Viral Infections (Cytomegalovirus, Herpesvirus, and Others)
Michael J. Thrall, MD
Key Facts
Cytopathology
Common lung viruses with identifiable cytopathic effect include CMV and herpesvirus
CMV produces nuclear enlargement with a prominent intranuclear inclusion and marginated chromatin
Herpesvirus shows the triad of multinucleation, margination, and molding
Other viruses that may involve lung and be identified by cytology include adenovirus, respiratory syncytial virus, and measles
Consider other viruses when nuclear enlargement and homogenization are seen without typical CMV or herpes features
Top Differential Diagnoses
Nuclear changes due to inflammation or cytotoxic therapy may mimic viral cytopathic effect
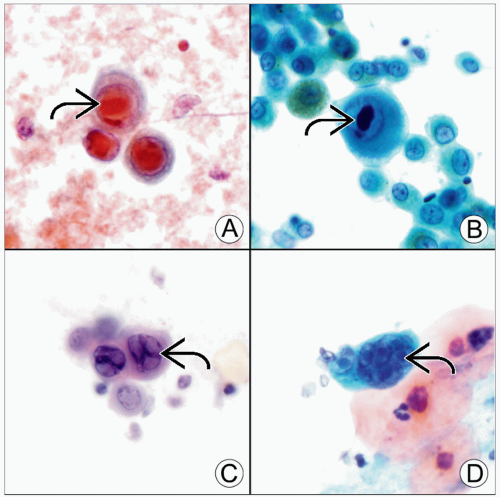 (A) CMV infection produces classic Cowdry type A nuclear inclusions within a markedly enlarged nucleus
 . This Pap-stained example has a typical red inclusion. (B) In some instances, such as in this ThinPrep containing CMV, the inclusion . This Pap-stained example has a typical red inclusion. (B) In some instances, such as in this ThinPrep containing CMV, the inclusion  may not stain red, but nuclear enlargement and homogenization aid recognition. (C) This example of herpesvirus in a Pap-stained smear shows the typical nuclear features of chromatin margination, multinucleation, and nuclear molding may not stain red, but nuclear enlargement and homogenization aid recognition. (C) This example of herpesvirus in a Pap-stained smear shows the typical nuclear features of chromatin margination, multinucleation, and nuclear molding  . (D) Sometimes prominent central inclusions may be seen within herpesvirus nuclei, as in this ThinPrep specimen . (D) Sometimes prominent central inclusions may be seen within herpesvirus nuclei, as in this ThinPrep specimen  . .Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel
Full access? Get Clinical Tree
 Get Clinical Tree app for offline access
Get Clinical Tree app for offline access

|