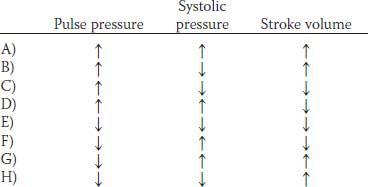
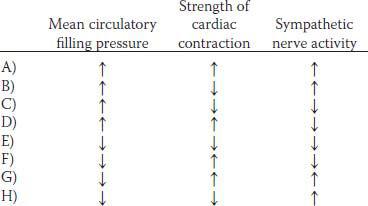
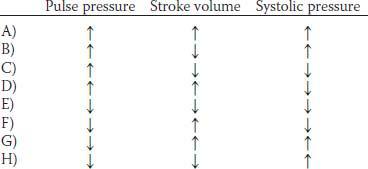
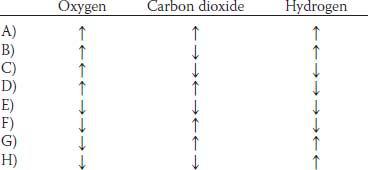
2. A healthy 25-year-old male medical student has an exercise stress test at a local health club. Which of the following sets of physiological changes is most likely to occur in this man’s skeletal muscles during exercise?
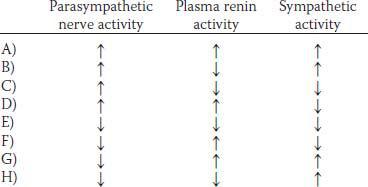
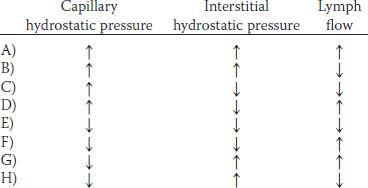
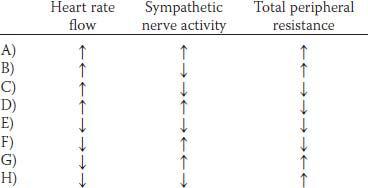
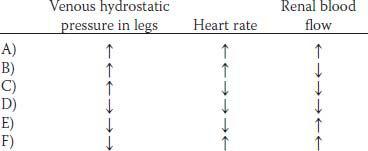
3. A 60-year-old woman has experienced dizziness for the past 6 months when getting out of bed in the morning and when standing up. Her mean arterial pressure is 130/90 mm Hg lying down and 95/60 sitting. Which of the following sets of physiological changes would be expected in response to moving from a supine to an upright position?
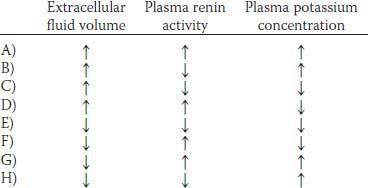
4. Which of the following sets of physiological changes would be expected to occur in response to an increase in atrial natriuretic peptide?
6. Listed below are the hydrostatic and oncotic pressures and filtration rate across a muscle capillary wall:
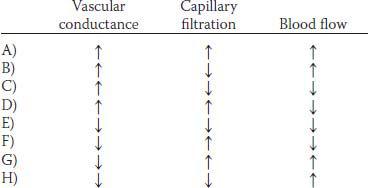
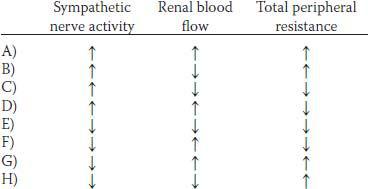
7. Administration of a drug decreases the diameter of arterioles in the muscle bed of an experimental animal. Which of the following sets of physiological changes would be expected to occur in response to the decrease in diameter?
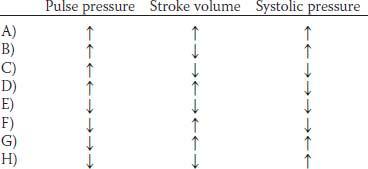
8. A 35-year-old woman visits her family practitioner for an examination. She has a blood pressure of 160/75 mm Hg and a heart rate of 74 beats/min. Further tests by a cardiologist reveal that the patient has moderate aortic regurgitation. Which of the following sets of changes would be expected in this patient?
9. A 65-year-old man with a 5-year history of congestive heart failure is being treated with an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor. Which of the following sets of changes would be expected to occur in response to the ACE inhibitor drug therapy?
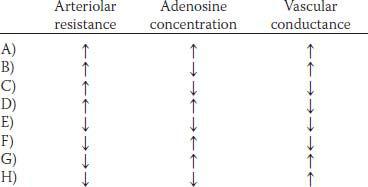
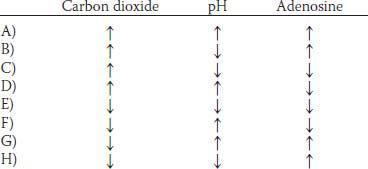
10. Cognitive stimuli such as reading, problem solving, and talking all result in significant increases in cerebral blood flow. Which of the following changes in cerebral tissue concentrations is the most likely explanation for the increase in cerebral blood flow?
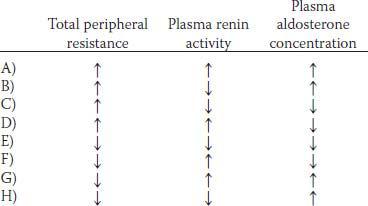
11. A 55-year-old man with a history of normal health visits his physician for a checkup. The physical examination reveals that his blood pressure is 170/98 mm Hg. Further tests indicate that he has renovascular hypertension as a result of stenosis in the left kidney. Which of the following sets of findings would be expected in this man with renovascular hypertension?
12. Histamine is infused into the brachial artery. Which of the following sets of microcirculatory changes would be expected in the infused arm?
13. Bradykinin is infused into the brachial artery of a 22-year-old man. Which of the following sets of microcirculatory changes would be expected in the infused arm?
15. A 72-year-old man had surgery to remove an abdominal tumor. Pathohistologic studies reveal that the tumor mass contains a large number of blood vessels. An increase in which of the following is the most likely stimulus for the growth of vessels in a solid tumor?
16. The diameter of a precapillary arteriole is increased in a muscle vascular bed. A decrease in which of the following would be expected?
17. Under control conditions, flow through a blood vessel is 100 ml/min with a pressure gradient of 50 mm Hg. What would be the approximate flow through the vessel after increasing the vessel diameter by 50%, assuming the pressure gradient is maintained at 100 mm Hg?
18. A 24-year-old woman delivers a 6-lb, 8-oz female baby. The newborn is diagnosed as having patent ductus arteriosus. Which of the following sets of changes would be expected in this baby?
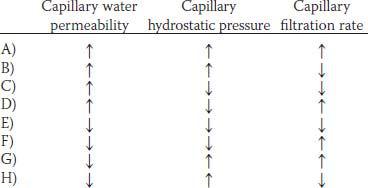
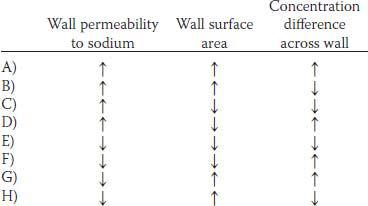
19. Which of the following sets of changes would be expected to cause the greatest increase in the net movement of sodium across a muscle capillary wall?
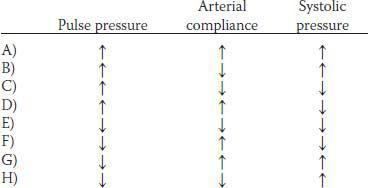
20. A 60-year-old man visits his family practitioner for an annual examination. He has a mean blood pressure of 130 mm Hg and a heart rate of 78 beats/min. His plasma cholesterol level is in the upper 25th percentile, and he is diagnosed as having atherosclerosis. Which of the following sets of changes would be expected in this patient?
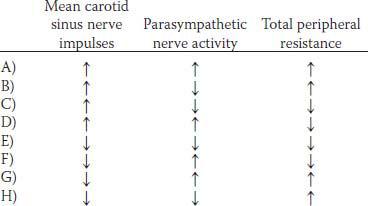
21. While participating in a cardiovascular physiology laboratory, a medical student isolates the carotid artery of an animal and partially constricts the artery with a tie around the vessel. Which of the following sets of changes would be expected to occur in response to constriction of the carotid artery?
22. A balloon catheter is advanced from the superior vena cava into the heart and inflated to increase atrial pressure by 5 mm Hg. An increase in which of the following would be expected to occur in response to the elevated atrial pressure?
23. The diameter of a precapillary arteriole is decreased in a muscle vascular bed. Which of the following changes in the microcirculation would be expected?
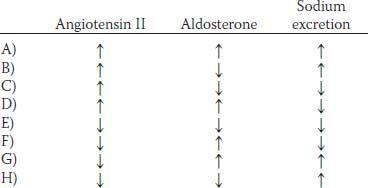
24. A 50-year-old man has a 3-year history of hypertension. He complains of fatigue and occasional muscle cramps. There is no family history of hypertension. The patient has not had any other significant medical problems in the past. Examination reveals a blood pressure of 168/104 mm Hg. Additional laboratory tests indicate that the patient has primary hyperaldosteronism. Which of the following sets of findings would be expected in this man with primary hyperaldosteronism hypertension?
25. A 72-year-old man had surgery to remove an abdominal tumor. Pathohistologic studies revealed that the tumor mass contained a large number of vessels. A decrease in which of the following is the most likely stimulus for the growth of vessels in a solid tumor?
26. Under control conditions, flow through a blood vessel is 100 ml/min under a pressure gradient of 50 mm Hg. What would be the approximate flow through the vessel after increasing the vessel diameter to four times normal, assuming that the pressure gradient was maintained at 50 mm Hg?
27. While participating in a cardiovascular physiology laboratory, a medical student isolates an animal’s carotid artery proximal to the carotid bifurcation and partially constricts the artery with a tie around the vessel. Which of the following sets of changes would be expected to occur in response to constriction of the carotid artery?
28. A 22-year-old man enters the hospital emergency room after severing a major artery in a motorcycle accident. It is estimated that he has lost approximately 700 ml of blood. His blood pressure is 90/55 mm Hg. Which of the following sets of changes would be expected in response to hemorrhage in this man?
29. A 22-year-old man has a muscle blood flow of 250 ml/min and a hematocrit of 50. He has a mean arterial pressure of 130 mm Hg, a muscle venous pressure of 5 mm Hg, and a heart rate of 80 beats/min. Which of the following is the approximate vascular resistance in the muscle of this man?
30. A healthy 28-year-old woman stands up from a supine position. Moving from a supine to a standing position results in a transient decrease in arterial pressure that is detected by arterial baroreceptors located in the aortic arch and carotid sinuses. Which of the following sets of cardiovascular changes is most likely to occur in response to activation of the baroreceptors?
31. A 35-year-old woman visits her family practice physician for an examination. She has a mean arterial blood pressure of 105 mm Hg and a heart rate of 74 beats/min. Further tests by a cardiologist reveal that the patient has moderate aortic valve stenosis. Which of the following sets of changes would be expected in this patient?
32. A 25-year-old man enters the hospital emergency room after severing a major artery during a farm accident. It is estimated that the patient has lost approximately 800 ml of blood. His mean blood pressure is 65 mm Hg, and his heart rate is elevated as a result of activation of the chemoreceptor reflex. Which of the following sets of changes in plasma concentration would be expected to cause the greatest activation of the chemoreceptor reflex?
34. Under normal physiological conditions, blood flow to the skeletal muscles is determined mainly by which of the following?
35. Which of the following substances in plasma is the major factor that contributes to plasma colloid osmotic pressure?
36. A healthy 22-year-old female medical student has an exercise stress test at a local health club. An increase in which of the following is most likely to occur in this woman’s skeletal muscles during exercise?
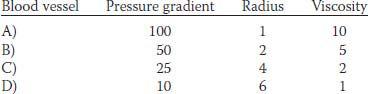
38. Which blood vessel has the highest vascular resistance?
| Blood vessel | Blood flow (ml/min) | Pressure gradient (mm Hg) |
|---|---|---|
| A) | 1000 | 100 |
| B) | 1200 | 60 |
| C) | 1400 | 20 |
| D) | 1600 | 80 |
| E) | 1800 | 40 |
39. A twofold increase in which of the following would result in the greatest increase in the transport of oxygen across the capillary wall?
40. Which of the following vessels has the greatest total cross-sectional area in the circulatory system?
41. Which of the following components of the circulatory system contains the largest percentage of the total blood volume?
43. Which of the following segments of the circulatory system has the highest velocity of blood flow?
50. A 65-year-old man is suffering from congestive heart failure. He has a cardiac output of 4 L/min, arterial pressure of 115/85 mm Hg, and a heart rate of 90 beats/min. Further tests by a cardiologist reveal that the patient has a right atrial pressure of 10 mm Hg. An increase in which of the following would be expected in this patient?
53. Which of the following sets of physiological changes would be expected to occur in a person who stands up from a supine position?
54. Blood flow to a tissue remains relatively constant despite a reduction in arterial pressure (autoregulation). Which of the following would be expected to occur in response to the reduction in arterial pressure?
56. Autoregulation of tissue blood flow in response to an increase in arterial pressure occurs as a result of which of the following?
57. Which of the following pressures is normally negative in a muscle capillary bed in the lower extremities?
59. Movement of solutes such as Na+ across the capillary walls occurs primarily by which of the following processes?
61. A decrease in which of the following would be expected to occur in response to a direct increase in renal arterial pressure?
63. A decrease in which of the following would be expected to occur in response to an increase in sodium intake?
64. Which of the following would be expected to occur in response to constriction of the renal artery?
66. Which of the following would be expected to occur during a Cushing reaction caused by brain ischemia?
68. An angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitor is administered to a 65-year-old man with a 20-year history of hypertension. The drug lowers arterial pressure and increases plasma levels of renin and bradykinin. Which of the following would best explain the elevation in plasma bradykinin?
69. A 60-year-old man has a mean arterial blood pressure of 130 mm Hg, a heart rate of 78 beats/min, a right atrial pressure of 0 mm Hg, and a cardiac output of 3.5 L/min. He also has a pulse pressure of 35 mm Hg and a hematocrit of 40. What is the approximate total peripheral vascular resistance in this man?
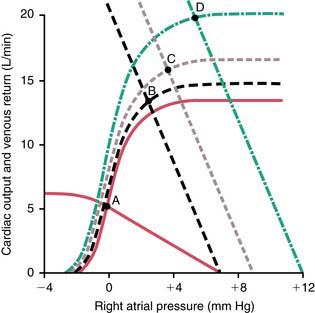
70. In the following graph, for the cardiac output and venous return curves defined by the solid red lines (with the equilibrium at A), which of the following is true?
71. A 30-year-old male is resting, and his sympathetic output increases to maximal values. Which of the following sets of changes would be expected in response to this increased sympathetic output?
72. If a patient has an oxygen consumption of 240 ml/min, a pulmonary vein oxygen concentration of 180 ml/L of blood and a pulmonary artery oxygen concentration of 160 ml/L of blood units, what is cardiac output in liters per minute?
73. If the thorax of a normal person is surgically opened, what will happen to the cardiac output curve?
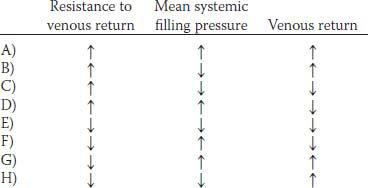
74. Which of the following normally cause the cardiac output curve to shift to the left along the right atrial pressure axis?
76. Which of the following normally cause the cardiac output curve to shift to the right along the right atrial pressure axis?
78. Which of the following is normally associated with an increased venous return of blood to the heart?
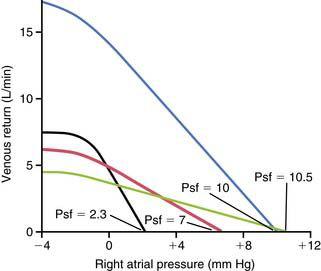
79. Which of the curves in the following graph (redrawn from Guyton AC, Jones CE, Coleman TB: Circulatory Physiology: Cardiac Output and Its Regulation, 2nd ed., Philadelphia: WB Saunders, 1973) has the highest resistance to venous return?
81. In which of the following conditions would you normally expect to find a decreased cardiac output?
84. If a person has been exercising for 1 hr, which of the following organs will experience the smallest decrease in blood flow?




Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree