Yolk Sac Tumor
Key Facts
Terminology
Yolk sac tumor (YST)
Endodermal sinus tumor, infantile type embryonal carcinoma
Clinical Issues
Most common nonseminomatous germ cell tumor in mediastinum
May account for ˜ 20% of all nonteratomatous germ cell tumors in mediastinum
Tumor is more common in young adults in 3rd decade of life
Yolk sac tumors appear predominantly in males
Macroscopic Features
Variable size from a few cm to over 20 cm in diameter
Rarely YST may present as cystic anterior mediastinal tumor
Microscopic Pathology
Reticulated
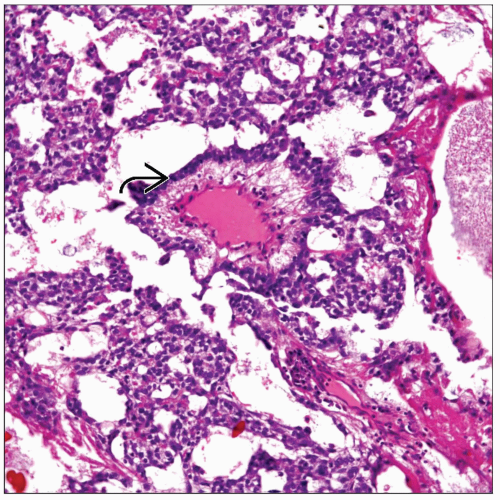
Cells growing in multiple communicating channels resembling immature glomeruli (Schiller-Duval bodies)
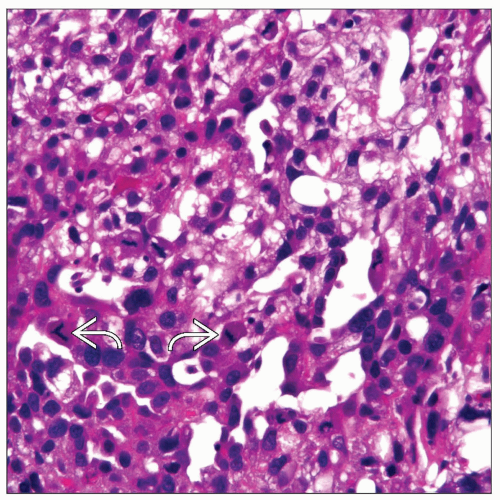
Numerous intracellular and extracellular hyaline globules
Loose reticular network
Top Differential Diagnoses
Embryonal carcinoma
Sarcoma
Metastatic carcinoma
Multilocular thymic cyst
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Yolk sac tumor (YST)
Synonyms
Endodermal sinus tumor, infantile-type embryonal carcinoma
Definitions
Malignant germ cell tumor
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Unknown Etiology
Some authors have stated the possibility of misplaced germ cells in mediastinum
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Most common nonseminomatous germ cell tumor in the mediastinum
May account for approximately 20% of all nonteratomatous germ cell tumors in the mediastinum
Age
Tumor is more common in young adults in 3rd decade of life
Gender
Appears to occur predominantly in males
Site
Anterior mediastinum
Presentation
Cough
Difficulty breathing
Superior vena cava syndrome
Chest pain
Klinefelter syndrome
Sexual precocity
Idiopathic thrombocytopenia
Acute megakaryoblastic leukemia
Malignant histiocytosis
Patients may also be asymptomatic
Laboratory Tests
Increased α-fetoprotein in serum
Treatment
Options, risks, complications
Surgery, if possible
Chemotherapy, platinum-based
Prognosis
Poor
Survival: ˜ 6-24 months
IMAGE FINDINGS
General Features
Heterogeneous attenuation
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Significant necrosis and hemorrhage
Sections to Be Submitted
Approximately 1 section per cm of tumor
Include transitional areas of thymus (if present) and tumor
Size
Variable, from a few cm to > 20 cm in diameter
Rarely, YST may present as cystic anterior mediastinal tumor
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Cells growing in multiple communicating channels resembling immature glomeruli (Schiller-Duval bodies)
Numerous intracellular and extracellular hyaline globules
Loose reticular network
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Reticulated
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Germ, nonseminomatous
ANCILLARY TESTS
Histochemistry
Periodic acid-Schiff
Reactivity: Positive
Staining pattern
Cytoplasmic inclusion
Stromal matrix
Mucicarmine
Reactivity: Negative
Staining pattern
Not applicable
PAS-diastase
Reactivity: Negative
Staining pattern
Not applicable
Electron Microscopy
Transmission
Large amounts of basal lamina outlining cells
Zonula occludens junctions joining cells
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Embryonal Carcinoma
Most often shows the presence of nucleoli in tumor cells
Shows more nuclear pleomorphism
More often shows abortive gland-like structures
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree