Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Key Facts
Terminology
Malignant epithelial neoplasm with squamous (epidermoid) differentiation
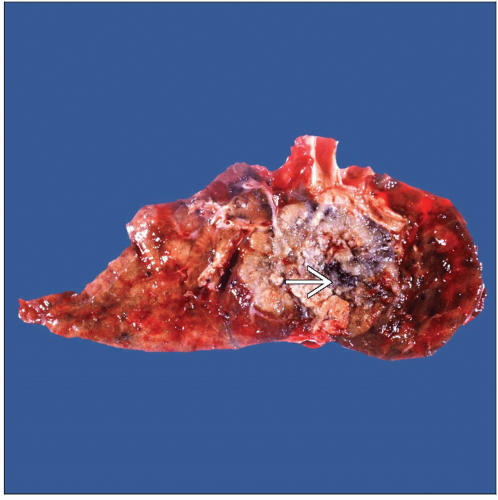
Macroscopic Features
Central or peripheral tumors
White or light brown in color with homogeneous cut surface; cut surface may show areas of hemorrhage &/or necrosis
Tumors may be predominantly cystic
Tumor size may vary from 2 cm to > 10 cm in diameter
Microscopic Pathology
Solid
Cystic
Spindled
Top Differential Diagnoses
Small cell carcinoma
In cases of small cell variant of squamous cell carcinoma, may be able to identify in situ squamous component
Chromatin pattern of small cell carcinoma, “salt and pepper,” not present in small cell variant of squamous cell carcinoma
Sarcoma
In spindle cell variant of squamous cell carcinoma, may identify residual focal areas of squamous differentiation
Large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma
In cases of basaloid squamous cell carcinoma, large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma may enter the differential diagnosis
TERMINOLOGY
Synonyms
Epidermoid carcinoma
Definitions
Malignant epithelial neoplasm with squamous (epidermoid) differentiation
ETIOLOGY/PATHOGENESIS
Environmental Exposure
Associated with tobacco smoke
CLINICAL ISSUES
Presentation
Cough
Shortness of breath
Hemoptysis
Chest pain
Treatment
Surgical approaches
Wedge resection
Lobectomy
Pneumonectomy
Radiation
Chemotherapy or radiation therapy
Prognosis
Depends on stage at time of diagnosis
MACROSCOPIC FEATURES
General Features
Central or peripheral tumors
White or light brown in color with homogeneous cut surface
Cut surface may show areas of hemorrhage &/or necrosis
Tumors may be predominantly cystic
Tumor size may vary from 2 cm to > 10 cm in diameter
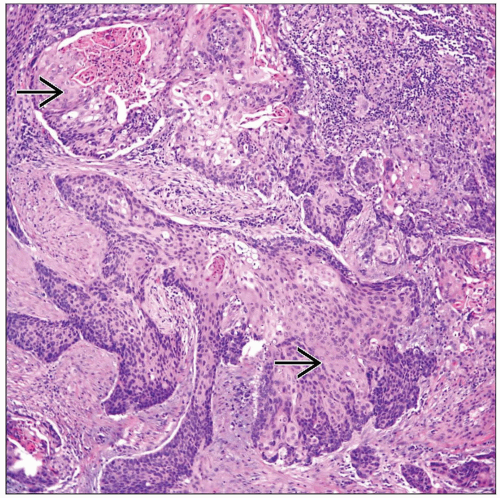
MICROSCOPIC PATHOLOGY
Histologic Features
Keratinization
Keratin pearls
Intercellular bridges
Predominant Pattern/Injury Type
Solid
Cystic
Spindled
Predominant Cell/Compartment Type
Epithelial, squamous
DIFFERENTIAL DIAGNOSIS
Small Cell Carcinoma
In cases of small cell variant of squamous cell carcinoma, the presence of an in situ squamous component will be helpful for diagnosis
Chromatin pattern of small cell carcinoma (“salt and pepper”) not present in small cell variant of squamous cell carcinoma
May show positive staining for neuroendocrine markers and TTF-1
Sarcoma
Large Cell Neuroendocrine Carcinoma
In cases of basaloid squamous cell carcinoma, large cell neuroendocrine carcinoma may enter the differential diagnosis
Basaloid squamous cell carcinoma is negative for neuroendocrine markers
Immunomarkers for neuroendocrine origin will show positive staining
DIAGNOSTIC CHECKLIST
Pathologic Interpretation Pearls
Presence of keratinization, keratin pearls, &/or intercellular bridges
GRADING
Well-differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Tumor shows obvious keratinization, and at high-power view, intercellular bridges are apparent
Moderately Differentiated Squamous Cell Carcinoma
Tumors show more cellular and nuclear atypia
Stay updated, free articles. Join our Telegram channel

Full access? Get Clinical Tree