Transient Erythroblastopenia of Childhood
Kathryn Foucar, MD
Key Facts
Terminology
Idiopathic, self-limited red cell aplasia characterized by
Normocytic/normochromic anemia with reticulocytopenia
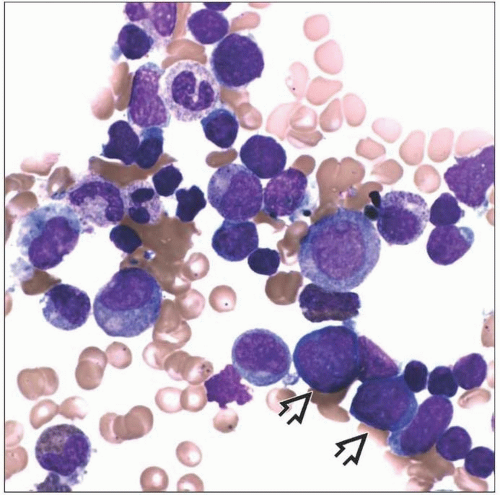
Decreased erythroid lineage in bone marrow (red cell aplasia)
Etiology/Pathogenesis
Unclear; usually no causative factor identified
Postulated immune-related disruption of erythropoiesis
Clinical Issues
Rare disorder; 4.3 per 100,000 children ≤ 3 years
Children usually ≥ 1 year of age
Reticulocyte count inappropriately low
Erythropoietin levels increased
Spontaneous recovery within 1-2 months
Does not recur
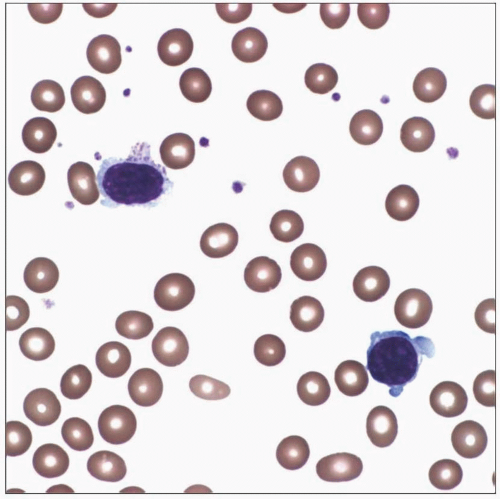 Peripheral blood smear shows a profound normocytic/normochromic anemia without polychromasia. There is minimal, if any, anisopoikilocytosis of RBCs. |
TERMINOLOGY
Abbreviations
Transient erythroblastopenia of childhood (TEC)
Synonyms
Transient red cell aplasia
Definitions
Idiopathic, self-limited red cell aplasia characterized by
Normocytic/normochromic anemia
Marked reticulocytopenia
Decreased erythroid lineage cells in bone marrow (red cell aplasia)
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Multifactorial Causes
Unclear; usually no causative factor identified
Underlying viral infection or immune aberration postulated but not well documented
Usually not linked to constitutional or familial conditions
Pathogenesis
Postulated immune-related disruption of erythropoiesis
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree