CASE 41
WHAT IS THE ORGANIZATION OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS?
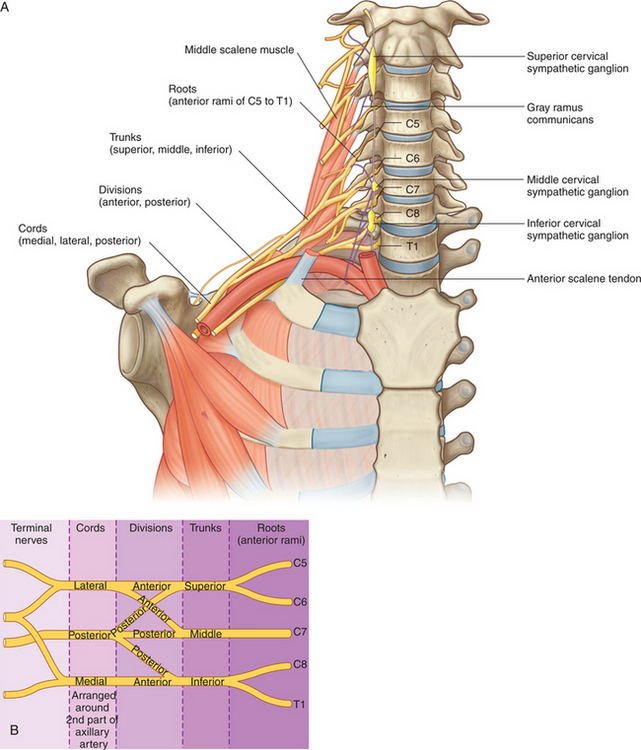
The brachial plexus is composed of the following elements: roots, trunks, divisions, cords, and branches (Fig. 6-1). The following mnemonic can be used to remember this basic organization: red tigers drink cold beer. The roots of the brachial plexus are ventral primary rami from C5, C6, C7, C8, and T1. The first pair, C5 and C6, joins to form the superior trunk, whereas C8 and T1 converge to form the inferior trunk. The middle trunk is simply a continuation of C7. Each trunk divides into an anterior division and a posterior division. The divisions then converge to form cords. The posterior cord is formed exclusively by the three posterior divisions, one from each of the three trunks. The anterior divisions form the lateral and medial cords. The anterior divisions from the superior and middle trunks unite to form the lateral cord, whereas the medial cord is simply a continuation of the anterior division from the inferior trunk. Each cord ends by dividing into two terminal branches. These are:
DESCRIBE THE SENSORY AND MOTOR FUNCTIONS OF THE VARIOUS ANATOMICAL LEVELS OF THE BRACHIAL PLEXUS.
The sensory and motor functions of various structural elements of the brachial plexus are described in Table 6-1.
TABLE 6-1 Sensory and Motor Functions of the Brachial Plexus at Different Anatomical Levels
| Anatomical Level | Sensory Function | Motor Function |
|---|---|---|
| Root of C5 | Skin of lateral surface of arm and lateral surface of proximal forearm | Lateral (external) rotation and abduction of the shoulder |
| Root of C6 | Cubital fossa, lateral side of forearm inferior to C5, and thumb | Flexion of elbow and extension and abduction of wrist (extensor carpi radialis longus muscle) |
| Root of C7 | Digits 2,3, and 4 and dorsal-radial surface of hand |