CASE 57
WHAT STRUCTURE OF THE BRAIN, WHEN DAMAGED, PRODUCES THE SYMPTOMS OF PARKINSON’S DISEASE?
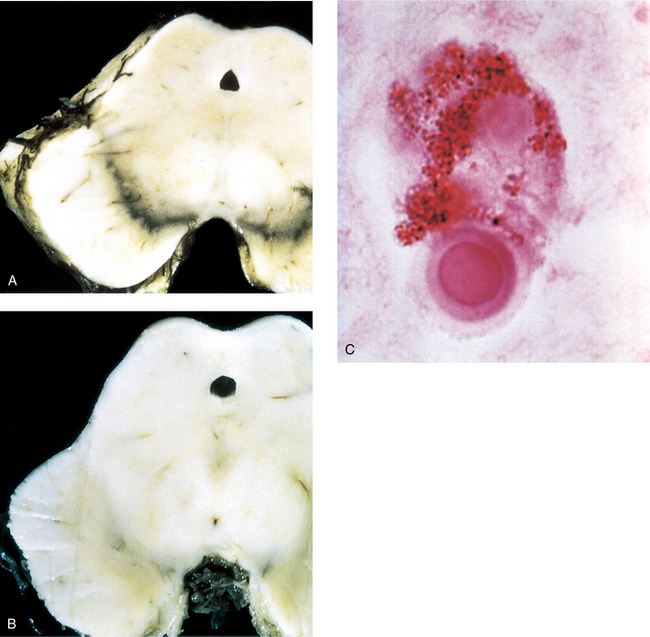
Parkinson’s disease is a lesion of the basal ganglia characterized by a loss of dopaminergic neurons in the substantia nigra, a bilateral nucleus that extends through the length of the midbrain (Fig. 7-26A). The neurons, which project to the corpus striatum (composed of the caudate nucleus, putamen, and globus pallidus), are responsible for inhibiting movements. Loss of this inhibition through the degeneration of the neurons in the substantia nigra permits movements that the patient does not want to perform but cannot prevent.