Transanal Excision of Rectal Tumors
Ryan M. Thomas
Barry Feig
DEFINITION
Transanal excision (TAE) of rectal tumors refers to the complete resection of a benign or malignant neoplasm of the distal rectum such that negative surgical margins are achieved while avoiding the morbidity of transabdominal resection procedures.
PATIENT HISTORY AND PHYSICAL FINDINGS
Not all patients are candidates for TAE of rectal tumors and many factors may prove to be a contraindication to such treatment. The surgeon must take into account physiologic, anatomic, and pathologic factors in order to deem a patient an appropriate candidate for TAE of a benign or malignant rectal tumor (Table 1).
A full history must be performed with special focus on any changes in bowel habits including stool caliber, the presence of melena or hematochezia, personal or family history of colorectal cancer, and the use of any antiplatelet or anticoagulant medications in preparation for surgical excision.
Physiologic factors and patient desires may make TAE a viable option, namely in patients who physiologically cannot tolerate an extensive transabdominal resection or have a short life expectancy because of metastatic disease yet have a bleeding tumor in need of palliation. In addition, some patients may not desire an abdominoperineal resection and resultant permanent colostomy or the possibility of sexual dysfunction. Given appropriate physical and pathologic criteria, these patients may be appropriate candidates for TAE as well.
A thorough physical examination must be performed with special focus on rectal tone, location of the rectal tumor, distance of the tumor from the anal verge, and mobility/fixation of the tumor to underlying structures. These physical factors are critical to determine the feasibility of resection as the criteria for resection demands that the lesion:
Be within 8 to 10 cm of the anal verge in order to technically reach the lesion
Must be mobile and not fixed to underlying tissue
Must involve less than 30% of the circumference of the rectal wall on endoscopic evaluation, as anything greater risks nodal involvement or narrowing the rectal lumen after excision is performed.
Often, patients are referred for TAE of a rectal tumor after having undergone endoscopic evaluation that diagnosed a malignant mass or a benign mass not amenable to endoscopic resection.
Established pathologic criteria for TAE of a malignant lesion include T1 lesions, no evidence of lymphovascular invasion (LVI) or perineural invasion (PNI), moderately to well-differentiated tumors, or an endoscopically removed polyp with indeterminate pathology.
IMAGING AND OTHER DIAGNOSTIC STUDIES
Endoscopy plays an essential role in the management of midto low rectal lesions in patients who may be candidates for TAE. Endoscopy defines the anatomy of the lesion and special attention should be made to the anatomic location, as this will affect surgical positioning. The tumor diameter, location from the anal verge, and degree of circumferential involvement are noted as they dictate the appropriateness of TAE as well.
Assuming that a malignant lesion is technically resectable via a transanal approach, one must ensure that the lesion is a T1 stage and without nodal involvement. The transanal approach for rectal tumors has garnered support because of the decreased morbidity compared with a transabdominal approach but lymph node metastasis has been reported in 10% to 18% of T1 lesions.
Imaging therefore plays an essential role in the preoperative planning for patients considered candidates for TAE of rectal tumors. In the case of malignancy, staging imaging should include the following:
A chest x-ray and computed tomography (CT) of the abdomen and pelvis to assess for metastatic disease
Critical to the determination of the local resectability of a rectal lesion is the assessment of the T stage and N stage of the tumor. The accuracy of determining the depth of invasion by CT scan, magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and endoscopic rectal ultrasound (ERUS) is 73%, 82%, and 87%, respectively. Nodal metastases are accurately assessed by CT scan, MRI, and ERUS in 66%, 74%, and 74% of cases, respectively. The use of endorectal coils during MRI has been found to be equivalent to ERUS for T stage determination but superior in terms of nodal status.
Table 1: Criteria for Transanal Excision of Rectal Tumors
Patient Factors
Anatomic Factors
Pathologic Factors
Comorbidities that preclude transabdominal resection
Short life expectancy in need of surgical palliation
Refusal of abdominoperineal resection and resultant permanent colostomy
Lesion ≤8-10 cm from the anal verge
Lesion involves ≤30% of rectal circumference
Lesion ≤3cm in diameter
Mobile and not fixed to underlying tissue
Negative margins achievable depending on pathology of primary lesion (0.3-1 cm)
Moderately or well-differentiated tumor
T1 tumor
No lymphovascular or perineural invasion
Indeterminate pathology on polypectomy
No evidence of lymphadenopathy on preoperative imaging
Any biopsies that are performed of the rectal tumor prior to definitive excision should be re-reviewed to confirm the tumor depth of invasion, differentiation, and the presence of LVI or PNI.
SURGICAL MANAGEMENT
Preoperative Planning
In most cases, patients should be instructed to discontinue anticoagulation and antiplatelet medications 7 to 10 days prior to the planned procedure if medically feasible.
A specific bowel preparation does not have to be performed except that the patient should self-administer a sodium phosphate enema the evening prior to the procedure in order to evacuate the rectal vault.
Patient Positioning
Positioning of the individual depends on the anatomic location of the rectal tumor to be excised, which should be determined on preoperative physical examination and endoscopy.
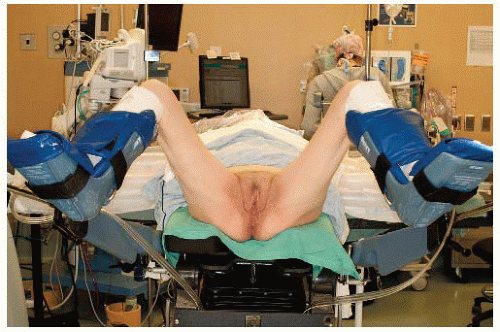
Because it is technically easier to visualize and resect rectal tumors when they are located closer to the operating room (OR) table, patients with a rectal tumor along the posterior rectal wall should be positioned in high lithotomy such that their coccyx can be easily palpated (FIG 1). In contrast, patients with lesions located along the anterior rectal wall should be placed in the prone jackknife position.
For patients placed in the prone position, heavy tape should be applied to the buttocks so that they can be retracted laterally and secured to the OR table. A 2-in-wide tape should be used and secured to the buttocks with benzoin ointment to prevent the tape from slipping during the procedure.
Once in position with pressure points appropriately padded, a digital rectal exam is performed to confirm tumor location and the rectum is irrigated with saline until all solid material has been removed. The perineum is then prepped with Betadine and appropriately draped.
TECHNIQUES
EXPOSURE OF THE LESION
Because of the limited working area, exposure is key to safe TAE with adequate margins.
The operating surgeon must have a high-intensity headlight to aid visualization and a long, narrow suction apparatus is helpful for both smoke evacuation and fluid removal.
The goal of exposure for TAE is to bring the lesion closer to the anus and avoid retractors that tend to push the lesion away. There are several methods and instruments that are available to achieve this goal.
A Lone Star retractor may be used to help evert the anus and gain better exposure. Alternatively, a series of nylon sutures placed circumferentially in a simple fashion from the internal sphincter to the thigh can achieve a similar result. The use of these techniques is particularly helpful for posterior lesions when the patient is in the lithotomy position.
For men in the lithotomy position, it may be helpful to secure the scrotum to the inner thigh with a 2-0 silk or other similar suture in order to remove it from the operative field. This is not necessary in the prone jackknife position as gravity provides the necessary retraction.
A Parks self-retaining retractor, with the option of the additional center blade, is then placed in the anus to provide exposure, with an assistant using an appropriately sized lighted Hill-Ferguson retractor for additional exposure (FIG 2). A variety of other self-retaining and handheld retractors may be considered depending on the patient’s anatomy.
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree