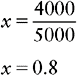Reconstitution and Dosages Measured in Units
Reconstitution and Dosages Measured in Units
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
On completion of the materials provided in this chapter, you will be able to perform computations accurately by mastering the following mathematical concepts:
2 Using a proportion to solve problems involving drugs measured in unit dosages
3 Drawing a line through an insulin syringe to indicate the number of units desired
![]() A unit is the amount of a drug needed to produce a given result. Various drugs are measured in units; the examples used in this chapter are among the more common drugs prescribed.
A unit is the amount of a drug needed to produce a given result. Various drugs are measured in units; the examples used in this chapter are among the more common drugs prescribed.
Drugs used in this chapter include:
Epogen—A drug that increases the production of red blood cells
Fragmin—An anticoagulant that prevents the clotting of blood
Penicillin—An antibiotic that reduces organisms within the body that cause infection
Heparin—An anticoagulant that inhibits clotting of the blood
Insulin—A hormone secreted by the pancreas that lowers blood glucose
Epogen is a drug that helps to combat the effects of anemia caused by chemotherapy or chronic renal failure. After administering the medicine, the nurse should monitor the patient’s blood pressure and laboratory results on a routine basis.
Fragmin is used in the prevention of deep vein thrombosis after abdominal surgery, hip replacements, and unstable angina/non–Q wave myocardial infarction. It may also be used with patients who have restricted mobility during an acute illness. Fragmin may only be given by subcutaneous injections—never intramuscularly or intravenously. The patient’s blood studies must be monitored on a routine basis during treatment with Fragmin.
Penicillin can be administered orally or parenterally, but heparin, insulin, and epogen must be given subcutaneously or intravenously.
Before administering penicillin, the nurse must confer with the patient regarding previous allergies to the drug. After administering the drug, the nurse must still observe the patient for signs of an allergic reaction.
Because heparin prolongs the time blood takes to clot, the dosage must be accurate. A larger dose may cause hemorrhage, and an insufficient dose may not have the desired result. After administering the drug, the nurse should observe the patient for signs of hemorrhage.
INSULIN
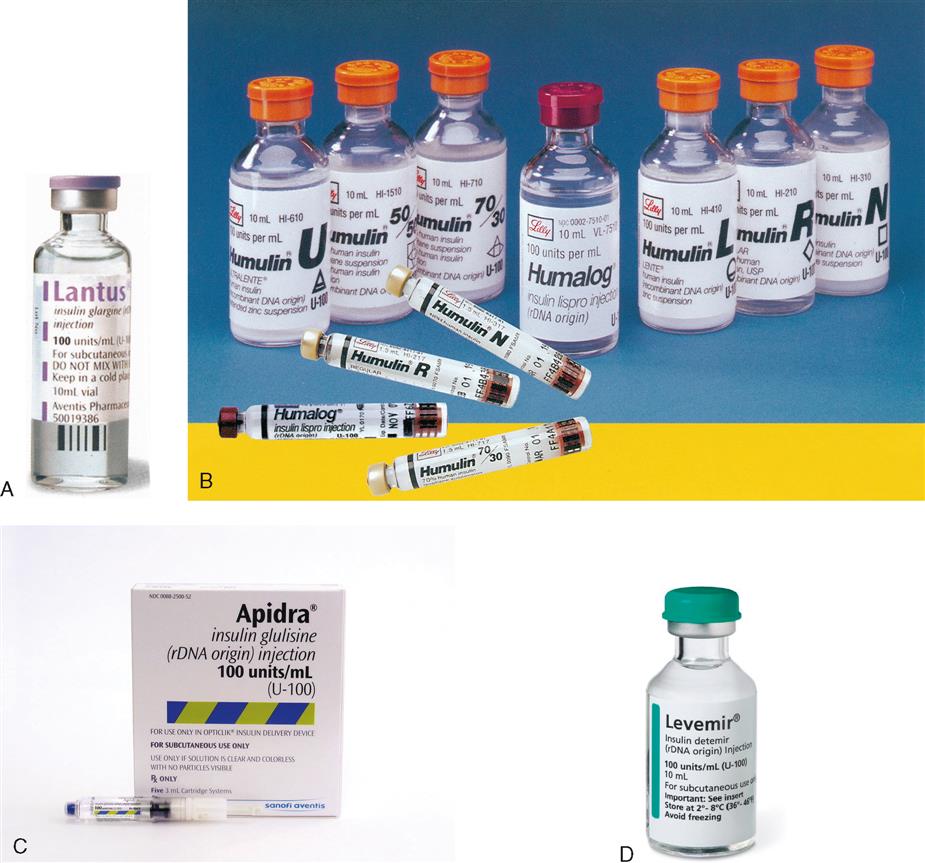
Insulin is used in the treatment of diabetes mellitus. Accuracy is important in the preparation of insulin. A higher dosage than needed may cause insulin shock. An insufficient amount of insulin may result in diabetic coma. Both conditions are extremely serious, and the nurse must be able to recognize the symptoms of each condition so that immediate treatment can be initiated to stabilize the patient. In many institutions, both insulin and heparin dosages are checked for accuracy by another nurse before the drug is administered to the patient. Figure 15-1 shows examples of different types of insulin.
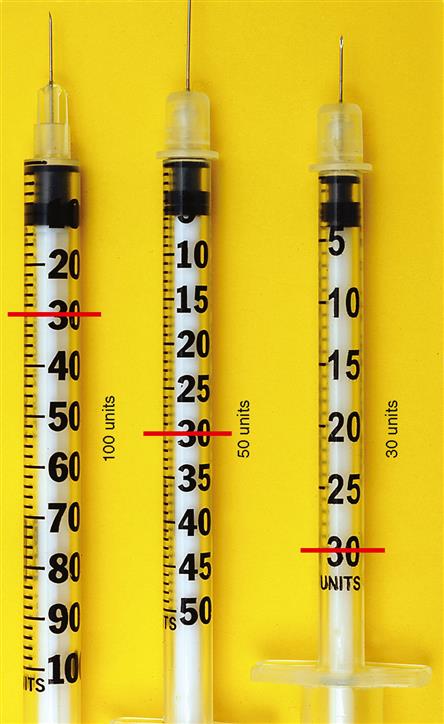
Insulin Syringes
Insulin syringes were developed specifically for the administration of insulin. They are calibrated in units and are available in 30 units, 50 units, and 100 units (Figure 15-2). A U-100 insulin syringe and U-100 insulin are necessary to ensure an accurate insulin dosage. U-100 insulin means that 100 units of insulin are contained in 1 mL of liquid. U-100 insulin is a universal insulin preparation that all persons requiring insulin can use. Another type of U-100 syringe is the U-100 Lo-Dose syringe, which measures 50 units; however, for accuracy, no more than 40 units should be measured in the U-100 Lo-Dose syringe. Because the doses are minute, the U-100 syringe provides the most accurate measurement of insulin dosages. The 30-unit U-100 syringe is used for insulin doses that equal less than 30 units.
IMPORTANT NOTE: Only insulin is measured and given in the syringes that are marked in units.* Heparin, penicillin, and other medication measured in units can be measured and given only in syringes marked in milliliters.
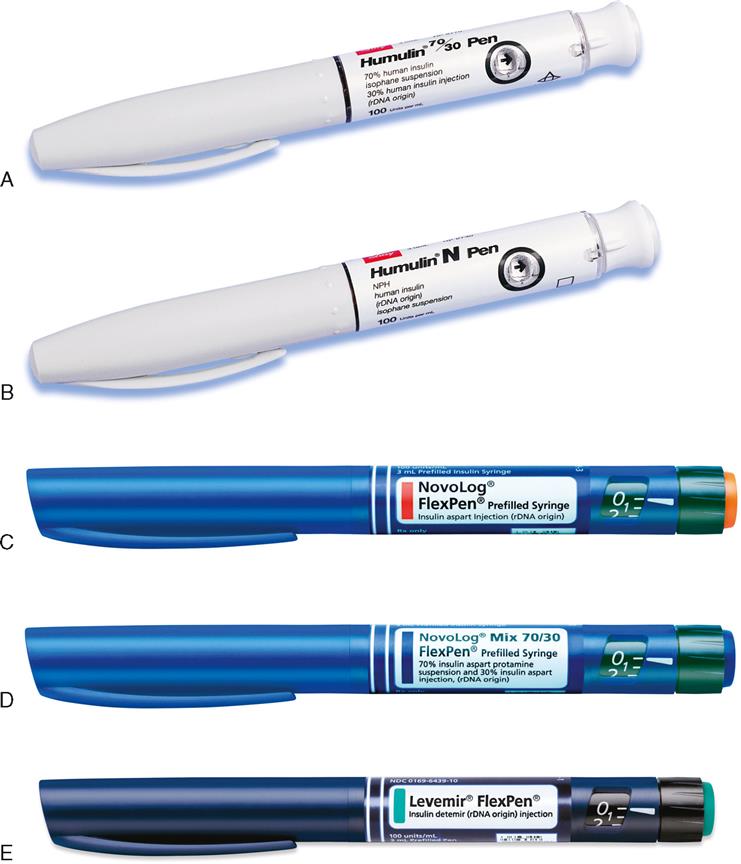
Insulin Pens
Insulin is also available in prefilled insulin pens. The insulin pens require a special needle to be attached. Each insulin pen contains a dial to choose the desired number of units to be administered. For example, if 6 units of Novolog insulin are desired, the dial on the Novolog insulin pen would be turned to the Number 6. See Figure 15-3 for examples of insulin pens.
Powder Reconstitution
A drug in powdered form is necessary when a medication is unstable as a liquid form for a long period. This powdered drug must be reconstituted—dissolved with a sterile diluent—before administration. The diluents commonly used include sterile water, sterile normal saline solution, 5% dextrose solution (D5W), and bacteriostatic normal saline.
Before reconstituting the medication, the nurse must follow several principles:
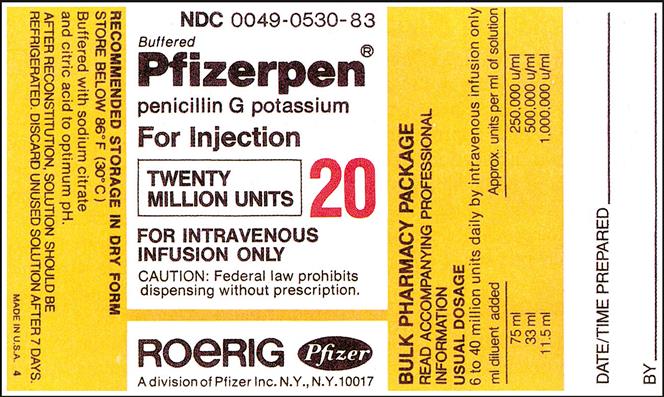
EXAMPLE:
| a. | What is the route of administration? | IV |
| b. | What type of diluent can be used? | Check insert |
| c. | How much diluent must be added? | 75 mL, 33 mL, or 11.3 mL |
| d. | If 75 mL of diluent is added, what is the medication concentration? | 250,000 units/mL |
| e. | How long will the medication maintain its potency at room temperature? | 7 days |
| f. | The physician orders 2,000,000 units IV q4 h. How many milliliters will you give? | 8 mL |
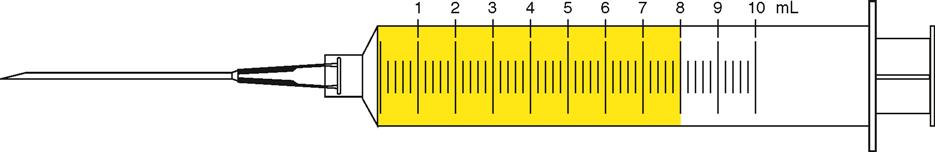
| Shade the syringe. |
b. 250,000 units 1 mL ::_______units_______mL
c. 250,000 units 1 mL:: 2,000,000 units: x mL
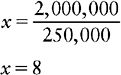
e. x = 8 mL
Dosages Measured in Units Involving Oral Medications
EXAMPLE: The physician orders mycostatin 400,000 units po four times a day. The drug is supplied 100,000 units/mL after reconstitution. How many milliliters will the nurse administer?
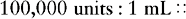
b. The right side of the proportion is determined by the physician’s order and the abbreviations on the left side of the proportion. Only two different abbreviations may be used in a single proportion. The abbreviations must be in the same position on the right side as on the left side.
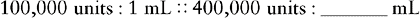
We need to find the number of milliliters to be administered, so we use the symbol x to represent the unknown.
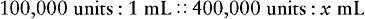
c. Rewrite the proportion without the abbreviations.
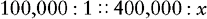
d. Solve for x.
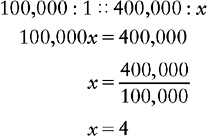
e. Label your answer as determined by the abbreviation placed next to x in the original proportion.
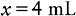
The nurse would measure 4 mL to administer 400,000 units of mycostatin.
Dosages Measured in Units Involving Parenteral Medications
EXAMPLE: The physician orders heparin 4000 units subcutaneous q8 h. How many milliliters will the nurse administer?