31 CASE 31
PHYSICAL EXAMINATION
PE: Patient’s breathing is labored and involving abdominal muscles. The thoracic cage is asymmetrical, with the left side protruding more than the right side. The left side shows much less movement than the right during breathing. Breath sounds are decreased on the left side, and the left side shows hyperresonance to percussion.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF KEY SYMPTOMS
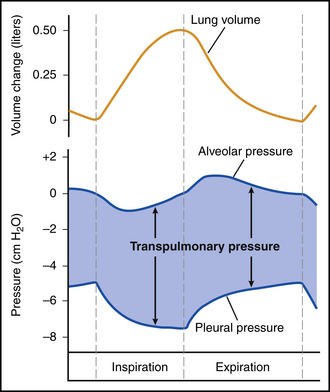
Intrapleural pressure in the thorax is negative, created by the inward directed elastic recoil of the lung and the outward directed elastic recoil of the chest wall. During inspiration, contraction of the diaphragm creates a more negative intrapleural pressure and the consequent expansion of the lungs creates a negative alveolar pressure. Air flows into the lungs from outside the body in response to the pressure gradient between the alveoli and the atmospheric air (Fig. 31-1).
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree