21 CASE 21
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY OF KEY SYMPTOMS
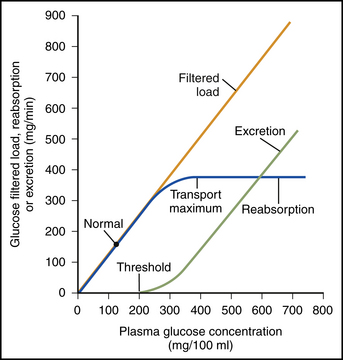
The renal glucose transport capacity is determined by the number of transport protein molecules. The maximum glucose transport capacity is about twice as high as the normal filtered load of glucose. Consequently, glucose is not normally excreted in the urine. When the filtered load exceeds the glucose reabsorption, some glucose remains in the tubular filtrate and ultimately is excreted in the urine. For most individuals, the glucose renal threshold occurs when plasma glucose levels exceed 250 mg/dL (Fig. 21-1).
< div class='tao-gold-member'>
Only gold members can continue reading. Log In or Register to continue
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree