CASE 42
WHAT STRUCTURES FORM THE BOUNDARIES OF THE CARPAL TUNNEL?
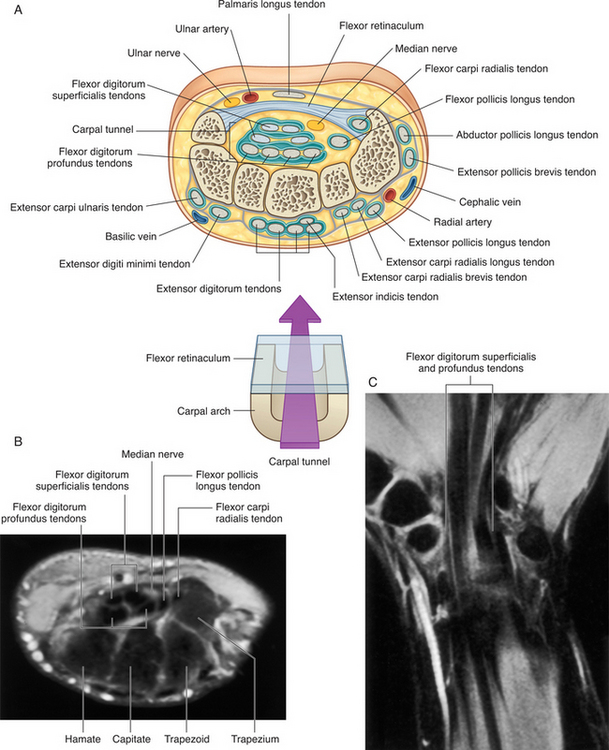
The carpal tunnel (Fig. 6-3), an osseofibrous opening, is formed as follows: the proximal and distal rows of the carpal bones constitute the lateral and medial walls and the floor of the tunnel. The lateral wall is composed proximally of the triquetrum and pisiform and distally by the hamate. The hook of the hamate (hamulus) makes a minor contribution to the lateral roof of the carpal tunnel. The medial wall is formed proximally by the tubercle of the scaphoid and distally by the trapezium. The roof of the tunnel is principally formed by the fibrous flexor retinaculum. The retinaculum is attached laterally to the pisiform and hamulus and medially to the tubercle of the scaphoid and the trapezium.