4 CASE 4
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF KEY SYMPTOMS
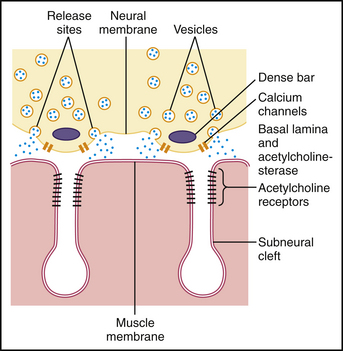
Acetylcholine is stored in vesicles in the presynaptic terminal of alpha (α)-motor neurons. After an action potential arrives, calcium enters the presynaptic terminal, causing the vesicles to migrate toward the presynaptic membrane. There are numerous proteins involved in vesicle exocytosis. The SNAP-SNARE mechanism includes proteins that mediate vesicle docking and fusion, including synapsin 1, synaptobrevin, SNAP-25, syntaxin, synaptotagmin, and synaptophysin. The series of SNAP and SNARE proteins allow docking of the vesicles with the cell membrane, fusion, and, finally, exocytosis of the acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft (Fig. 4-1). The acetylcholine diffuses across the synaptic cleft and binds to receptors on the end plate region of the skeletal muscle cell.
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree