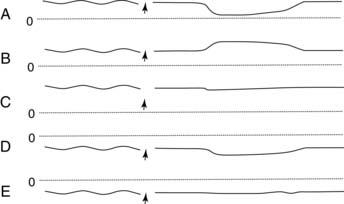
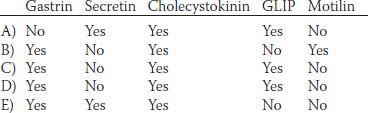4. A 19-year-old woman visits her physician because of nausea, diarrhea, light headedness, and flatulence. The physician administers 50 g of oral lactose at time zero, and measures breath hydrogen every 30 min for 3 hr using a hand-held monitor. The results are shown above. Which of the following best describes this patient’s condition?
5. Digestion of which of the following foodstuffs is impaired to the greatest extent in patients with achlorhydria?
7. Compared to plasma, saliva has the highest relative concentration of which of the following ions under basal conditions?
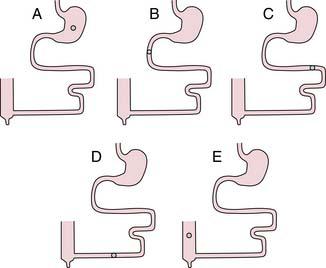
9. A 33-year-old man comes to the physician because his chest hurts when he eats, especially when he eats meat. He also belches excessively and has heartburn. His wife complains about bad breath. X-ray shows a dilated esophagus. Which one of the pressure tracings was most likely taken at the lower esophageal sphincter of this patient before and after swallowing (indicated by arrow)? The dashed line represents a pressure of 0 mm Hg.
10. Biopsies are taken from the antral and duodenal mucosa of a 65-year-old woman. Which of the following hormones can be found in tissue homogenates from both locations?
11. A 10-year-old boy consumes a cheeseburger, fries, and chocolate shake. The meal stimulates the release of several gastrointestinal hormones. The presence of fat, carbohydrate, or protein in the duodenum stimulates the release of which of the following hormones from the duodenal mucosa?
12. Which of the following hormones is released by the presence of fat and protein in the small intestine and has a major effect to decrease gastric emptying?
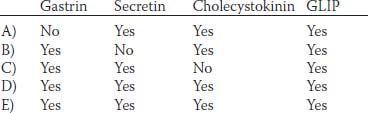
13. A clinical experiment is conducted in which one group of subjects is given 50 g of glucose intravenously and another group is given 50 g of glucose orally. Which of the following factors can explain why the oral glucose load is cleared from the blood at a faster rate compared to the intravenous glucose load? (CCK, cholecystokinin; GLIP, glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide; VIP, vasoactive intestinal peptide)
14. Which of the following factors can inhibit gastric acid secretion? (GLIP, glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide)
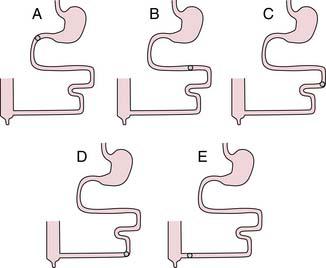
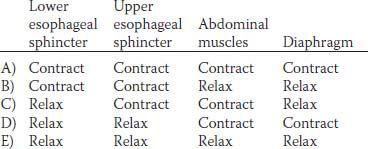
15. The gastrointestinal hormones have physiological effects that can be elicited at normal concentrations as well as pharmacological effects that require higher than normal concentrations. What is the direct physiological effect of the various hormones on gastric acid secretion? (GLIP, glucose-dependent insulinotropic peptide)
16. The cephalic phase of gastric secretion accounts for about 30% of the acid response to a meal. Which of the following can totally eliminate the cephalic phase of gastric secretion?
17. A newborn boy does not pass meconium in the first 24 hr. His abdomen is distended and he begins vomiting. Various tests lead to a diagnosis of Hirschsprung disease. An obstruction is most likely found in which portion of the gut?
18. Migrating motility complexes (MMC) occur about every 90 min between meals and are thought to be stimulated by the gastrointestinal hormone, motilin. An absence of MMCs causes an increase in which of the following?
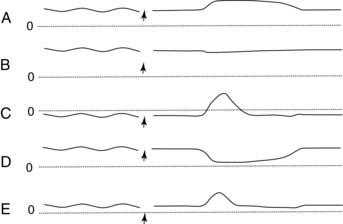
19. Which one of the following manometric recordings illustrate normal function of the esophagus at mid-thoracic level before and after swallowing (indicated by arrow)? The dashed lines represent a pressure of 0 mm Hg.
20. Gastric emptying is tightly regulated to ensure that chyme enters the duodenum at an appropriate rate. Which of the following events promotes gastric emptying under normal physiological conditions in a healthy person?
21. Parasympathetic stimulation increases gastrointestinal motility and sympathetic stimulation decreases motility. The autonomic nervous system controls gut motility by changing which of the following?
22. Swallowing is a complex process that involves signaling between the pharynx and swallowing center in the brainstem. Which of the following structures is critical for determining whether a bolus of food is small enough to be swallowed?
23. A 54-year-old woman eats a healthy meal. Approximately 20 min later the woman feels the urge to defecate. Which of the following reflexes results in the urge to defecate when the stomach is stretched?
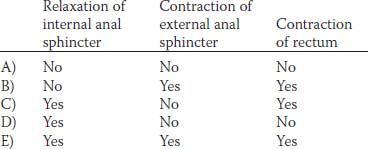
24. A 60-year-old woman severs her spinal cord at T6 in an automobile accident. She devises a method to distend the rectum to initiate the rectosphincteric reflex. Rectal distension causes which of the following in this woman?
25. The gastrointestinal hormones have physiological effects that can be elicited at normal concentrations as well as pharmacological effects that require higher than normal concentrations. What is the physiological effect of the various hormones on gastric emptying?
26. A 48-year-old woman consumes a healthy meal. At which location are smooth muscle contractions most likely to have the highest frequency in the diagrams shown?
27. Cholecystokinin (CCK) and gastrin share multiple effects at pharmacological concentrations. Which of the following effects do CCK and gastrin share (or not share) at physiological concentrations?
28. Vomiting is a complex process that requires coordination of numerous components by the vomiting center located in the medulla. Which of the following occurs during the vomiting act?
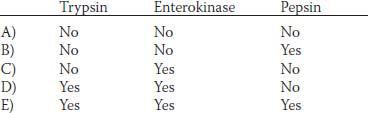
29. Various proteolytic enzymes are secreted in an inactive form into the lumen of the gastrointestinal tract. Which of the following substances is/are important for activating one or more proteolytic enzymes, converting them to an active form?
30. Mass movements constitute an important intestinal event that lead to bowel movements. Mass movements cause which of the following?
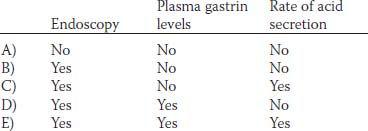
31. An 82-year-old woman with upper abdominal pain and blood in the stool has been taking NSAIDS for arthritis. Endoscopy revealed patchy gastritis throughout the stomach. Biopsies were negative for Helicobacter pylori. Pentagastrin administered intravenously would lead to a less than expected (i.e., less than normal) increase in which of the following?
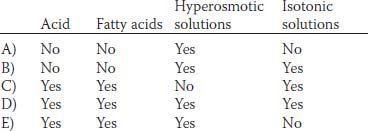
33. Which of the following factors have a physiologic role to stimulate the release of hormones or stimulate nervous reflexes, which in turn can inhibit gastric acid secretion?
34. A 23-year-old medical student consumes a cheeseburger, fries, and chocolate shake. Which of the following hormones produce physiological effects at some point over the next several hours?
35. A 68-year-old woman with hematemesis has heartburn and stomach pain. Endoscopy shows inflammation involving the gastric body and antrum as well as a small gastric ulcer. Biopsies were positive for Helicobacter pylori. H. pylori damages the gastric mucosa primarily by increasing mucosal levels of which substance?
36. A 71-year-old man with hematemesis and melena has a cresenteric ulcer in the duodenum. Lavage dislodged the clot, revealing an underlying raised blood vessel, which was successfully eradicated via cautery with a bipolar gold probe. Which of the following factors are diagnostic for duodenal ulcer?
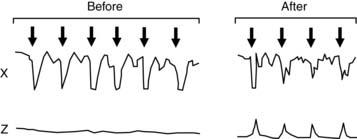
The following diagram shows manometric recordings from a patient before and after pelvic floor training. A balloon placed in the rectum was blown up (arrows) and deflated repeatedly. Tracing Z is a manometric recording obtained from the external anal sphincter before and after pelvic floor training.
38. Which of the following best describes the condition for which the patient received pelvic floor training?
39. A clinical study is conducted in which gastric acid secretion is stimulated using pentagastrin before and after treatment with a histamine H2 blocker. Which of the following rates of gastric acid secretion (in mEq/hr) is most likely to have occurred in this experiment?
| Pentagastrin alone | Pentagastrin + H2 blocker | |
|---|---|---|
| A) | 15 | 15 |
| B) | 25 | 25 |
| C) | 25 | 15 |
| D) | 26 | 28 |
| E) | 40 | 45 |
40. A tsunami tidal wave hits the east coast of South America and the people living there are forced to drink unclean water. Within the next several days, a large number of people develop severe diarrhea and about half of these people expire. Samples of drinking water are positive for Vibrio cholerae. Which of the following types of ion channels is most likely to be irreversibly opened in the epithelial cells of the crypts of Lieberkühn in these people with severe diarrhea?
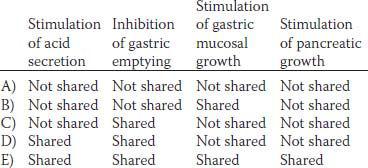
41. One of the following hormones can stimulate growth of the intestinal mucosa and two other hormones can stimulate pancreatic growth. Which three hormones are these?
42. Which of the following structures undergoes receptive relaxation when a bolus of food is swallowed?
43. A 65-year-old man eats a healthy meal. Approximately 40 min later the ileocecal sphincter relaxes and chyme moves into the cecum. Gastric distention leads to relaxation of the ileocecal sphincter by way of which reflex?
44. A healthy, 21-year-old woman eats a big meal and then takes a 3-hr ride on a bus that does not have a bathroom. Twenty minutes after eating, the woman feels a strong urge to defecate, but manages to hold it. Which of the following have occurred in this woman?
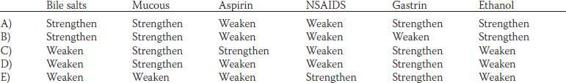
45. The gastric mucosal barrier has a physiological and an anatomical basis to prevent back-leak of hydrogen ions into the mucosa. Some factors are known to strengthen the integrity of the gastric mucosal barrier, whereas other factors can weaken the barrier. Which of the following factors strengthen or weaken the barrier?
46. A 48-year-old man consumes a healthy meal. At which of the following locations is vitamin B12 most likely to be absorbed?
47. A 45-year-old man presents with abdominal pain and hematemesis. An abdominal exam was relatively benign, and abdominal x-rays were suggestive of a perforated viscus. Endoscopy revealed a chronically perforated gastric ulcer, through which the liver was visible. Which of the following is a forerunner to gastric ulcer formation?
48. A 19-year-old man is fed intravenously for several weeks following a severe automobile accident. The intravenous feeding leads to atrophy of the gastrointestinal mucosa most likely because the blood level of which of the following hormones is reduced?
49. A 62-year-old man with dyspepsia and a history of chronic gastric ulcer has abdominal pain. Endoscopy shows a large ulcer in the proximal gastric body. Biopsies were positive for Helicobacter pylori. Which of the following are used clinically for treatment of gastric ulcers of various etiologies?