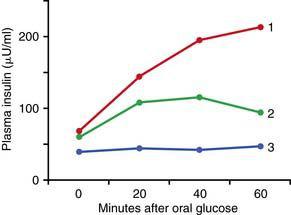
The red lines in the figure above illustrate the normal relationships between plasma insulin concentration and glucose production in the liver and between plasma insulin concentration and glucose uptake in muscle.
6. In the figure, which lines most likely illustrate these relationships in a patient with type 2 diabetes?
7. In the figure, which lines most likely illustrate these relationships in a patient with acromegaly?
9. One treatment for erectile dysfunction requires the injection of a substance into the corpora cavernosa of the penis. The injection of which of the following causes an erection?
10. A baby is born with a penis, a scrotum with no testes, no vagina, and XX chromosomes. This condition is referred to as hermaphroditism. Which of the following could cause this abnormality?
11. A young woman is given daily injections of a substance beginning on the 16th day of her normal menstrual cycle and continuing for 3 weeks. As long as the injections continue, she does not menstruate. The injected substance could be which of the following?
15. If a radioimmunoassay is properly conducted and the amount of radioactive hormone bound to antibody is low, this would indicate which of the following?
16. Spermatogenesis is regulated by a negative feedback control system in which follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) stimulates the steps in sperm cell formation. What is the negative feedback signal associated with sperm cell production that inhibits pituitary formation of FSH?
19. Some cells secrete chemicals into the extracellular fluid that act on cells in the same tissue. Which of the following refers to this type of regulation?
20. Which of the following pairs is an example of the type of regulation referred to in question 19?
21. Estrogen is required for normal reproductive function in the male. Where is the principal site of estrogen synthesis in the male?
22. A professional athlete in her mid-20s has not had a menstrual cycle for 5 years, although a bone density scan revealed normal skeletal mineralization. Which of the following facts elicited during the taking of her medical history may explain these observations?
23. In the circulatory system of a fetus, which of the following is greater before birth than after birth?
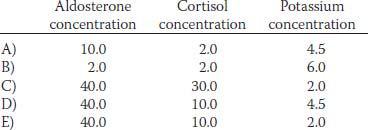
Match each of the patients described in questions 24 to 26 with the correct set of plasma values listed in the table below. Normal values are as follows: plasma aldosterone concentration, 10 ng/dL; plasma cortisol concentration, 10 mg/dL; plasma potassium concentration, 4.5 mEq/L.
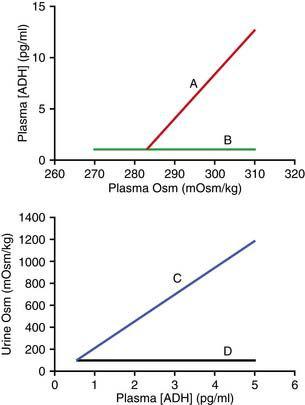
27. In the following figure, which lines most likely reflect the responses in a patient with nephrogenic diabetes insipidus?
31. In order for male differentiation to occur during embryonic development, testosterone must be secreted from the testes. What stimulates the secretion of testosterone during embryonic development?
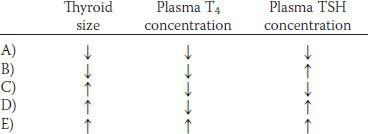
32. A patient has an elevated plasma thyroxine (T4) concentration, a low plasma thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) concentration, and a thyroid gland that is smaller than normal. Which of the following is the most likely explanation for these findings?
34. As menstruation ends estrogen levels in the blood rise rapidly. What is the source of the estrogen?
35. Which of the following anterior pituitary hormones plays a major role in the regulation of a nonendocrine target gland?
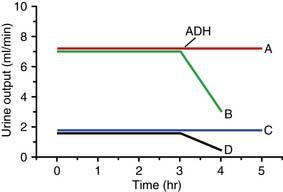
36. An experiment is conducted in which antidiuretic hormone (ADH) is administered at hour 3 to four subjects (A to D). In the following figure, which lines most likely reflect the response to ADH administration in a normal patient and in a patient with central diabetes insipidus?
| Normal | Central diabetes insipidus | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | B | A |
| B) | B | D |
| C) | D | A |
| D) | D | B |
37. A female athlete who took testosterone-like steroids for several months stopped having normal menstrual cycles. What is the best explanation for this observation?
B) Testosterone binds to receptors in the endometrium, resulting in the endometrium’s failure to develop during the normal cycle
C) Testosterone binds to receptors in the anterior pituitary that stimulate the secretion of follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH)
38. Which of the following would be expected in a patient with a genetic deficiency in 11β-hydroxysteroid dehydrogenase type 2?
39. Which of the following decreases the resistance in the arteries leading to the sinuses of the penis?
40. A patient has a goiter associated with high plasma levels of both thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) and thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH). Her heart rate is elevated. This patient most likely has which of the following?
41. A 40-year-old woman comes to the emergency room with a fracture in the neck of the femur. Radiographs reveal generalized demineralization of the bone in the area. Her plasma calcium ion concentration is significantly greater than normal: 12.2 mg/dL. Which of the following conditions is consistent with this presentation?
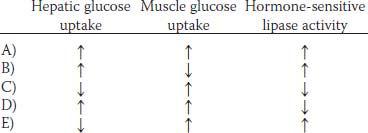
42. A man eats a low carbohydrate meal rich in proteins containing the amino acids that stimulate insulin secretion. Which of the following responses accounts for the absence of hypoglycemia?
43. A 46-year-old man has “puffy” skin and is lethargic. His plasma thyroid-stimulating hormone concentration is low and increases markedly when he is given thyrotropin-releasing hormone. Which of the following is the most likely diagnosis?
45. A man is taking a number of medications, one of which appears to be interfering with the emission phase of the sexual act. Which of the following medications could cause this problem?
47. Giving prostaglandin E2 (PGE2) to a pregnant woman may result in an abortion. What is the best explanation for this finding?
48. During the first few years after menopause, follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) levels are normally extremely high. A 56-year-old woman completed menopause 3 years ago. However, she is found to have low levels of FSH in her blood. Which of the following is the best explanation for this finding?
A) She has been receiving hormone replacement therapy with estrogen and progesterone since she completed menopause
50. A large dose of insulin is administered intravenously to a patient. Which of the following sets of hormonal changes is most likely to occur in the plasma in response to the insulin injection?
51. Delayed breathing at birth is a common danger faced by newborn infants. What is a frequent cause of delayed breathing?
53. A 3-week-old infant is brought to the emergency room in a comatose condition. The history reveals that her parents have been feeding her concentrated, undiluted formula for 5 days. (Infant formula preparations are often sold in concentrated forms that must be properly diluted with water before feeding.) The infant’s plasma osmolality is 352 mOsm/L (normal is 280 to 300 mOsm/L), and the osmolality of the urine is 497 mOsm/L. What is the explanation for the hyperosmotic condition of the plasma?
C) The infant is unable to form urine sufficiently concentrated to excrete the solute load from the formula without losing more water than required to maintain normal plasma osmolality
54. Why is milk produced only after delivery, not before?
A) Levels of luteinizing hormone and follicle-stimulating hormone are too low during pregnancy to support milk production
55. In an experiment, patients in group 1 are given compound X, and patients in group 2 are given compound Y. After 1 week, group 1 patients have a lower metabolic rate and a larger thyroid gland than group 2 patients do. Identify compounds X and Y. (T4, thyroxine; TRH, thyrotropin-releasing hormone; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone)
| Compound X | Compound Y | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | TSH | Placebo |
| B) | T4 | Placebo |
| C) | Placebo | TSH |
| D) | Placebo | T4 |
| E) | Placebo | TRH |
57. A patient has hyperthyroidism due to a pituitary tumor. Which of the following sets of physiological changes would be expected?
58. A 25-year-old man is severely injured when hit by a speeding vehicle and loses 20% of his blood volume. Which of the following sets of physiological changes would be expected to occur in response to the hemorrhage? (ADH, antidiuretic hormone)
59. A patient with normal thyroid function has been given the wrong medication. Which of the following sets of changes would most likely be reported if this patient took propylthiouracil for several weeks? (T4, thyroxine; TSH, thyroid-stimulating hormone)
60. If a woman has a tumor secreting large amounts of estrogen from the adrenal gland, which of the following will occur?
62. When compared with the postabsorptive state, which of the previous sets of metabolic changes would most likely occur during the postprandial state?
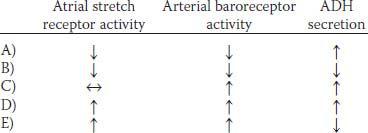
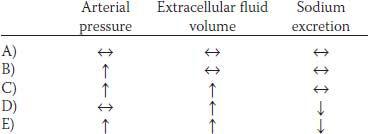
63. When compared with resting conditions, which of the previous sets of metabolic changes would most likely occur during exercise?
64. Very early in embryonic development, testosterone is formed within the male embryo. What is the function of this hormone at this stage of development?
65. Which of the following changes would be expected to occur with increased binding of a hormone to plasma proteins?
66. A patient arrives in the emergency room apparently in cardiogenic shock due to a massive heart attack. His initial arterial blood sample reveals the following concentrations of ions:
| Sodium | 137 mmol/L |
| Bicarbonate | 14 mmol/L |
| Free calcium | 2.8 mmol/L |
| Potassium | 4.8 mmol/L |
| pH | 7.16 |
To correct the acidosis, the attending physician begins an infusion of sodium bicarbonate and after 1 hr takes another blood sample, which reveals the following values:
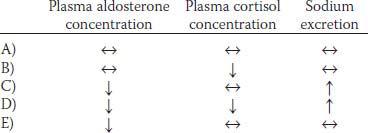
| Sodium | 138 mmol/L |
| Bicarbonate | 22 mmol/L |
| Free calcium | 2.3 mmol/L |
| Potassium | 4.5 mmol/L |
| pH | 7.34 |
What is the cause of the decrease in calcium ion concentration?
A) The increase in arterial pH resulting from the sodium bicarbonate infusion inhibited parathyroid hormone secretion
B) The increase in pH resulted in the stimulation of osteoblasts, which removed calcium from the circulation
C) The increase in pH resulted in an elevation in the concentration of HPO4−, which shifted the equilibrium between HPO4− and Ca++ toward CaHPO4
67. A 30-year-old woman is breast-feeding her infant. During suckling, which of the following hormonal responses is expected?
68. A 30-year-old man has Conn’s syndrome. Which of the following sets of physiological changes is most likely to occur in this patient compared with a healthy person?
69. Why is it important to feed newborn infants every few hours?
A) The hepatic capacity to store and synthesize glycogen and glucose is not adequate to maintain the plasma glucose concentration in a normal range for more than a few hours after feeding
B) If adequate fluid is not ingested frequently, the plasma protein concentration will rise to greater than normal levels within a few hours
C) The function of the gastrointestinal system is poorly developed and can be improved by keeping food in the stomach at all times
70. Which of the following would be associated with parallel changes in aldosterone and cortisol secretion?
71. RU486 causes abortion if it is administered before or soon after implantation. What is the specific effect of RU486?
A) It binds to luteinizing hormone receptors, stimulating the secretion of progesterone from the corpus luteum
72. Following ejaculation, arterial blood flow into the corpora cavernosa decreases back to the normal resting level resulting in the flaccid state. What is the best explanation for this decrease in blood flow?
D) Formation of nitric oxide in the endothelial cells of the arterioles supplying the corpora cavernosa is stimulated by the increase in parasympathetic nervous system activity
74. A 55-year-old man has developed the syndrome of inappropriate antidiuretic hormone secretion due to carcinoma of the lung. Which of the following physiological responses would be expected?
75. During pregnancy, the uterine smooth muscle is quiescent. During the 9th month of gestation the uterine muscle becomes progressively more excitable. What factors contribute to the increase in excitability?
76. A 40-year-old man who is sodium-depleted is administered an angiotensin-converting enzyme (ACE) inhibitor for 2 weeks. Which of the following sets of physiological changes would most likely occur in this patient after taking the ACE inhibitor for 2 weeks?
77. A 20-year-old woman is not having menstrual cycles. Her plasma progesterone concentration is found to be minimal. What is the explanation for the low level of progesterone?
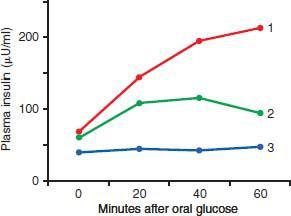
79. Based on the following figure, which set of curves most likely reflects the responses in a healthy individual and in patients with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus (DM)?
80. Based on the figure above, which set of curves most likely reflects the responses in a healthy individual and in a patient in the early stages of Cushing’s syndrome?
| Healthy | Cushing’s syndrome | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | 3 |