CASE 10
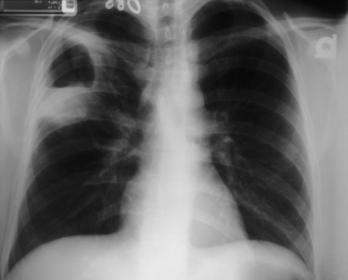
A 66-year-old white man presented with a cough, fever, night sweats, and chest pain. He also noted a 12-lb weight loss over 3 weeks.
LABORATORY STUDIES
Diagnostic Work-Up
Table 10-1 lists the likely causes of illness (differential diagnosis). Investigational approach to delineating the etiology may include:
TABLE 10-1 Differential Diagnosis and Rationale for Inclusion (consideration)
Rationale: A clinical diagnosis of pneumonia should be considered. The presence of cavitary lesions often implies an abscess with polymicrobial infection although TB is also an important consideration. K. pneumoniae is one of the more common causes of pneumonia in the homeless population (may be a part of the mixed anaerobic infection). Pneumococcal and staphylococcal pneumonias are commonly community acquired. The other causes listed above are less likely in this setting. Homelessness should generally prompt ruling out tuberculosis.
COURSE
The patient was admitted to the hospital. Sputum was collected and sent for routine and acid-fast bacillus cultures, and two sets of blood were drawn for culture. Based on the initial sputum Gram stain that showed mixed microbes and many PMNs, he was initially treated with cefotaxime, erythromycin, and clindamycin. Within 24 hours he became hypotensive and was transferred to the ICU. Blood and sputum cultures yielded the diagnosis.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree