Acquired Cystic Disease
Anthony Chang, MD
Aleksandr Vasilyev, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Presence of 3 or more cysts in native kidneys of patients with end-stage renal disease satisfies clinical diagnosis of ACD
Clinical Issues
60-80% of patients on dialysis for more than 4 years may be diagnosed with ACD
Increased risk of developing renal cell carcinoma
2-7% of patients with ACD will develop cystic renal cell carcinoma
Rapid change in cyst size warrants nephrectomy
Renal transplantation may decrease cyst size
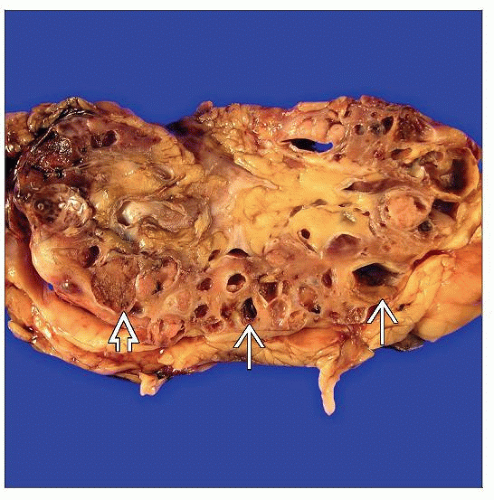
Macroscopic Features
ACD kidney weights range from 5-800 grams with an average of 130 grams
Bilateral involvement
Masses or nodules that may represent carcinoma are common
Microscopic Pathology
Tubular cysts
Present throughout cortex and medulla
Lined by flat cuboidal epithelial cells
Most stain for proximal tubular markers
Intracystic hemorrhage may be present
Diffuse interstitial fibrosis and tubular atrophy
Calcium oxalate crystal deposition
Top Differential Diagnoses
Autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease
Autosomal recessive polycystic kidney disease
Medullary cystic disease/juvenile nephronophthisis
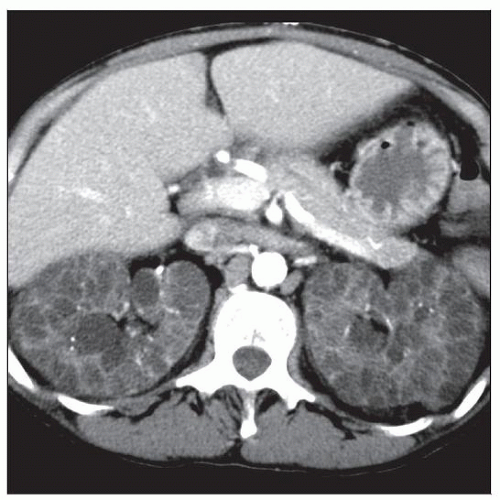 Axial CECT shows innumerable cysts in bilaterally enlarged kidneys of a patient who has been on dialysis for many years. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Acquired cystic disease (ACD)
Synonyms
Acquired cystic kidney disease
Acquired cystic renal disease
Definitions
Presence of 3 or more cysts in native kidneys of patients with end-stage renal disease satisfies clinical diagnosis of ACD
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Unknown Pathogenesis
Believed to involve physiologic response to chronic renal failure
Possible uncharacterized humoral factor
Successful renal transplantation may decrease size of cysts
Increased proliferation of cyst-lining epithelium
Unclear role of calcium oxalate crystals
Not necessarily secondary to dialysis
Cyst formation occurs in some patients even before dialysis therapy
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
60-80% of patients on dialysis for more than 4 years may be diagnosed with ACD
Age
All ages
Gender
Male predilection
Ethnicity
Africans may be more likely than Caucasians to develop ACD
Presentation
Asymptomatic
Cysts
Back pain
Possible infection of kidney cysts
Hematuria
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree