H2-Blockers

ACTIONS
Histamine H2-antagonists inhibit histamine action on H2-receptors, which are found on the gastric parietal cells. This action reduces the secretion of gastric acid, as well as hydrogen ion concentration.
USES
• Prevention and treatment of gastric and duodenal ulcers
• Heartburn, acid indigestion, and gastroesophageal reflux disease
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
• Hepatic and renal dysfunction
• Caution in older adult patients
SIDE EFFECTS
• **Diarrhea,** constipation
• Older adults: **confusion,** agitation
• Decrease in stomach acid may increase growth of Candida and bacteria in stomach, resulting in increased risk for pneumonia.
• Cimetidine: May bind with androgens to cause gynecomastia and impotence.
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Oral medications may be taken without regard to meals.*
2. ‡Teach patient to avoid alcohol.‡
3. ‡Smoking may decrease effectiveness.‡
4. ‡Teach patient the signs of gastric bleeding and to notify health care provider if any occur.‡
5. ‡Teach patient to notify health care provider for any indication of respiratory problems.‡
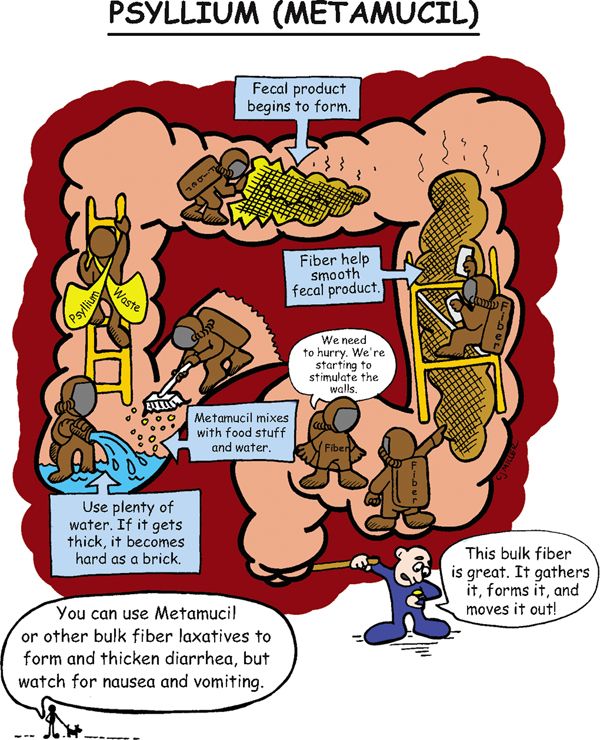
Psyllium (Metamucil)

CLASSIFICATION
Bulk-forming laxative
ACTIONS
Acts similar to dietary fiber. This medication is not digested or absorbed. After ingestion, it will swell to form a viscous solution or gel, softening the fecal mass and increasing the bulk. A fecal mass stretches the intestinal wall to stimulate peristalsis and passage of a soft-formed stool in 1 to 3 days.
USES
• Prevents constipation and straining after myocardial infarction or rectal surgery.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Bowel obstruction or undiagnosed acute abdominal pain
PRECAUTIONS
• Intestinal adhesions, ulcers
SIDE EFFECTS
• Impaction and obstruction if not given with adequate liquids
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Mix powder with at least 8 ounces of water; mix at the bedside immediately before administration.*
2. ‡Instruct patient to drink at least 8 ounces of water after each dose and drink at least 6 to 8 glasses of water each day to facilitate peristalsis and to prevent obstruction.‡
3. Bowel movement should occur in 12 to 36 hours.
4. *Administer at least 2 hours before or after medications.*
Metoclopramide Hydrochloride (Reglan)

CLASSIFICATION
Peristaltic stimulant, antiemetic
ACTIONS
Suppresses emesis by blocking dopamine receptors in the chemoreceptor trigger zone; increases tone and accelerates intestinal transit and gastric emptying by enhancing action of acetylcholine.
USES
• Provides antiemetic properties for suppressing nausea and vomiting associated with cancer therapy and postoperatively.
• Suppresses gastroparesis in patients with diabetes.
• Suppresses gastroesophageal reflux.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Gastrointestinal obstruction or perforation; gastrointestinal hemorrhage
• Concurrent use with medications that produce extrapyramidal reactions
PRECAUTIONS
• Impaired renal function, congestive heart failure, cirrhosis
SIDE EFFECTS
• **Drowsiness, restlessness, fatigue, lethargy**
• Dizziness, headache, insomnia, dry mouth
• †Extrapyramidal symptoms (toxic)†
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. Assess status of hydration.
2. *Monitor for anxiety, restlessness, extrapyramidal symptoms.*
3. Monitor pattern of bowel response.
4. Monitor for therapeutic response.
5. *To prevent nausea, administer 30 minutes before chemotherapy; give 30 minutes before meals and at bedtime for gastroparesis.*
6. Monitor renal function, blood pressure, and heart rate.
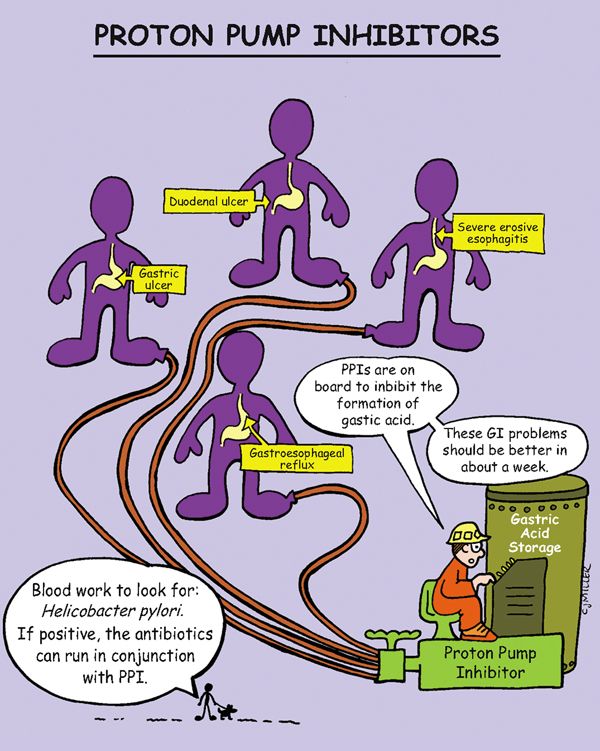
Proton Pump Inhibitors

EXAMPLES
ACTIONS
Suppress the secretion of gastric acid by combining with an enzyme on the gastric parietal cells; block the final common pathway for gastric acid formation; decrease hydrogen ion transport into the gastric lumen.
USES
• Short-term (4 to 8 weeks): Duodenal ulcers associated with Helicobacter pylori, gastric ulcers, erosive gastritis, and gastroesophageal reflux disease
• Long-term: Hypersecretory conditions (Zollinger-Ellison syndrome)
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
• Long-term use may predispose patient to the risk of developing gastric cancer.
• Long-term therapy may predispose patient to the risk of osteoporosis and fractures.
SIDE EFFECTS
• **Headache**
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. ‡Instruct patient to avoid opening, chewing, or crushing capsules.‡
2. ‡Instruct patient to return for follow-up if symptoms are unresolved after 4 to 8 weeks of therapy.‡
3. ‡Should be taken before meals.‡
4. *Notice that the generic names end in “zole.”*
5. ‡Encourage patients to maintain adequate intake of calcium and vitamin D.‡
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree