18.D) Neurons of the nucleus raphe magnus release serotonin at their nerve endings. In the endogenous pain suppression system, the termination of these neurons is in the spinal cord on interneurons that in turn release enkephalin and block the incoming signals from the pain fibers.
19.B) The sensations of highly localized touch and body position are carried in the dorsal column–medial lemniscal system.
20.C) Individuals experiencing severe chronic pain have difficulty sleeping because the ascending pain pathways provide input to reticular formation elements that comprise the reticular activating system. The latter system maintains the alert, waking state.
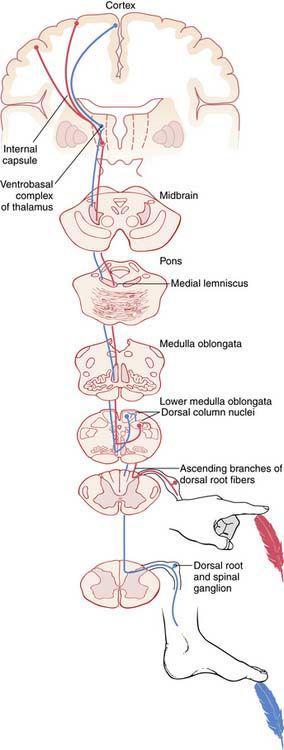
22.D) The medial lemniscus conveys axons from the nucleus gracilis and cuneatus to the thalamus (see
23.A) A central issue in the sensory transduction mechanism is the change (increase) in ion permeability that occurs in the receptor membrane.
24.C) The internal capsule conveys axons from the ventral posterolateral thalamic nucleus to the primary somatosensory cortex.
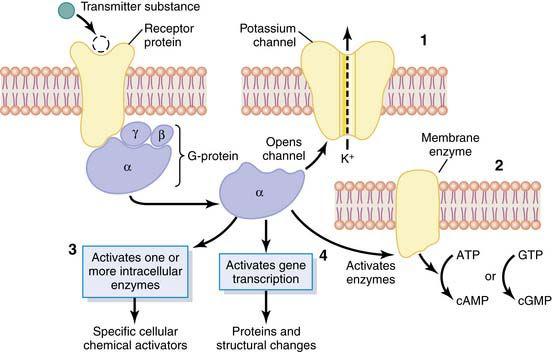
25.D) Ligand-gated channels open and allow sodium entry. This is accompanied by the influx of calcium, binding of synaptic vesicles to the presynaptic membrane, and electrical changes in the postsynaptic membrane.
26.B) The Nernst potential for chloride is −70 millivolts. This value is closest to the average resting membrane potential of a typical neuron. As such it represents the least electrochemical potential.
27.C) The periaqueductal gray in the midbrain contains neurons that contribute to the descending pain suppression system.
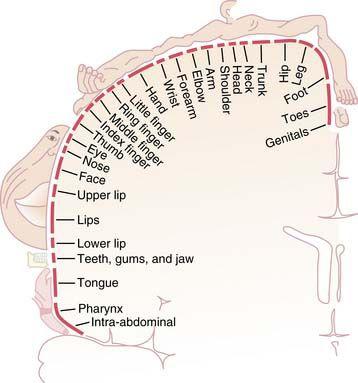
28.B) The lower limb representation is found in the superior and medial portion of the postcentral gyrus (see figure; from Penfield/Rasmussen. THE CEREBRAL CORTEX OF MAN. © 1950 Gale, a part of Cengage Learning, Inc. Reproduced by permission.
30.B) As the receptor potential increases above threshold, action potential frequency will increase.
31.C) A spinal cord interneuron in the dorsal horn utilizes enkephalin as a transmitter agent that effectively inhibits pain signaling.




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree