Tubulocystic Carcinoma
Satish K. Tickoo, MD
Danielle E. Westfall, MD
Victor E. Reuter, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Tubulocystic carcinoma (TC) of kidney
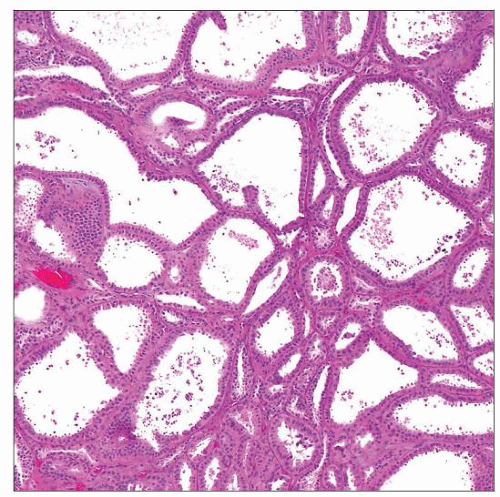
Well-circumscribed carcinoma with pure tubular and cystic architectural growth
Cysts and tubules lined by single layer of atypical cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and variable “hobnailed” appearance
Clinical Issues
Uncommon; < 60 cases reported in literature
Considered potentially of low malignant behavior
Strong male preponderance; M:F = 7:1 or greater
Macroscopic Features
Well-circumscribed tumors with spongy “bubble wrap” appearance
Microscopic Pathology
Composed of small to intermediate-sized tubules admixed with cystically dilated tubules, dispersed evenly in frequently fibrotic stroma
Tubule and cyst lining composed of single layer of flat, “hobnail,” or cuboidal to columnar cells
Cellular stratification and papillations very focal and uncommon
Ancillary Tests
Majority are positive for CK7, CK19, parvalbumin, CD10, AMACR, and Ksp-cadherin
Top Differential Diagnoses
Collecting duct carcinoma with TC-like areas
Other adult renal epithelial tumors with predominant tubules and cysts
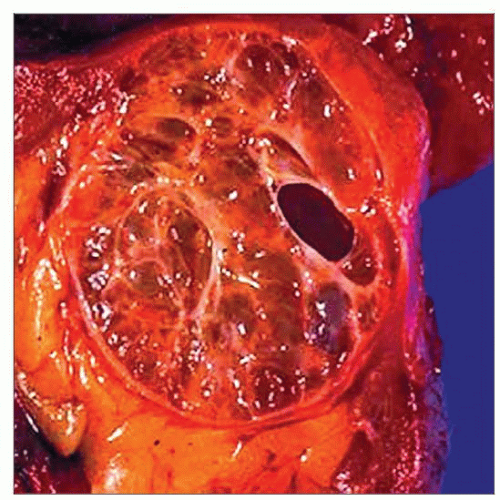 Gross photograph demonstrates a well-circumscribed tumor with a spongy cut surface and variable sized cysts, the typical gross appearance of a tubulocystic carcinoma. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Tubulocystic carcinoma (TC) of kidney
Definitions
Well-circumscribed renal cell carcinoma (RCC) with pure tubular and cystic architectural growth
Cysts and tubules lined by single layer of atypical cells with abundant eosinophilic cytoplasm and variable “hobnail” appearance
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Historic Perspective
Initially described in 1956 by Masson and designated as Bellinien epithelioma
Examples illustrated in 3rd AFIP fascicle as collecting duct carcinoma (CDC), subsequently designated low-grade CDC
This group also contained some cases now regarded as mucinous tubular and spindle cell carcinoma
Recently considered as distinct entity
Exact relationship with collecting duct carcinoma still unclear
Particularly because areas with TC-like morphology are occasionally observed in otherwise typical CDCs
Molecular Abnormalities
Unique molecular signature distinct from clear cell and chromophobe RCC reported in Affymetrix X3P oligonucleotide microanalysis
Overexpression of genes related to
Amino acid metabolism
Cell cycle
Underexpression of many biopolymer metabolism genes
Based on a single case, using clustering analysis, molecular signature also reported to be closely related to papillary RCC
No published large molecular study analyzing relationship to, or distinction from, collecting duct carcinoma
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Uncommon; < 60 cases reported in literature
Age
34-94 years (mean: 60 years)
Gender
Strong male preponderance; M:F = 7:1 or greater
Presentation
Majority asymptomatic, incidentally discovered radiologically; occasionally abdominal fullness, flank pain, or hematuria
Treatment
Usually amenable to surgical treatment due to low tumor stage at presentation
Single reported case of metastatic disease treated with multikinase inhibitor sunitinib as adjuvant with documented clinical and radiographic regression
Prognosis
Tumor with relatively less aggressive clinical behavior
Overwhelming majority with stage pT1 at presentation; possible contributing factor for favorable prognosis
< 10% reported with stage pT3 disease
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree