CASE 60
WHAT ARE THE SENSORY AND MOTOR DISTRIBUTIONS OF THE TRIGEMINAL NERVE?
The motor and sensory distribution (Figs. 7-31 and 7-32) of the trigeminal nerve and its branches are described in Table 7-2.
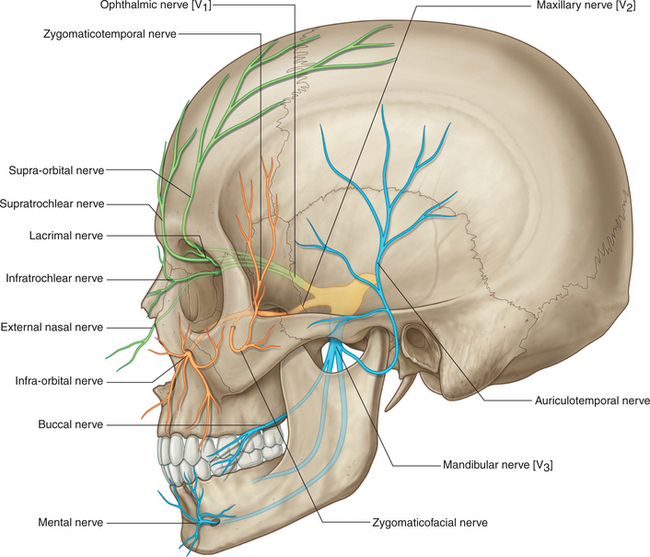
FIGURE 7-31 Trigeminal nerve (CN V).
(Drake R, Vogl W and Mitchell A: Gray’s Anatomy for Students. Churchill Livingstone, 2004. Fig. 8-58)
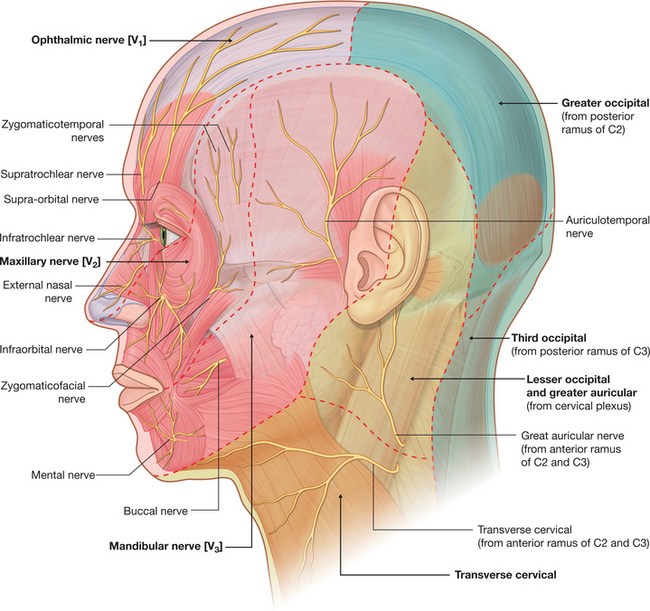
FIGURE 7-32 Cutaneous distribution of the trigeminal nerve (CN V).
(Drake R, Vogl W and Mitchell A: Gray’s Anatomy for Students. Churchill Livingstone, 2004. Fig. 8-59)
TABLE 7-2 Sensory and Motor Distribution of the Trigeminal Nerve
| Division | Branch of Division | Distribution |
|---|---|---|
| Ophthalmic nerve | Lacrimal nerve (smallest of the main branches of the ophthalmic nerve) | Sensory to lacrimal gland, adjoining conjunctiva, and upper eyelid |
| Ophthalmic nerve | Frontal nerve (largest branch of the ophthalmic nerve) | Sensory via supratrochlear nerve to conjunctiva, skin of upper eyelid, and skin of inferior forehead near midline
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|