Cortisol, a glucocorticoid (the most important C21 steroid), is formed by progressive addition of hydroxyl groups at C-17, C-21 and C-11.
Androgens (for example androstenedione) are formed after the removal of the side chain to produce C19 steroids.
the breakdown of protein and fat, that is, they antagonize some of insulin’s action. Glucocorticoids in excess may impair glucose tolerance and alter the distribution of adipose tissue. Cortisol helps maintain the extracellular fluid volume and normal blood pressure.
 Figure 8.1 Numbering of the steroid carbon atoms of cholesterol and the synthetic pathway of steroid hormones; the chemical groups highlighted determine the biological activity of the steroid. |
action is especially important for sodium and water homeostasis. It is discussed more fully in Chapters 2, 3 and 4. Like the glucocorticoids, it is inactivated by hepatic conjugation and is excreted in the urine.
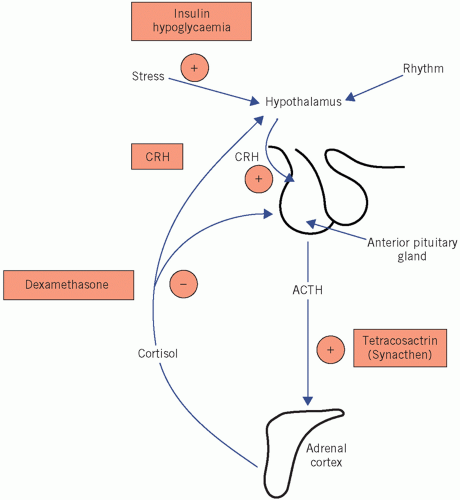
Addison’s disease,
Nelson’s syndrome: after bilateral adrenalectomy for Cushing’s disease (see Causes of Cushing’s syndrome), removal of the cortisol feedback causes a further rise in plasma ACTH concentrations from already high levels.
Obesity, typically involving the trunk and face, and a characteristic round, red ‘cushingoid’ face (Fig 8.3).
Impaired glucose tolerance and hyperglycaemia. Cortisol has the opposite action to that of insulin, causing increased gluconeogenesis, and some patients may have diabetes mellitus.
Table 8.1 Disorders of adrenocortical function
Altered hormone secretion
Associated clinical disorder
Hypersecretion
Cortisol
Cushing’s syndrome
Aldosterone
Primary hyperaldosteronism (Conn’s syndrome)
Androgens
Congenital adrenal hyperplasia Adrenocortical carcinoma
Hyposecretion
Cortisol and aldosterone
Primary adrenal disorders, e.g. Addison’s disease or congenital adrenal hyperplasia
Cortisol and adrenocorticotrophic hormone
Adrenal insufficiency secondary to pituitary disease
Increased protein catabolism, which also increases urinary protein loss. Thus, there is a negative nitrogen balance associated with proximal muscle wasting with weakness, thinning of the skin and osteoporosis. The tendency to bruising and the purple striae (most obvious on the abdominal wall) are probably due to this thinning.
Hypertension, caused by urinary retention of sodium and therefore of water, which are due to the mineralocorticoid effect of cortisol. Increased urinary potassium loss may cause hypokalaemia.
Androgen excess, which may account for the common findings of greasy skin with acne vulgaris and hirsutism, and menstrual disturbances in women.
Psychiatric disturbances, such as depression.
Cushing’s disease It is associated with bilateral adrenal hyperplasia, often secondary to a basophil adenoma of the anterior pituitary gland.
Ectopic ACTH secretion In this condition, usually from a small-cell carcinoma of the bronchus, ACTH concentrations may be high enough to cause skin pigmentation. The patient may have weight loss with cachexia. One metabolic complication is a hypokalaemic alkalosis. The clinical features may be indistinguishable from those of Cushing’s disease, although sometimes patients do not have the characteristic cushingoid features as the cortisol rises so quickly.
 Figure 8.4 Cushing’s disease, indicating excess cortisol production caused either by hyperstimulation of the adrenal gland by adrenocorticotrophic hormone (ACTH), from either the pituitary or an ectopic source, or by autonomous hormone secretion from an adrenal tumour. |
Is there abnormal cortisol secretion?
If so, does the patient have any other condition that may cause it?
If Cushing’s syndrome is confirmed, what is the cause?
ACTH secretion. Determinations of 24-h urinary free cortisol have about a 5 per cent false-negative rate, but if three separate determinations are normal, Cushing’s syndrome is most unlikely.
Table 8.2 Some biochemical test results in patients with Cushing’s syndrome | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree