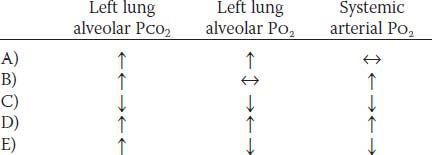
8. A 22-year-old woman has a pulmonary compliance of 0.2 L/cm H2O and a pleural pressure of −4 cm H2O. What is the pleural pressure (in cm H2O) when the woman inhales 1.0 L of air?
9. A preterm infant has a surfactant deficiency. Without surfactant, many of the alveoli collapse at the end of each expiration, which in turn leads to pulmonary failure. Which of the following sets of changes are present in the preterm infant, compared to a normal infant?
| Alveolar surface tension | Pulmonary compliance | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | Decreased | Decreased |
| B) | Decreased | Increased |
| C) | Decreased | No change |
| D) | Increased | Decreased |
| E) | Increased | Increased |
| F) | Increased | No change |
| G) | No change | No change |
10. A patient has a dead space of 150 ml, functional residual capacity of 3 L, tidal volume of 650 ml, expiratory reserve volume of 1.5 L, total lung capacity of 8 L, and respiratory rate of 15 breaths/min. What is the residual volume?
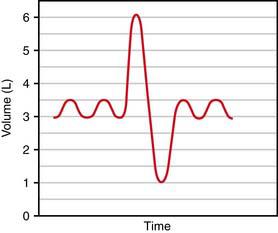
11. A 27-year-old man is breathing quietly. He then inhales as much air as possible and exhales as much air as he can, producing the spirogram shown in the previous figure. What is his expiratory reserve volume (in liters)?
12. A 22-year-old woman inhales as much air as possible and exhales as much air as she can producing the spirogram shown in the figure. A residual volume of 1.0 L was determined using the helium dilution technique. What is her functional residual capacity (in liters)?
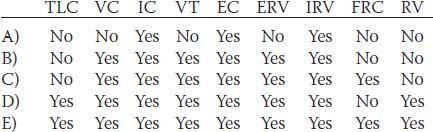
13. The various lung volumes and capacities include the total lung volume (TLC), vital capacity (VC), inspiratory capacity (IC), tidal volume (VT), expiratory capacity (EC), expiratory reserve volume (ERV), inspiratory reserve volume (IRV), functional residual capacity (FRC), and residual volume (RV). Which of the following lung volumes and capacities can be measured using direct spirometry without additional methods?
14. A patient has a dead space of 150 ml, functional residual capacity of 3 L, tidal volume of 650 ml, expiratory reserve volume of 1.5 L, a total lung capacity of 8 L, respiratory rate of 15 breaths/min. What is the alveolar ventilation?
16. An experiment is conducted in two individuals (subjects T and V) with identical tidal volumes (1000 ml), dead space volumes (200 ml), and ventilation frequencies (20 breaths per minute). Subject T doubles his tidal volume and reduces his ventilation frequency by 50%. Subject V doubles his ventilation frequency and reduces his tidal volume by 50%. Which of the following best described the total ventilation (also called minute ventilation) and alveolar ventilation of subjects T and V?
| Total ventilation | Alveolar ventilation | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | T < V | T = V |
| B) | T < V | T > V |
| C) | T = V | T < V |
| D) | T = V | T = V |
| E) | T = V | T > V |
| F) | T > V | T < V |
| G) | T > V | T = V |
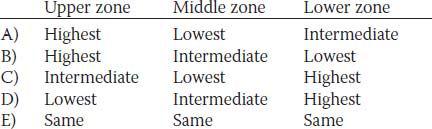
17. A healthy 10-year-old boy breathes quietly under resting conditions. His tidal volume is 400 ml and ventilation frequency is 12/min. Which of the following best describes the ventilation of the upper, middle, and lower lung zones in this boy?
18. A 34-year-old male sustains a bullet wound to the chest that causes a pneumothorax. Which of the following best describes the changes in lung volume and thoracic volume in this man, compared to normal?
| Lung volume | Thoracic volume | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | Decreased | Decreased |
| B) | Decreased | Increased |
| C) | Decreased | No change |
| D) | Increased | Decreased |
| E) | Increased | Increased |
| F) | No change | Decreased |
19. The resistance of the pulmonary tree is so low that a 1 cm of water pressure gradient is sufficient to cause normal air flow during resting conditions. Which of the following often has a substantial resistance during pulmonary disease states that can limit alveolar ventilation?
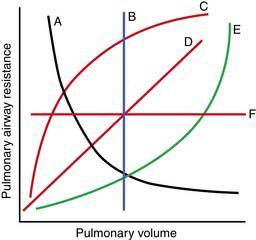
20. The following diagram shows pulmonary airway resistance expressed as a function of pulmonary volume. Which relationship best describes the normal lung?
21. The respiratory passageways have smooth muscle in their walls. Which of the following best describes the effect of acetylcholine and epinephrine on the respiratory passageways?
| Acetylcholine | Epinephrine | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | Constrict | Constrict |
| B) | Constrict | Dilate |
| C) | Constrict | No effect |
| D) | Dilate | Constrict |
| E) | Dilate | Dilate |
| F) | Dilate | No effect |
| G) | No effect | Constrict |
| H) | No effect | Dilate |
22. A 67-year-old man is admitted as an emergency to University Hospital because of severe chest pain. A Swan-Ganz catheter is floated into the pulmonary artery, the balloon is inflated, and the pulmonary wedge pressure is measured. The pulmonary wedge pressure is used clinically to monitor which of the following pressures?
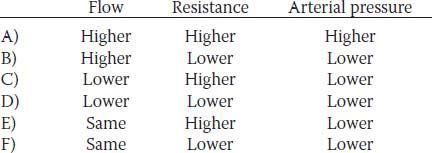
23. Which of the following sets of differences best describes the hemodynamics of the pulmonary circulation when compared to the system circulation?
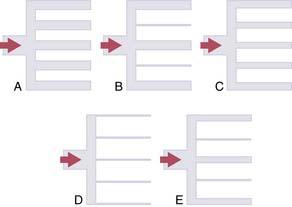
24. Which diagram best illustrates the pulmonary vasculature when the cardiac output has increased to a maximum extent?
25. A 30-year-old woman performs a valsalva maneuver about 30 min after eating lunch. Which of the following best describes the changes in pulmonary and systemic blood volumes that occur in this woman?
| Pulmonary volume | Systemic volume | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | Decreases | Decreases |
| B) | Decreases | Increases |
| C) | Decreases | No change |
| D) | Increases | Decreases |
| E) | Increases | Increases |
| F) | Increases | No change |
| G) | No change | Decreases |
| H) | No change | Increases |
| I) | No change | No change |
26. A 32-year-old man drives to the top of Pikes Peak where the oxygen tension is 85 mm Hg. Which of the following best describes the effects of a hypoxic environment on the pulmonary and systemic vascular resistances?
| Pulmonary vascular resistance | Systemic vascular resistance | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | Decreases | Decreases |
| B) | Decreases | Increases |
| C) | Decreases | No change |
| D) | Increases | Decreases |
| E) | Increases | Increases |
| F) | Increases | No change |
| G) | No change | Decreases |
| H) | No change | Increases |
| I) | No change | No change |
27. Going from a quiet, standing position to climbing a set of stairs, which of the following conditions will be present?
| Apical flow | Basal flow | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | ↑ | ↑ |
| B) | ↑ | ↓ |
| C) | ↓ | ↑ |
| D) | ↓ | ↓ |
| E) | ↑ | ↔ |
| F) | ↓ | ↔ |
28. A 65-year-old man with emphysema due to 34 years of cigarette smoking is admitted to hospital due to dyspnea. With further tests the mean pulmonary arterial pressure is determined to be 45 mm Hg at rest. He is hypoxic (Po2 = 49 mm Hg), hypercapnic (85 mm Hg), and slightly acidotic. The cardiovascular and oxygen changes are due to which of the following?
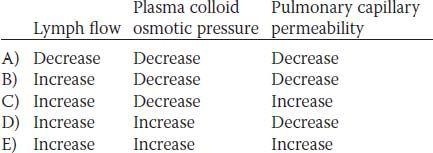
30. A 19-year-old man suffers a full-thickness burn over 60% of his body surface area. A systemic Pseudomonas aeruginosa infection occurs and severe pulmonary edema follows 7 days later. Data collected from the patient follow: plasma colloid osmotic pressure, 19 mm Hg; pulmonary capillary hydrostatic pressure, 7 mm Hg; and interstitial fluid hydrostatic pressure, 1 mm Hg. Which of the following sets of changes has occurred in the lungs of this patient as a result of the burn and subsequent infection?
31. A person’s normal tidal volume is 400 ml with a dead space of 100 ml. The respiratory rate is 12 breaths/min. The person is placed on ventilator for surgery and the tidal volume is 700 with a rate of 12. What is the approximate alveolar Pco2 for this person?
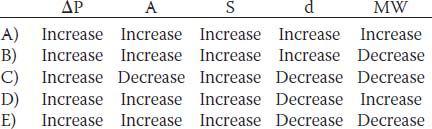
32. The forces governing the diffusion of a gas through a biological membrane include the pressure difference across the membrane (ΔP), the cross-sectional area of the membrane (A), the solubility of the gas (S), the distance of diffusion (d), and the molecular weight of the gas (MW). Which of the following changes increases the diffusion of a gas through a biological membrane?
33. A person with normal lungs at sea level (760 mm Hg) is breathing 50% oxygen. What is the approximate alveolar Po2?
34. A child has been eating round candies approximately 1 and 1.5 cm in diameter and inhaled one down his airway blocking his left bronchiole. Which of the following will describe the changes that occur?
35. During exercise, the oxygenation of blood is increased not only by increased alveolar ventilation but also by a greater diffusing capacity of the respiratory membrane for transporting oxygen into the blood. Which of the following sets of changes occur during exercise?
| Surface area of respiratory membrane | Ventilation-perfusion ratio | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | Decrease | Improvement |
| B) | Increase | Improvement |
| C) | Increase | No change |
| D) | No change | Improvement |
| E) | No change | No change |
36. The diffusing capacity of a gas is the volume of gas that will diffuse through a membrane each minute for a pressure difference of 1 mm Hg. Which of the following gases is often used to estimate the oxygen diffusing capacity of the lungs?
37. A 23-year-old medical student has mixed venous oxygen and carbon dioxide tensions of 40 mm Hg and 45 mm Hg, respectively. A group of alveoli are not ventilated in this student because mucus blocks a local airway. What are the alveolar oxygen and carbon dioxide tensions distal to the mucus block (in mm Hg)?
| Carbon dioxide | Oxygen | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | 40 | 100 |
| B) | 40 | 40 |
| C) | 45 | 40 |
| D) | 50 | 50 |
| E) | 90 | 40 |
38. A 45-year-old man at sea level has an inspired oxygen tension of 149 mm Hg, nitrogen tension of 563 mm Hg, and water vapor pressure of 47 mm Hg. A small tumor pushes against a pulmonary blood vessel that completely blocks the blood flow to a small group of alveoli. What are the oxygen and carbon dioxide tensions of the alveoli that are not perfused (in mm Hg)?
| Carbon dioxide | Oxygen | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | 0 | 0 |
| B) | 0 | 149 |
| C) | 40 | 104 |
| D) | 47 | 149 |
| E) | 45 | 149 |
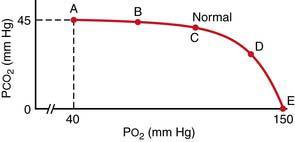
39. The O2-CO2 diagram here shows a ventilation-perfusion ratio line for the normal lung. Which of the following best describes the effect of decreasing ventilation-perfusion ratio on the alveolar Po2 and Pco2?
| Carbon dioxide tension | Oxygen tension | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | Decrease | Decrease |
| B) | Decrease | Increase |
| C) | Decrease | No change |
| D) | Increase | Decrease |
| E) | Increase | Increase |
41. A 67-year-old man has a solid tumor that pushes against an airway partially obstructing air flow to the distal alveoli. Which point on the ventilation-perfusion line of the O2-CO2 diagram corresponds to the alveolar gas of these distal alveoli?
42. A 55-year-old male has a pulmonary embolism that partially blocks the blood flow to his right lung. Which point on the ventilation-perfusion line of the O2-CO2 diagram corresponds to the alveolar gas of his right lung?
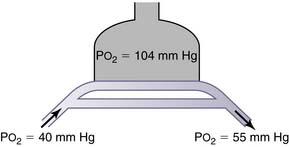
43. The following diagram shows a lung with a large shunt in which mixed venous bypasses the oxygen exchange areas of the lung. Breathing room air produces the oxygen partial pressures shown on the diagram. What is the oxygen tension of the arterial blood (in mm Hg) when the person breathes 100% oxygen and the inspired oxygen tension is over 600 mm Hg?
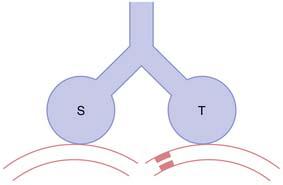
44. The next diagram shows two lung units (S and T) with their blood supplies. Lung unit S has an ideal relationship between blood flow and ventilation. Lung unit T has a comprised blood flow. What is the relationship between alveolar dead space (DALV), physiologic dead space (DPHY) and anatomic dead space (DANAT) for these lung units?
| Lung unit S | Lung unit T | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | DPHY < DANAT | DPHY = DANAT |
| B) | DPHY = DALV | DPHY > DALV |
| C) | DPHY = DANAT | DPHY < DANAT |
| D) | DPHY = DANAT | DPHY > DANAT |
| E) | DPHY > DANAT | DPHY < DANAT |
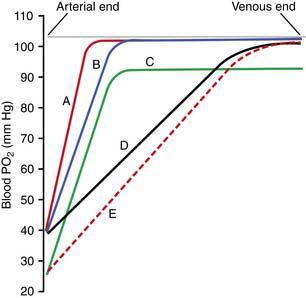
45. A 32-year-old medical student has a fourfold increase in cardiac output during strenuous exercise. Which of the curves on the following diagram most likely represents the changes in oxygen tension that occur as blood flows from the arterial end to the venous end of the pulmonary capillaries in this student?
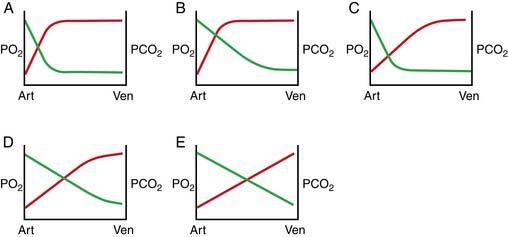
46. The diagrams show changes in the partial pressures of oxygen and carbon dioxide as blood flows from the arterial end to the venous of the pulmonary capillaries. Which diagram best depicts the normal relationship between Po2 (red line) and Pco2 (green line) during resting conditions?
47. A 17-year-old female was bicycling without a helmet when she fell and hit her head. In the emergency room, she was not conscious and was receiving ventilator assistance. Her blood gases follow:




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree