Antiepileptic Drugs

ACTIONS
Stabilizes neuronal membranes, and limits the spread of seizure activity by affecting the motor cortex.
USES
• Control grand mal (tonic-clonic) and psychomotor seizures (in all age groups).
• Can be used for status epilepticus.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Pregnancy (teratogenic effects)
PRECAUTIONS
• Hepatic, hematologic, and respiratory disorders
• Sinus bradycardia, sinoatrial block, second- and third-degree block (Dilantin)
SIDE EFFECTS
• **Constipation, nausea, vomiting—Valproic acid**
• Headache, drowsiness, somnolence, or insomnia
• Blood dyscrasias, **visual disturbances, ataxia, vertigo—Tegretol**
• Cardiac dysrhythmias, hypotension, **gingival hyperplasia, rash—Dilantin**
• Hepatotoxicity, pancreatitis—Valproic acid
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. Usually give orally. Administer by deep intramuscular (IM) or intravenous (IV) injection in emergencies. *Do not mix IV Dilantin with other medications.* Give IV Dilantin slowly (do not exceed 50 mg/min).
2. *Perform periodic blood studies for therapeutic levels.*
3. Check hepatic and renal functions.
4. ‡Teach patient to purchase a Medic-Alert bracelet or carry a medical ID card.‡
5. ‡Teach patient to never abruptly discontinue medication.‡
6. ‡With Dilantin, watch for gingival hyperplasia; encourage routine prophylactic dental care, and instruct patient to take with meals.‡
7. *Do not give Tegretol with grapefruit juice.*
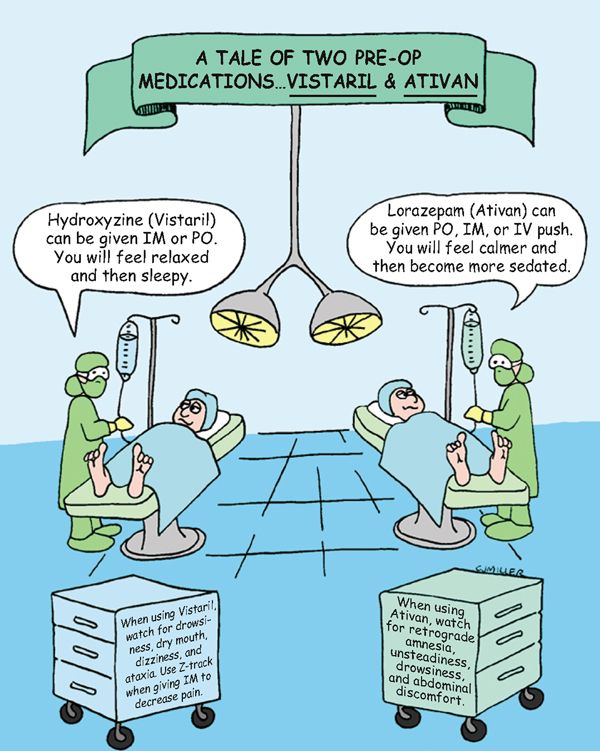
Hydroxyzine (Vistaril) and Lorazepam (Ativan) Preoperative and Postoperative Sedation

CLASSIFICATION
Antianxiety, sedative hypnotic
ACTIONS
• Vistaril: Produces anticholinergic, antihistaminic, analgesic effects; relaxes skeletal muscles; helps control nausea and vomiting.
• Ativan: Produces muscle relaxation; has anticonvulsant, sedative, antiemetic effects; decreases anxiety, status epilepticus.
USES
• Vistaril: Preoperative and postoperative sedation; antiemetic
• Ativan: Preoperative sedation, seizures, anxiety, status epilepticus
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Ativan: Pregnancy, sleep apnea
• Vistaril: Third-trimester-pregnancy, breast-feeding women, newborns
PRECAUTIONS
• Vistaril: Open-angle glaucoma, prostatic hypertrophy, asthma, COPD
• Ativan: Patients with suicidal tendencies and substance abuse
SIDE EFFECTS
• Vistaril: **Sedation,** anticholinergic effects (dry mouth), GI upset
• Ativan: Central nervous system (CNS) depression, paradoxical effect (excitement, heightened anxiety), physical dependence
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. Offer emotional support; *assess motor response; monitor vital signs and fluids and electrolytes; monitor bowel and bladder activity.*
2. Assess for desired preoperative effects.
3. ‡Teach patient that oral preparations of Ativan should be taken with meals.‡
4. *Administer intravenous (IV) medications slowly to avoid life-threatening reactions* †(severe hypotension, respiratory and cardiac arrest).†
5. ‡Teach patient to never abruptly discontinue oral medications.‡
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree