 How to Read Drug Labels
How to Read Drug Labels
LEARNING OBJECTIVES
On completion of the materials provided in this chapter, you will be able to identify the following parts of each drug label:
1 Trade name of the medication
2 Generic name of the medication
3 Strength of the medication dosage
4 Form in which the medication is provided
6 Total amount or volume of the medication provided in the container
7 Directions for mixing or preparation of the medication if required
The safe administration of medications to patients begins with the nurse accurately reading and interpreting the drug label. Thus it is important for the nurse to be familiar and comfortable with the information that is found on the drug label.
 PARTS OF A DRUG LABEL
PARTS OF A DRUG LABEL
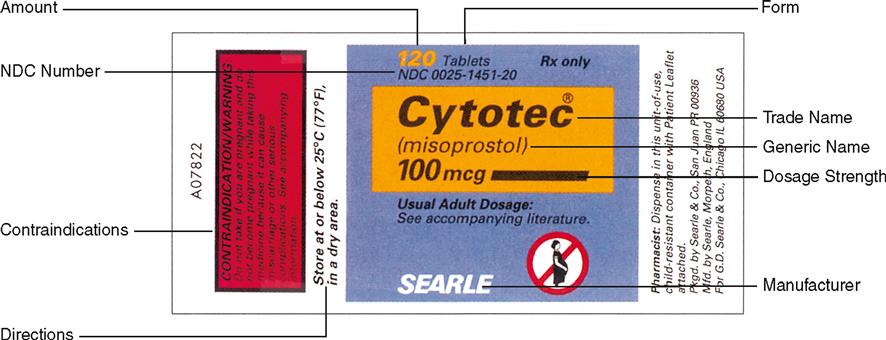
Other information may be found on drug labels: the name of the manufacturer, expiration date, special instructions for storage, a National Drug Code (NDC) number, and contraindications.
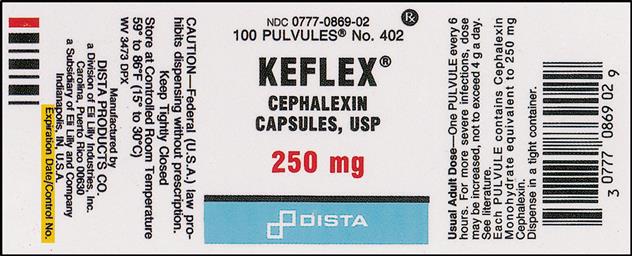
EXAMPLES FOR PRACTICE IN READING DRUG LABELS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree


