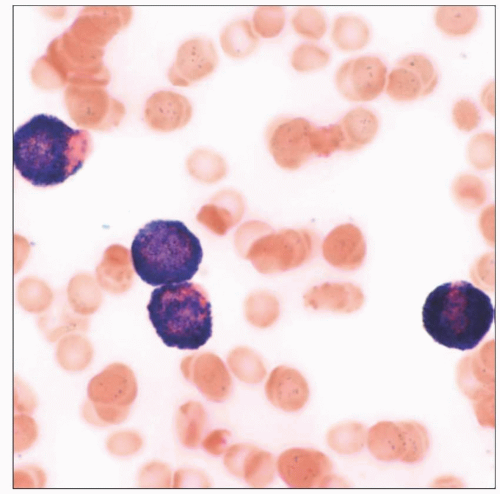
Hypogranular (microgranular) variant
Frequent marked leukocytosis
Absent or scant cytoplasmic granules by light microscopy
Presence of abundant submicroscopic granules highlighted by strong MPO reactivity
Frequent bilobed nuclei (sliding plates)
Clinical Issues
Chief clinical feature is bleeding diathesis due to
Plasmin-dependent primary fibrinolysis
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
All-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA)
Can induce complete response in APL with PML-RARA fusion
AML with t(5;17) variant translocation also ATRA responsive
AML with t(11;17) variant translocation is resistant to ATRA
Induction therapy typically includes anthracyclines and ATRA
Maintenance ATRA and chemotherapy after achievement of complete remission
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Acute promyelocytic leukemia (APL)
Synonyms
APL with t(15;17)(q22;q21), PML-RARA (current 2008 WHO classification)
Acute myeloid leukemia (AML), M3 subtype, FAB classification (AML-M3)
Definitions
Acute promyelocytic leukemia with t(15;17)(q22;q21), PML-RARA
Distinct subtype of AML with increased abnormal promyelocytes and blasts
Blockage of maturation of granulocytic lineages at promyelocyte stage
15;17 balanced reciprocal translocation represents karyotypic hallmark of disease
3 subtypes of APL
Typical APL or hypergranular variant
Abnormal promyelocytes with irregular and often bilobed nuclei
Numerous large cytoplasmic granules
Abnormal cells with numerous Auer rods (faggot cells) can be identified in majority of cases
Hypogranular (microgranular) APL variant
Frequent marked leukocytosis
Absent or scant cytoplasmic granules by light microscopy
Presence of abundant submicroscopic granules highlighted by strong myeloperoxidase reactivity
Frequent bilobed nuclei (sliding plates)
Rare “faggot cells” present in most cases
APL variants with non-PML gene rearranged with RARA gene
AML with t(5;17)(q35;q21), NPM1-RARA
AML with t(11;17)(q23;q21), ZBTB16-RARA
AML with t(11;17)(q13;q21), NUMA1-RARA
AML with t(17;17)(q11.2;q21), STAT5B-RARA
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Molecular Pathogenesis
Classic APL is caused by (15:17)(q22;q21) chromosomal translocation
t(15;17)(q22;q21) occurs exclusively in APL
Retinoic acid receptor alpha (RARA) gene on 17q21 fused with promyelocytic leukemia (PML) gene on 15q22
Wild-type PML gene acts as tumor suppressor gene
RARA gene promotes cell differentiation and suppresses cell growth
Breakpoint in RARA gene consistently occurs in intron 2
Breakpoints in PML gene occur in 3 different sites
Intron 6 (bcr1), resulting in long form transcript
Exon 6 (bcr2), resulting in variable form transcript
Intron 3 (bcr3), resulting in short form transcript
Novel PML-PARA fusion gene generated on chromosome 15
PML-RARA fusion gene encodes PML-RARA fusion protein
Functions of novel PML-RARA fusion protein
Key role in molecular pathogenesis of APL
Disrupts endogenous signaling pathways of both PML and RARA
Blocks myeloid differentiation
Myeloid differentiation block appears necessary but not sufficient for development of APL
Mutations in oncogenes such as FLT3 may cooperate with PML-RARA to induce leukemia
APL with cryptic PML-RARA rearrangement
Cryptic PML-RARA rearrangements not detectable by conventional cytogenetics
FISH using targeted probes usually detects cryptic PML-RARA rearrangements
FISH using targeted probes may fail to detect cryptic PML-RARA in rare cases
RT-PCR successfully detects and subtypes all 3 forms of PML-RARA transcripts
No major biologic differences compared to classic APL with t(15;17)(q22;q21)
APL with variant RARA translocations
Classified as AML with variant RARA translocations
AML with t(5;17)(q35;q21), NPM1-RARA
Nucleophosmin (NPM1) gene on 5q35 fused with RARA gene on 17q21
AML with t(11;17)(q23;q21), ZBTB16-RARA
ZBTB16 (previously PLZF) gene on 11q23 fused with RARA gene on 17q21
AML with t(11;17)(q13;q21), NUMA1-RARA
NUMA1 (nuclear mitotic apparatus) gene on 11q13 fused with RARA gene on 17q21
AML with t(17;17)(q11.2;q21), STAT5B-RARA
Signal transducer & activator of transcription STAT5B gene fused with RARA gene
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Accounts for 5-8% of AML cases
Independent risk factors of APL diagnosis among patients with AML are young age, Hispanic background, and obesity
Presentation
Acute promyelocytic leukemia with t(15;17) (q22;q21), PML-RARA
Chief clinical feature in APL is life-threatening coagulopathy and bleeding diathesis due to
Plasmin-dependent primary fibrinolysis
Disseminated intravascular coagulation (DIC)
Marked leukocytosis in hypogranular variant
(15;17)(q22;q21) chromosomal translocation is the hallmark of disease
Treatment
Rapid and accurate diagnosis of APL is crucial due to
Potential life-threatening coagulopathy
Unique response to all-trans-retinoic acid alpha (ATRA)
All-trans-retinoic acid (ATRA)
Allows reexpression of genes regulating promyelocyte differentiation
Can induce complete response in APL with PML-RARA fusion
Optimal therapy typically includes anthracyclines in addition to ATRA
ATRA-based maintenance after achievement of complete remission
Arsenic trioxide (ATO) currently regarded as best treatment option in setting of relapsed APL
Response to ATRA in AML with variant RARA translocations
AML with t(5;17)(q35;q21), NPM1-RARA is ATRA responsive
AML with t(11;17)(q23;q21), ZBTB16-RARA is resistant to ATRA
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree