Oxytocin (Pitocin)

CLASSIFICATION
Uterine smooth muscle stimulant
ACTIONS
Contracts uterine and mammary smooth muscle. Increases force, frequency, and duration of uterine contractions.
USES
• Managing incomplete or inevitable abortion
• Controlling postpartum hemorrhage
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Cephalopelvic disproportion, previous uterine surgery
• Unengaged fetal head, unfavorable fetal position or presentation
• Fetal distress without evidence of imminent delivery
• Placenta previa or cord prolapse or both
• Women with active genital herpes
PRECAUTIONS
• Used with great caution in women who are high parity (5 or more)
SIDE EFFECTS
• Tachycardia, premature ventricular contraction, hypotension
• Nausea, vomiting, water intoxication
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Frequently assess baseline vital signs, blood pressure, and fetal heart rate.*
2. *Constantly monitor frequency, duration, and strength of contractions.*
3. *Stop the infusion; notify the physician if the resting uterine pressure is above 15 to 20 mm Hg, if contractions are lasting longer than 1 minute, if they are occurring more frequently than every 2 to 3 minutes, or if an alteration in fetal heart rhythm or rate occurs.*
4. Maintain input and output; evaluate for excessive water retention.
5. Do not confuse with vasopressin (Pitressin), which is an antidiuretic hormone.
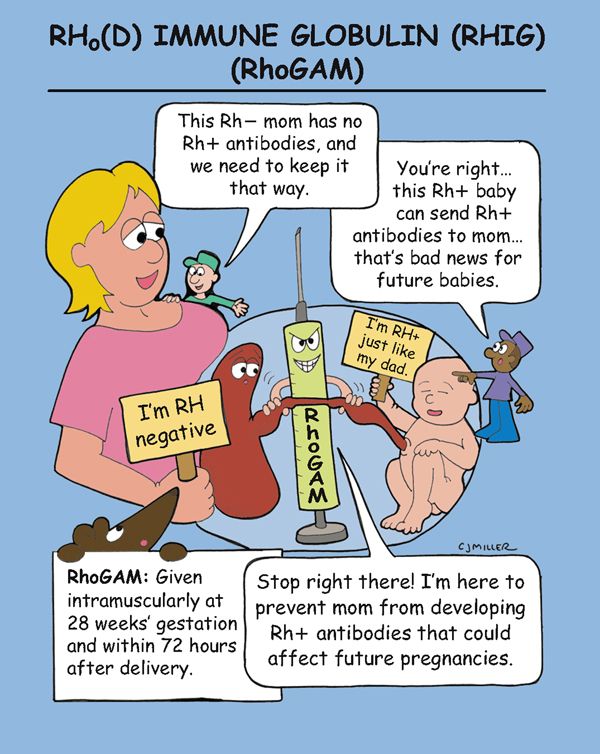
Rho(D) Immune Globulin (RhIG) (RhoGAM)

CLASSIFICATION
Immunosuppressant
ACTION
Rho(D) immune globulin (RhIG) is an immunoglobulin that is a concentrated preparation that contains antibodies to Rho(D). This prevents an Rh-negative woman from developing antibodies after exposure to Rho(D)-positive blood.
USES
• Prevents sensitization in Rh-negative pregnant patient given in the last trimester of pregnancy, as well as after abortion or miscarriage.
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Not given to Rh-positive women.
SIDE EFFECTS
• Slight temperature elevation
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. *Administered intramuscularly at 28 weeks’ gestation and again within 72 hours after delive*ry.
2. *May also be administered to Rh-negative women receiving a blood transfusion or who have had a spontaneous or induced abortion or amniocentesis.*
3. ‡Instruct Rh-negative patients to advise health care providers of their Rh-negative status.‡
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree