CASE 2
To rule out chromosomal abnormalities and birth defects in the fetus of her 40-year-old gravid patient, the physician performs an amniocentesis and an ultrasound. The chromosomal analysis ruled out any chromosomal abnormalities; however, the amniocentesis showed that the alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) level was elevated. The ultrasound revealed that the fetus had spina bifida cystica.
HOW DO THE VERTEBRAE AND INTERVERTEBRAL DISCS FORM EMBRYOLOGICALLY?
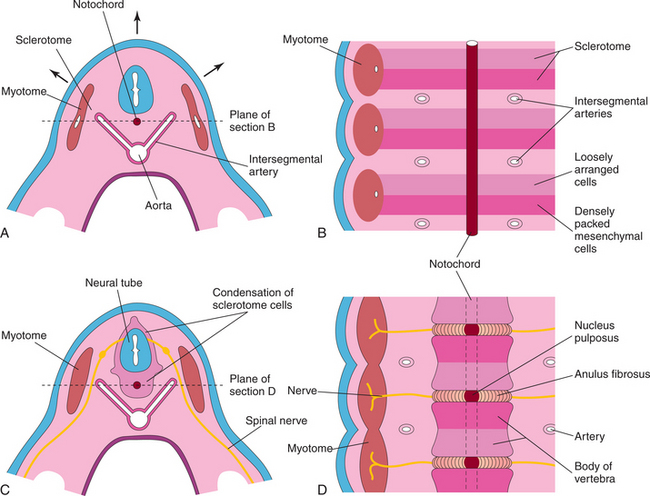
The vertebrae and intervertebral discs develop from the mesenchyme of sclerotomes around the notochord (Fig. 1-4). Each sclerotome contains two layers of mesenchyme arranged cranially and caudally. The cranial layer of mesenchymal cells is loosely organized, whereas the caudal layer is dense in its arrangement. Between the sclerotomes are mesenchyme and intersegmental arteries. The intersegmental arteries ultimately become the intercostal and lumbar arteries in the thorax and lumbar regions, respectively.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree