Trichoblastoma
David Cassarino, MD, PhD
Key Facts
Terminology
Trichoblastoma (TB)
Synonym: Giant trichoepithelioma
Benign adnexal tumor showing primitive follicular differentiation
Clinical Issues
Head and neck area, especially the scalp
Rare recurrences and association with, or progression to, malignancy (BCC)
Macroscopic Features
Nodular lesion involving the deep dermis and subcutis
Large, typically > 1 cm in diameter
Microscopic Pathology
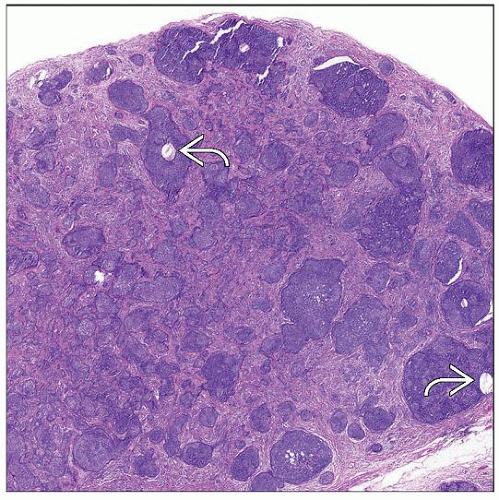
Large, basaloid-appearing deep dermal-based nodule
Composed of irregular lobules and nests of basaloid cells
No epidermal connections
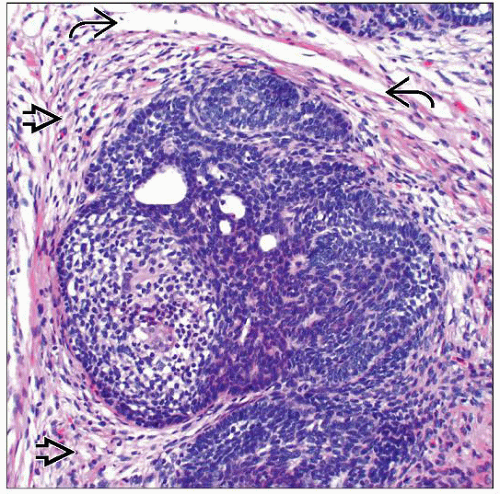
Associated fibrotic stroma with increased numbers of fibroblasts
Papillary mesenchymal bodies classically present, similar to TE
Subtypes include trichogerminoma, rippled pattern trichomatricoma, trichoblastic fibroma, and cutaneous lymphadenoma
Top Differential Diagnoses
Basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
Trichoepithelioma (TE)
Sebaceoma
Cylindroma
Spiradenoma
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Trichoblastoma (TB)
Synonyms
Giant trichoepithelioma (TE)
Trichogerminoma
Rippled pattern trichomatricoma
Trichoblastic fibroma
Cutaneous lymphadenoma
Definitions
Benign dermal-based adnexal tumor showing primitive follicular differentiation
CLINICAL ISSUES
Epidemiology
Incidence
Uncommon tumors
Age
Usually occur in adults
Site
Head and neck area, especially the scalp
Presentation
Dermal nodule/mass lesion
Usually single but may rarely be multiple
Usually asymptomatic
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Complete excision is curative
Should be recommended in cases of partial biopsy in order to exclude basal cell carcinoma (BCC)
Prognosis
Excellent in most cases
Rare recurrences and association with, or progression to, malignancy (BCC)
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Nodular lesion involving the deep dermis and subcutis
Size
Large, typically > 1 cm in diameter
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Large, basaloid-appearing deep dermal-based nodule
Usually symmetric and shows well-circumscribed borders
Composed of irregular lobules and nests of basaloid cells
No epidermal connections
May extend into superficial subcutis
Associated fibrotic stroma with increased numbers of fibroblasts
Stromal amyloid may be present
Calcifications and granulomatous inflammation occasionally seen but less common than in TE
Papillary mesenchymal bodies classically present, similar to TE
Invagination of fibroblastic stroma into primitive follicular structures
Represents abortive follicular induction
Subtypes
Trichogerminoma
Tightly packed lobules of primitive basaloid cells with minimal stroma
Rippled pattern trichomatricoma
Palisading ribbons of basaloid cells; may resemble Verocay bodies
Trichoblastic fibroma
Less epithelial structures, more prominent stroma, which may appear desmoplastic
Cutaneous lymphadenoma
Rare variant with a prominent lymphocytic infiltrate and clear cell features
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Basal Cell Carcinoma
BCC usually shows multiple attachments to the overlying epidermis (focal or absent in TB)
BCC also shows the following features (which are not seen in TB)
Prominent peripheral palisading
Mucinous stroma
Tumor-stromal retraction artifact (stromal-stromal retraction seen in TB)
Numerous mitotic and apoptotic figures
Immunohistochemistry may be useful in some cases (particularly small, partial biopsies)
Bcl-2, p53, and Ki-67 all elevated in BCC (should be low in TB)
CK20 highlights Merkel cells in TB (absent in BCC)
Trichoepithelioma
Small, papular lesion clinically
Overlapping histologic features, but TE is smaller, more superficial than TB
Usually shows more prominent folliculocysts, calcifications, and granulomatous inflammation
Sebaceoma
More superficial, epidermal- or follicular-based adnexal neoplasm
Composed of lobules and nests of predominantly basaloid cells with minor population of clear cells
May show rippled pattern with nuclear palisading, similar to rippled pattern trichomatricoma
Scattered mature sebaceous cells with multivacuolated cytoplasm
Cylindroma
Dermal-based neoplasm composed of basaloid cells with ductal differentiation
Irregular, “jigsaw puzzle” pattern of variably shaped lobules and nests
Surrounded by hyalinized basement membrane, and nests contain hyalinized globules
Focal ductal lumina present (may be highlighted by EMA &/or CEA)