CASE 10
A full-term, newborn infant was suffering from respiratory distress and cyanosis after his birth. Imaging studies demonstrated lung hypoplasia owing to a decreased thoracic volume.
HOW DO THE LUNGS DEVELOP?
The lungs and their bronchi develop from the lung bud (Fig. 2-23). The lung bud is an outgrowth of the caudal end of the laryngotracheal tube during the fourth week of development. The next event is division of the single lung bud into two bronchial buds (right and left) of endoderm. Each bronchial bud expands to form the primordium of its respective primary bronchus. As in the adult, the embryonic right primary bronchus is larger and more vertically oriented than the left. Each primary bronchus subsequently divides into two secondary or lobar bronchi. The superior secondary bronchus supplies the superior lobe of its respective lung. The right inferior secondary bronchus divides into middle and inferior secondary bronchi that supply the middle and inferior lobes of the right lung. The left inferior secondary bronchus supplies the inferior lobe of the left lung.
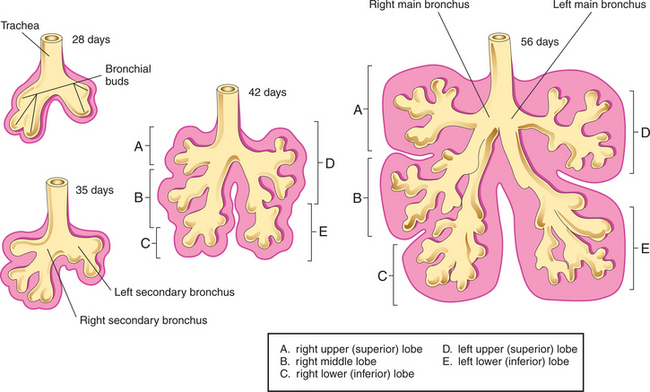
FIGURE 2-23 Developmental stages of bronchial buds, bronchi, and lungs.
(Moore K and Persaud TVN: The Developing Human, 7e. WB Saunders, 2003. Fig. 11-8.)
Lungs undergo four periods of maturation (Fig. 2-24) beginning at 5 weeks of development and ending in childhood. The four periods of lung maturation are described in Table 2-6.
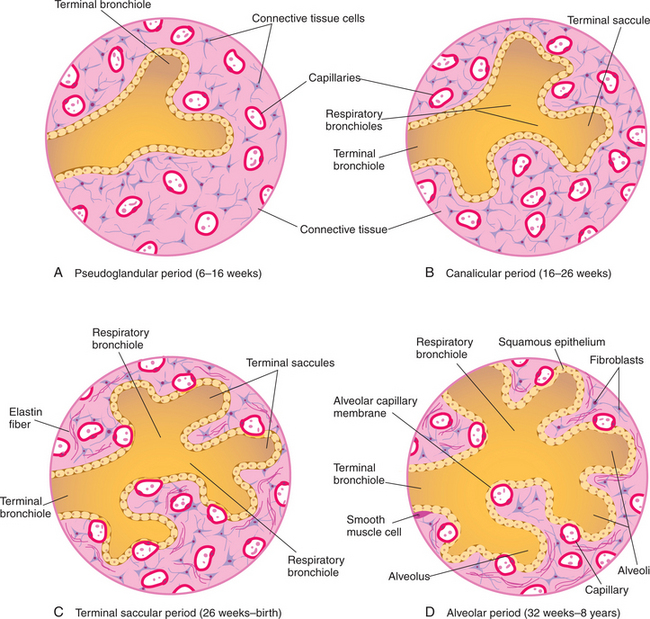
FIGURE 2-24 Illustrations of the four periods of lung development.
(Moore K and Persaud TVN: The Developing Human, 7e. WB Saunders, 2003. Fig. 11-9.)
TABLE 2-6 Periods of Lung Maturation
| Period of Maturation | Time Band | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Pseudoglandular | 5–17 weeks | |
| Canalicular | 16–25 weeks | |
| Terminal sac | 24 weeks–birth |



