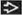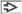Urothelial Carcinoma
Yimin Ge, MD
Key Facts
Clinical Issues
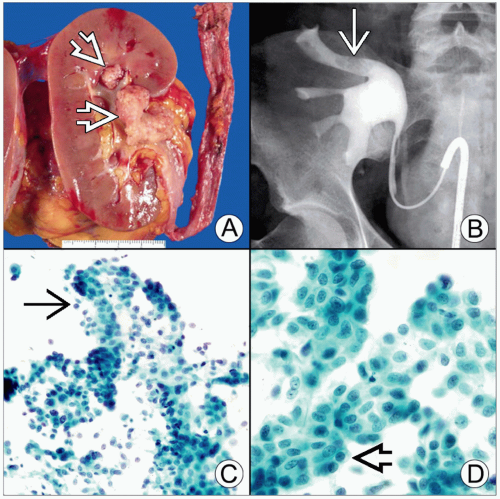
5-10% of renal tumors, 90% of pelvicalyceal tumors
Mean age: 67-70 years, M:F = 1.7-2:1
Cytopathology
Hypercellular aspirate
Multilayered sheets, papillae, or isolated cells
Dense or squamoid cytoplasm, well-defined borders
Coarse chromatin, pleomorphism, and prominent nucleoli are seen in high-grade tumors
High-grade UPC is common in FNA specimens
Ancillary Tests
Positive for CK7, CK20 (focal), p63, 34bE12
Negative for vimentin, RCC
Top Differential Diagnoses
Collecting duct carcinoma
High-grade renal cell carcinoma
Metastatic carcinoma
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Urothelial carcinoma of renal pelvis (UCP)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree