CASE 32
LABORATORY STUDIES
Diagnostic Work-Up
Table 32-1 lists the likely causes of the woman’s illness (differential diagnosis). Symptoms of vaginitis and vaginosis are nonspecific, and a diagnosis without laboratory investigation is unreliable. Investigative approach may include
TABLE 32-1 Differential Diagnosis and Rationale for Inclusion (consideration)
Rationale: Vaginal discharge can be caused by any of the above pathogens, and distinguishing them clinically is often difficult, if not impossible. Classically, the discharge from Candida is whitish, that of Trichomonas is yellow and frothy, and that of bacterial vaginosis is particularly foul smelling. Microbiologic examination is generally required for a definitive diagnosis.
In failed tests just mentioned, vaginal culture can be obtained.
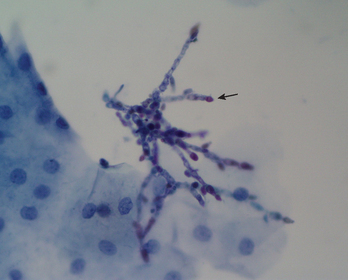
Microbiologic Properties
Candida species are yeasts. In secretions (wet preparations) and tissue sections, however, they may appear as elongated structures (pseudohyphae, or even true hyphae) after Gram or Papanicolaou stain (Fig. 32-1). The organism grows on routine fungal media as well in blood culture bottles and on agar plates (Fig. 32-2). Yeasts reproduce by budding under most culture conditions. The most common species isolated from clinical specimens is Candida albicans, with Candida glabrata, Candida tropicalis, Candida parapsilosis, and Candida krusei found less commonly. C. albicans can be rapidly differentiated from other species by its production of germ tubes (short hyphal filaments) after 2 hours of cultivation of yeast cells at 37°C in human serum. C. albicans also characteristically produces chlamydospores, the reproductive, thick-walled structures of the fungus, larger than the standard spores produced by the molds.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree