Selective Serotonin Reuptake Inhibitors (SSRIs)

ACTIONS
SSRIs decrease the reuptake of serotonin at selected nerve terminals in the central nervous system and increase serotonin activity at the nerve synapse. Increased availability of serotonin at the receptors results in mood elevation and reduced anxiety.
USES
• Obsessive-compulsive disorder
CONTRAINDICATIONS AND PRECAUTIONS
• Concurrent use of monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs)
SIDE EFFECTS
• Nausea, insomnia, weight gain
• **Sexual dysfunction: decreased libido, impotence, delayed ejaculation, delayed or absent orgasm**
• Hyponatremia, neonatal withdrawal, increased risk of gastrointestinal (GI) bleeding
• Serotonin syndrome: agitation, confusion, disorientation, hallucinations
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. †Treatment of depression places the patient at increased risk for suicide; monitor patient for mood changes.†
2. ‡Do not stop taking medication; withdrawal should be gradual, not abrupt.‡
3. Patient should advise health care provider if she might be pregnant; SSRIs are not recommended for use during pregnancy or lactation.
4. *Bleeding problems may occur if used concurrently with anticoagulants or nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs (NSAIDs).*
5. ‡Teach patient and family about the side effects, and advise them to notify the health care provider if any symptoms occur.‡
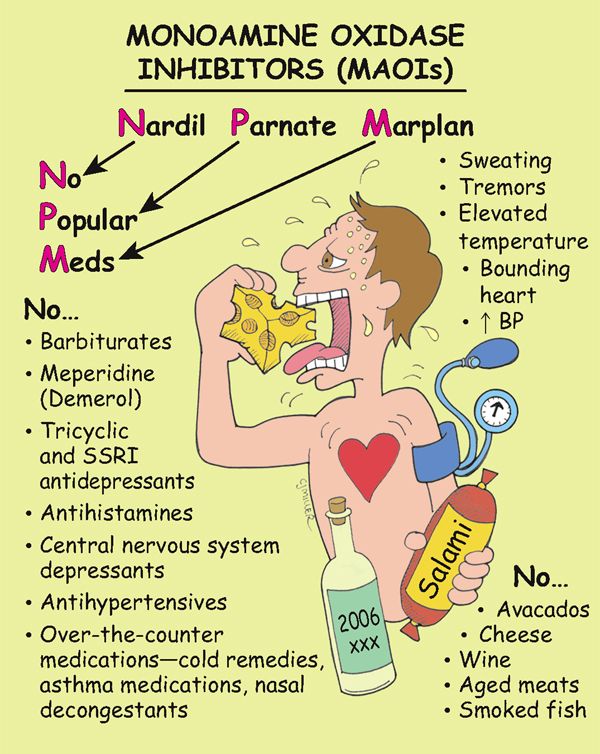
Monoamine Oxidase Inhibitors (MAOIs)

CLASSIFICATION
Antidepressant
ACTION
The antidepressant effects of the MAOIs are the result of blocking monoamine oxidase in nerve terminals. This action increases the availability and concentration of norepinephrine and serotonin for neurotransmission.
USES
• MAOIs are reserved for patients who are depressed and have not responded to tricyclic antidepressants and selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors (SSRIs).
CONTRAINDICATIONS
• Impaired renal or hepatic function
• Cardiovascular or cerebrovascular disease or both
PRECAUTIONS
• *Hypertensive crisis can be triggered by eating foods rich in tyramine (pickled, aged, caffeinated, or fermented food or drinks and medications containing diuretics, antihistamines, antihypertensives, and ephedrine).*
• MAOIs interact with many medications.
SIDE EFFECTS
• Central nervous system stimulation: anxiety, agitation, hypomania, mania
• **Orthostatic hypotension**
• **Headache, dry mouth, lethargy**
NURSING IMPLICATIONS
1. ‡Advise patient to avoid over-the-counter (OTC) drugs, especially cold remedies, nasal decongestants, and asthma medications.‡
2. ‡Advise patients to tell all health care professionals they are taking an MAOI.‡
3. Assess patient for changes in mood; evaluate suicidal tendencies.
4. Determine if patient needs help with dosing or is capable of self-dosing.
5. ‡Teach patient to avoid tyramine-rich foods that can lead to hypertensive crisis (fermented meats [smoked sausage, pepperoni, salami], dried or cured fish, all cheese, Chianti wine, dietary supplements with protein extract, soy sauce), ripe avocados.‡
6. Patient should also avoid chocolate and caffeinated beverages.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree