Special Considerations for the Administration of Medications to the Elderly
Special Considerations for the Administration of Medications to the Elderly
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
On completion of the materials provided in this chapter, you will be able to:
![]() People are now living longer than at any period in history, and we are continuing to increase our knowledge of how to protect our health and prevent illness. By practicing good health habits, such as proper diet, an exercise program, and a positive attitude, people are enjoying better health. As research continues, cures and maintenance regimens for major health problems are being found. Life expectancy continues to increase. “Old-old” persons over the age of 85 are the most rapidly increasing portion of the population in the United States. This group is also using more of the nation’s health care resources.
People are now living longer than at any period in history, and we are continuing to increase our knowledge of how to protect our health and prevent illness. By practicing good health habits, such as proper diet, an exercise program, and a positive attitude, people are enjoying better health. As research continues, cures and maintenance regimens for major health problems are being found. Life expectancy continues to increase. “Old-old” persons over the age of 85 are the most rapidly increasing portion of the population in the United States. This group is also using more of the nation’s health care resources.
Aging is a normal process, beginning at infancy and continuing throughout the life cycle. Aging is not the cause of specific diseases, but certain chronic illnesses are more prevalent in the elderly and may lead to additional health problems. Chronic illnesses usually require an increase in drug use to control the symptoms or progression of the condition.
Changes Experienced by the Elderly
Biological and physiological changes that affect all body systems occur and conflict with the action of some medications. Medication problems are more likely to occur in the older age group. These problems can be drug interactions, adverse reactions, drug and food interactions, or medication errors. Reflexes slow, and the body is unable to adapt quickly to changes in temperature. A decrease in the sense of touch may be a safety issue. There is a decrease in saliva, which may slow the absorption of buccal medications. Some elderly persons may have difficulty swallowing, especially large tablets. An advantage of aging is a diminished sense of taste: Elderly people may have no difficulty with some of the bitter-tasting medications.
Biological and physiological changes also affect the metabolism and excretion of drugs. Chronic conditions, such as hypertension, diabetes, heart conditions, and arthritis, interfere with homeostasis and may cause medications to be less effective. Absorption is affected by age-related changes in the motility of the gastrointestinal tract. A decrease in motility may cause an increase in drug actions. Many elderly persons resort to the regular use of laxatives. Laxatives increase the motility of the gastrointestinal tract and therefore allow less time for the prescribed medication to be absorbed.
Changes in cardiac output may also decrease the flow of blood to the liver and kidneys. Another major change with aging is the decrease in renal function. This may lead to medications being removed from the body more slowly and perhaps less completely.
A decrease in body weight of many elderly persons is reason to reassess the dosages of medications ordered. The patient’s actual weight should be used to validate the correct dosage of each drug. Many drug reference manuals now list the appropriate dosages for geriatric, pediatric, and adult patients. At times it may be difficult to select a proper site for an injection. This is because of a decrease in muscle mass. However, an advantage to aging may be a decrease in the perception of pain from injections because of a decrease in some sensory perceptions.
These changes, in concert with a person’s genetic programming, add to the severity of health problems in the elderly. It is difficult for a person who has had an active life to deal with these changes. The nurse must be understanding to help an elderly person adapt to a limited lifestyle.
Physical illness often affects a person’s mental state, adding to anxiety and further deterioration. Occasionally, an elderly person feels unable to make the most basic decisions. The nurse, in collaboration with other members of the health care team, can help the patient, the family, and the persons responsible for giving care to understand the process of change or aging. For example, Alzheimer’s disease negatively affects a person’s ability to safely assume responsibility for taking his or her own medications, especially as the stages advance. It is important for family members and caregivers to be aware of this.
Problems of the Elderly
Multiple Physicians.
Some older persons are in the habit of visiting an internist for an annual physical examination. Because the elderly have more aches and pains than those in other age groups, they may also visit a physician in family practice to deal with minor problems. If these aches and pains do not resolve, they may visit a third physician. If each physician writes prescriptions, the patient may be prescribed several medications that duplicate actions or cause drug interaction or overdosage.
The patient should be encouraged to visit only one physician unless referred to a specialist. If the patient visits another physician, he or she should prepare a list of all medications taken routinely or as needed and give it to the new physician. The physician can then prescribe medication and instruct the patient to stop taking duplicate medications or those that cause drug interactions.
Prescriptions.
Older patients should be encouraged to have all their prescriptions filled at the same pharmacy. This allows the pharmacist to have a complete listing of the medications that have been prescribed. The pharmacist is then able to monitor for adverse interactions of the patient’s medicines. When an older patient uses many different pharmacies, this safety check does not occur.
Inadequate income is a major problem for many older people. To lower medical costs, they may take less than the prescribed amount of a prescription drug so that it will last longer. They may also stop taking the medication if they perceive it to be ineffective. They may go to the drugstore and buy nonprescription drugs. Such drugs will save a physician’s fee and are less expensive than prescription drugs, but they may be ineffective. However, the patient may perceive them to be a cure. Another method used to lower costs of drugs is to take medication prescribed for a family member or friend. Misuse of drugs is widespread among the elderly and may cause various problems, such as fluid imbalance, nutritional disturbances, and psychological or neurological problems. The elderly may also experience a deterioration in their eyesight. There are many magnifying tools that can help them continue to administer the correct dose of their medication.
As older persons become forgetful, they may not take their medications or may not take them at the prescribed time. Often family members find medication bottles on the floor, and they do not know whether the medication was taken.
When it becomes unsafe for an elderly person to stay at home alone, a day-care center can relieve the pressure on family members. People enjoy being with others of their age to discuss memories and similar experiences. They can join in crafts and activities as they wish. There are opportunities to discuss thoughts and concerns with personnel at the center. Then the medication regimen can be continued during the day, and meals can be served and activities planned. Activities at the center stimulate the elderly and give them something interesting to discuss at home in the evening.
More elderly persons elect to live in their own homes rather than in a retirement home or a nursing home. Sometimes they share their home with someone near their age. If an elderly person or couple cannot care for themselves, they may choose to share their home with an individual or a couple who will not only be homemakers but also give care as needed. Apart from providing a home for the ones giving care, the elderly person may provide monetary compensation.
Medical Alert System
A medical alert system is a valuable tool for a homebound person living alone or for times when the caregiver must be away. It is also used in retirement homes. In an emergency a button is pushed on the monitoring system or on a device on a chain worn by the patient. The system alerts medical personnel to the emergency situation. Such a system gives a feeling of security to homebound persons and their families.
Medications for the Elderly in the Home
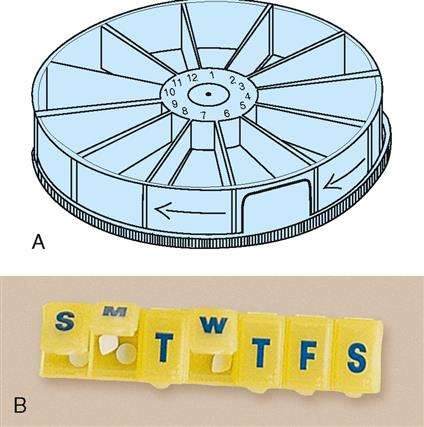
When purchasing medications from a pharmacy, elderly persons should request that childproof containers not be used. Containers that are available to prepare medications for a day or a week at a time should be purchased and used (Figure 21-1). Such containers have a special compartment for each hour the medications are to be given. The time can be written on the lid of the individual compartment and easily removed if the time changes. These containers are especially helpful if someone outside the home assists the patient in preparing medications.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree