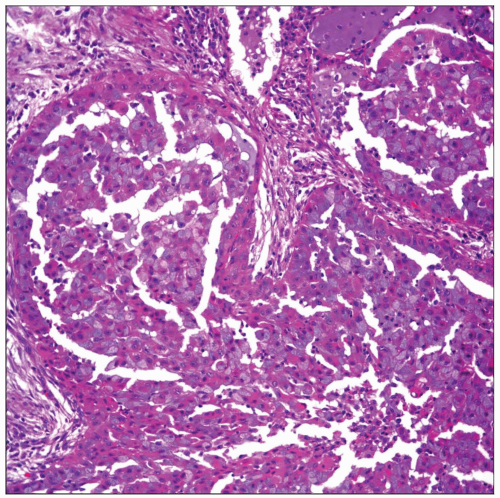
Acinic Cell Carcinoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Fechner tumor
Epithelial neoplasm similar to that in salivary glands
Clinical Issues
Cough
Chest Pain
Asymptomatic
Macroscopic Features
Necrosis and hemorrhage are not common
Tumor is well demarcated but not encapsulated
Intraparenchymal mass
Usually the tumors measure from 1-5 cm in greatest dimension
Top Differential Diagnoses
Adenocarcinoma
Shows positive cytoplasmic staining for mucin content with D-PAS and mucicarmine
Shows more nuclear atypia and mitotic figures
Oncocytic variant of neuroendocrine carcinoma
Acinic cell carcinoma negative for neuroendocrine markers
Metastatic acinic cell carcinoma
Previous history of acinic cell carcinoma of the head and neck region is crucial in establishing primary site
Diagnostic Checklist
Granular cytoplasm brightly positive for PAS
EM: Electron-dense zymogen granules
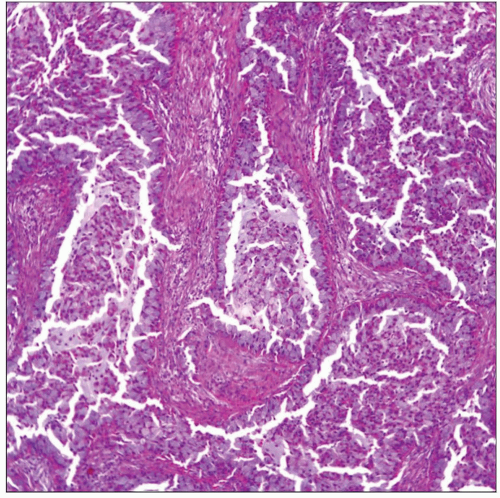 Acinic cell carcinoma of the lung with acinar pattern is shown. Note the presence of bands of fibroconnective tissue, giving the appearance of a lobulated neoplasm. |
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Fechner tumor
Definitions
Epithelial neoplasm similar to that in salivary glands
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Chest pain
Shortness of breath
Cough
Asymptomatic
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Lobectomy
Prognosis
Good in majority of cases
Tumor may follow aggressive behavior with metastasis
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Intraparenchymal mass
Tumor is well demarcated but not encapsulated
Necrosis and hemorrhage are not common
Size
Usually tumors measure 1-5 cm in greatest dimension
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Large cells with abundant granular cytoplasm
Signet ring-like cell appearance
Low mitotic count to complete absence of mitotic activity
Absence of nuclear atypia
Absence of necrosis &/or hemorrhage
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Acinar
Cystic
Organoid
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Epithelial
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Adenocarcinoma
Will show more nuclear atypia and mitotic figures
Will show positive cytoplasmic staining for mucin with D-PAS and mucicarmine
Cells in acinic cell carcinoma are larger with abundant granular cytoplasm
Acinic cell carcinoma will show by EM the characteristic dark electron-dense zymogen granules
Shows strong positive cytoplasmic reaction with PAS
Oncocytic Variant of Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
Acinic cell carcinoma negative for neuroendocrine markers
By electron microscopy, neuroendocrine carcinoma will display neurosecretory granules
May show mitotic activity and necrosis
Metastatic Acinic Cell Carcinoma
Previous history of acinic cell carcinoma of head and neck region is crucial in establishing primary site
DIAGNOSTIC CHECKLIST
Clinically Relevant Pathologic Features
EM: Electron-dense zymogen granules
Pathologic Interpretation Pearls
Granular cytoplasm brightly positive for PAS
Signet ring-like cells
Low mitotic activity
Oncocytic features
Papillocystic features
SELECTED REFERENCES
1. Chuah KL et al: Recurrence of pulmonary acinic cell carcinoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 130(7):932-3, 2006
2. Sabaratnam RM et al: Acinic cell carcinoma: an unusual cause of bronchial obstruction in a child. Pediatr Dev Pathol. 7(5):521-6, 2004
3. Watanabe K et al: Fine-needle aspiration cytology of bronchial acinic cell carcinoma: a case report. Diagn Cytopathol. 30(5):359-61, 2004
4. Lee HY et al: Primary acinic cell carcinoma of the lung with lymph node metastasis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 127(4):e216-9, 2003
5. Rodriguez J et al: Combined typical carcinoid and acinic cell tumor of the lung: a heretofore unreported occurrence. Hum Pathol. 34(10):1061-5, 2003
6. Ukoha OO et al: Acinic cell carcinoma of the lung with metastasis to lymph nodes. Chest. 115(2):591-5, 1999
7. Moran CA: Primary salivary gland-type tumors of the lung. Semin Diagn Pathol. 12(2):106-22, 1995
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree