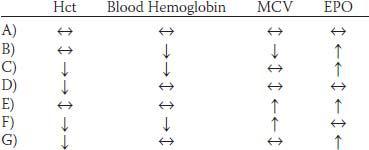
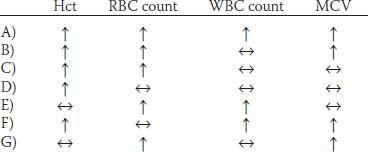
7. A 62-year-old female arrives for her annual physical. She complains of itching in her hands along with headaches and vertigo. A routine complete blood count (CBC) shows red blood cells (RBCs) of 8.2 million/μl, white blood cells (WBCs) 37,000/μl, and platelets 640,000/μl. Her erythropoietin levels are lower than normal. The primary diagnosis would be
8. A 40-year-old woman visits the clinic complaining of fatigue. She had recently been treated for an infection. Her laboratory values are RBC 1.8 × 106/μl, Hb 5.2 g/dL, hematocrit (Hct) 15, WBC 7.6 × 103/μl, platelet count 320,000/μl, mean corpuscular volume (MCV) 92 fL, and reticulocyte count 24%. What is the most likely explanation for this presentation?
10. A 34-year-old man with schizophrenia has had chronic fatigue for 6 months. He has a good appetite, but has refused to eat vegetables for 1 year because he hears voices saying that vegetables are poisoned. His physical and neurological examinations are normal. His hemoglobin level is 9.1 g/dL, leukocyte count is 10,000/μl3, and MCV is 122. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
11. A 24-year-old African-American man comes to the emergency room 3 hr after the onset of severe back and chest pain. These problems started while he was skiing. He lives in Los Angeles and had a previous episode of these symptoms 5 years ago while visiting Wyoming. He is in obvious pain. Laboratory studies show the following:
| Hemoglobin | 11 gm/dl |
|---|---|
| Leukocyte count | 22,000/μl3 |
| Reticulocyte count | 25% |
12. A 62-year-old man complains of headaches, visual difficulties, and chest pains. His examination shows a red complexion and a large spleen. His complete blood count follows: hematocrit, 58%, WBC 13,300/μl, and platelets 600,000/μl. His arterial oxygen saturation is 97% on room air. Which of the following would you recommend as a treatment?
13. A 45-year-old woman developed fatigue in July and had blood counts that were reported to be normal. She was hospitalized because of a very severe headache in December, and was found to have a blood pressure of 175/90. Her laboratory values were as follows: hemoglobin (8.3 g/dL), RBC count (2.2 × 106/μl), Hct (23%), MCV (89 fL), WBCs (5100/μl), platelets (262 × 103/μl), and reticulocyte count 0.8%. What is the diagnosis for this patient?
14. A 38-year-old healthy female comes to you for a routine visit. She has spent the last 2 months hiking through the Himalayas and climbed to the base camp of Mount Everest. Which of the following would you expect to see on her CBC (complete blood count)?
15. A patient presents to your office complaining of extreme fatigue and shortness of breath on exertion that has gradually worsened over the past 2 weeks. On physical examination, you observe a well-nourished woman who appears comfortable but somewhat short of breath. Her vital signs include a pulse of 120, respiratory rate of 20, and blood pressure of 120/70. When she stands up her pulse increases to 150 and her blood pressure falls to 80/50. Her hematologic values are Hgb 7 g/dL, Hct 20%, RBC count 2 × 106/μl, platelet count of 400,000/μl. On a peripheral smear, her RBCs are microcytic and hypochromic. What would be your diagnosis of this patient?
16. After a person is placed in an atmosphere with low oxygen, how long does it take before there are increased numbers of reticulocytes?
17. Over the past 12 weeks, a 75-year-old man with a moderate aortic stenosis has developed shortness of breath and chest pains during exertion. He appears pale. Test of his stool for blood is positive. Laboratory studies show the following: hemoglobin 7.2 g/dL, and mean corpuscular volume 75. A blood smear shows microcytic, hypochromic erythrocytes. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
18. A 24-year-old man came into the ER with a broken leg. A blood test was ordered and his WBC count was 22 × 103/μl. Five hours later, a second blood test resulted in values of 7 × 103/μl. What is the cause of the increased WBC count with the first test?
20. During an inflammatory response, which is the correct order for cellular events?
A) Filtration of monocytes from blood, increased production of neutrophils, activation of tissue macrophages, infiltration of neutrophils from the blood
B) Activation of tissue macrophages, infiltration of neutrophils from the blood, infiltration of monocytes from blood, increased production of neutrophils
C) Increased production of neutrophils, activation of tissue macrophages, infiltration of neutrophils from the blood, infiltration of monocytes from blood
22. A 45-year-old man presents to the emergency room with a 2-week history of diarrhea that has gotten progressively worse over the last several days. He has minimal urine output and is admitted to the hospital for dehydration. His stool specimen is positive for parasitic eggs. Which type of WBCs would have an elevated number?
23. An 8-year-old male is frequently coming to the clinic for persistent skin infections that do not heal within a normal time frame. He had a normal recovery from the measles. Checking his antibodies following immunizations yielded normal antibody responses. A defect in which of the following cells would most like be the cause of the continual infections?
25. A 65-year-old alcoholic developed chest pain and cough with an expectoration of sputum. A blood sample revealed that his white blood cell count was 42,000/μl. What is the origin of these WBCs?
26. A 26-year-old man received a paper cut. What substance is the major cause of pain of this acute inflammatory response?
27. A patient visits his dentist, who notices a sore on the patient’s lip. The sore was unusual in that there was no pain or drainage from the sore. The patient was subsequently admitted to the hospital with a violent shaking chill. His lab values were Hct 30%, platelets 400,000/μl, WBC 4200/μl, 68% lymphocytes, and 20% neutrophils. What is the diagnosis of this patient?
32. What is the term for adhesion of an invading microbe with IgG and complement to facilitate recognition?
33. Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is an important molecule in the immune response. What is the function of IL-2?
36. Activation of the complement system results in which of the following actions?




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree