Problem 18 A lady with diarrhoea and abdominal pain
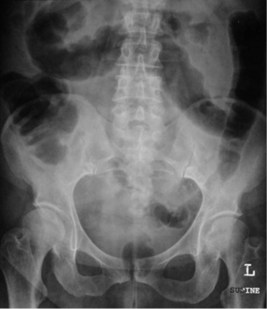
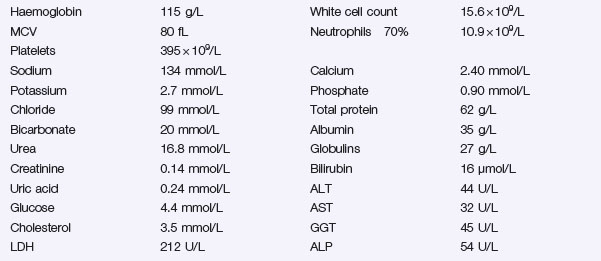
You prescribe loperamide. Blood tests are shown below. An abdominal X-ray is shown in Figure 18.1. Stool microscopy and culture are negative.
She is reviewed by the gastroenterologist and started on steroids.
She is reviewed by a dietician who starts a feeding programme.
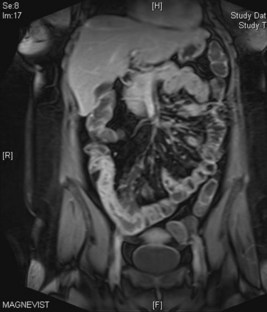
She is followed up for several years and her symptoms remain controlled. At a clinic appointment 3 years later she has developed abdominal pain and bloating after eating. This is sometimes accompanied by vomiting. The gastroenterologist sends her for a scan (shown in Figure 18.2).
Answers
Diarrhoea can be divided into acute or chronic. Acute is classified as lasting less than 14 days. It is usually secondary to infection which can be further subdivided by the presence of blood as shown in Table 18.1 below.
Table 18.1 Infectious causes of diarrhoea
| Acute Diarrhoea With Blood | Acute Diarrhoea Without Blood |
|---|---|
| Shigellosis | Viruses |
| Escherichia coli 0157 | Escherichia coli |
| Campylobacter | Cholera |
| Salmonella | Protozoa |
| Amoebic dysentery | Strongyloides |
| Antibiotic associated diarrhoea | Food toxins |
| Schistosoma (rarely) | Malaria |
| Milder infection with Shigella/Salmonella/Campylobacter |
Infections are often self-limiting and rarely require antibiotics.
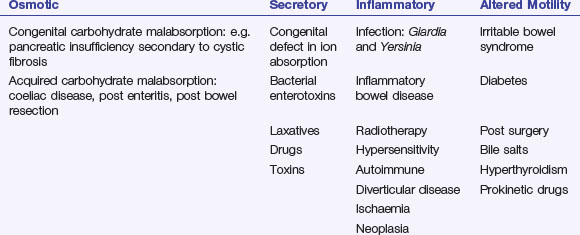
Chronic diarrhoea can be classified by its pathophysiology. There is overlap between aetiologies (Table 18.2):
A.2 Key questions when assessing patients with diarrhoea are:
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree